Which type of star ends its life cycle in the form of a neutron star or a black hole?
High-Mass Star
All stars start out as...
Protostars
Flat galaxies that form with no spiral structures and have no ability to form new stars due to the decrease in gas and dust are categorized as what type of galaxy?
A. Irregular
B. Spiral
C. Regular
D. Elliptical
D. Elliptical Galaxy
- What features of stars are plotted on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
Luminosity and Temperature
Put the colors of stars in order from HOTTEST to COOLEST.
Blue, White, Yellow, Orange, Red
What determines the life path a star will take?
Mass
Where are stars "born"?
What type of galaxies is most like our own galaxy?
Spiral Galaxy
Which of the following statements does not accurately describe the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
- A. Bright stars are located at the top of the diagram.
- B. Dim stars are located at the bottom of the diagram.
- C. Hot stars are located on the left side of the diagram.
- D. Cool stars are located on the left side of the diagram.
- D. Cool stars are located on the left side of the diagram.
Where are red giants and red supergiants located on an HR diagram?
The top right
Which stage in the life cycle of a high-mass star is characterized by the star collapsing and throwing its outer layers into space?
Super Nova
What type of stars go supernova?
High mass stars (only red SUPERgiants)
What does luminosity refer to?
Brightness
What band on the HR-Diagram represents the area where most stars live their life?
A. the upper-left quadrant
B. the lower-left quadrant
C. the upper-right quadrant
D. the diagonal band that runs from the upper-left to the lower-right
D. the diagonal band that runs from the upper-left to the lower-right
What type of stars are located in the bottom left corner of the HR diagram?
White dwarfs
At the end of its life cycle, a high-mass star sometimes leaves behind an invisible object in which gravity is so strong that radiation cannot escape. What do we call this object?
Black Hole
What will our sun eventually turn into?
Red giant in about 5.5 billion years
Fill in the blanks:
A white dwarf is but than the sun.
Hotter, Dimmer
Hotter, Smaller
Describe a star located at the top left corner of an HR diagram.
Bright and hot
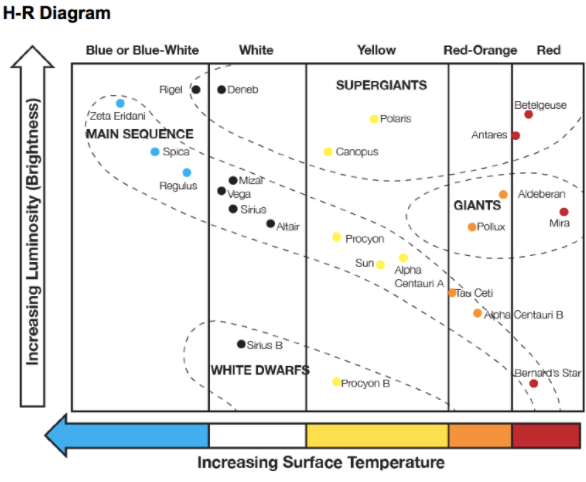
Zeta Eridani
What kind of star becomes a giant when fusion slows down, the outer atmosphere of the star expands, luminosity increases, and the star begins to fuse helium into carbon?
Low-Mass Star, Main Sequence Average Star
What process occurs throughout most of a star’s lifetime?
Nuclear Fusion
How is it possible for a star that is actually dimmer than another star to appear brighter to an observer on Earth?
Because it is closer to Earth so the apparent magnitude is greater. Distance
What percent of stars are in the main sequence stage of life and why?
90% because stars spend most of their lives in this stage.

Barnard's Star