The outer most whorl of a flower, often leaf-like and initially protecting the flower bud.
What is the sepal?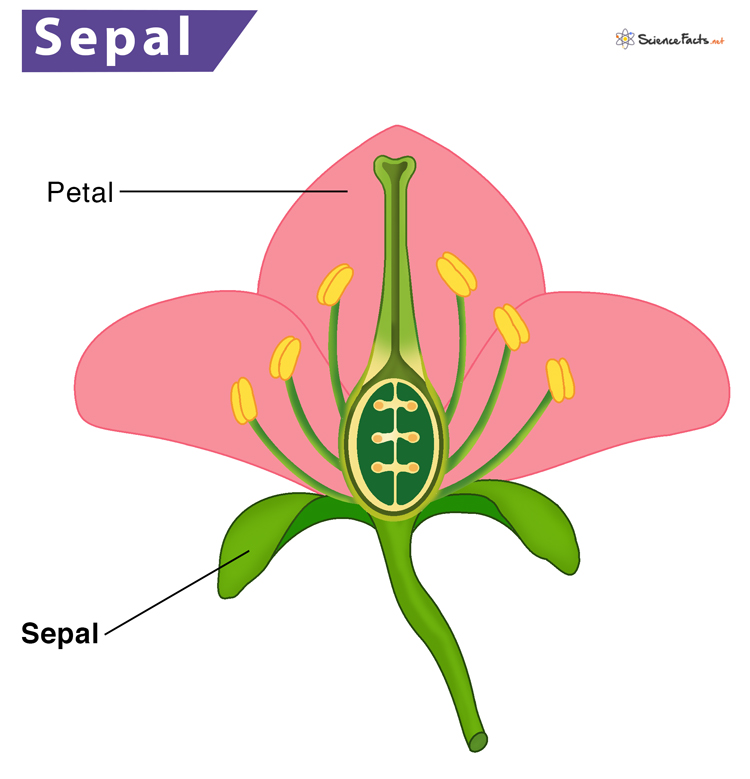
A modified leaf (often leaf-like, sometimes scale-like) at the base of a flower or inflorescence; often reduced.
What is bract?

The ripened ovary wall of a fruit.
What is the pericarp?

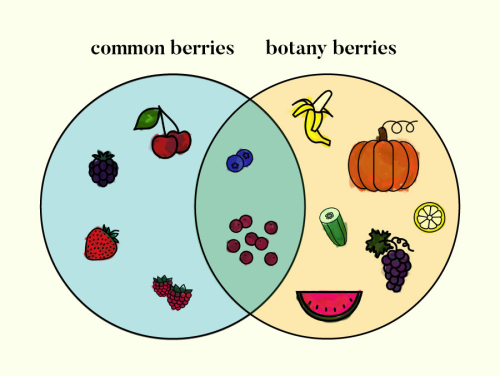
Fruits in this classification include: blueberries, bananas, watermelons, lemons, cucumbers, etc.
What are berries?
A dry dehiscent fruit that was derived from 2 or more carpels.
What is a capsule?

The receptive part of an ovary, which serves to catch pollen, often sticky.
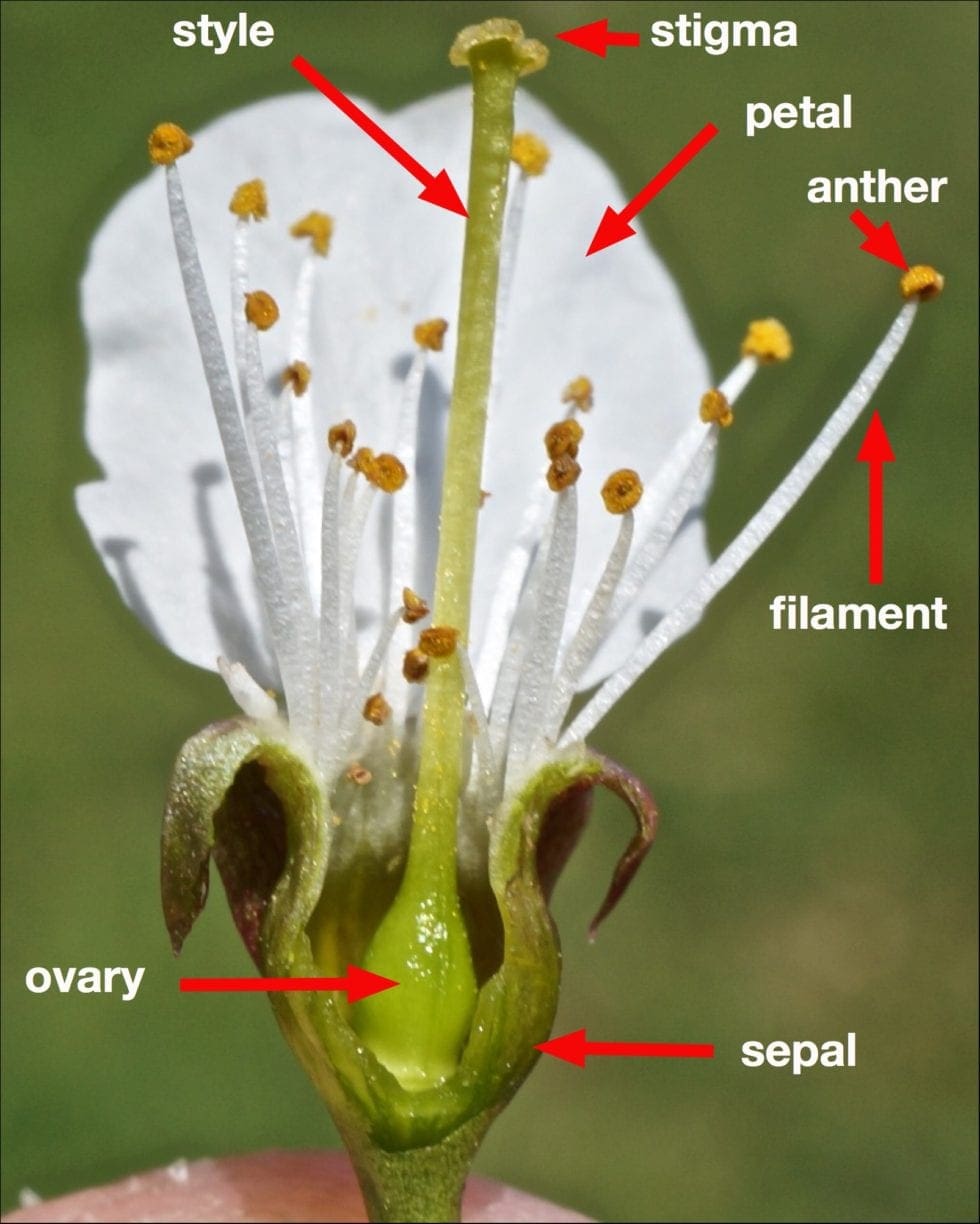 What is the stigma?
What is the stigma?
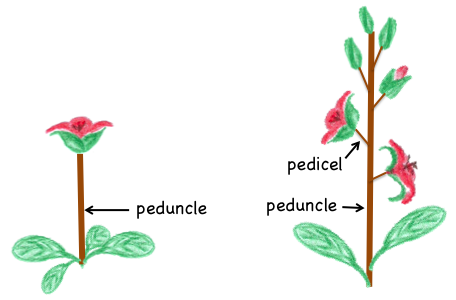
The stem of a solitary flower or an inflorescence.
What is the peduncle?
A fruit that develops from a single flower with many separate ovaries that fuse during ripening.
What is an aggregate fruit?

This is a special type of berry in which a leathery rind forms; the interior of the fruit divided by septa, indicating the number of carpels.
What is a hesperidium?

Dry fruits which do not open when mature to shed their seeds. Many of this group are one seeded fruits.
What are indehiscent fruits?

The collective term for sepals and petals.
What is the perianth?

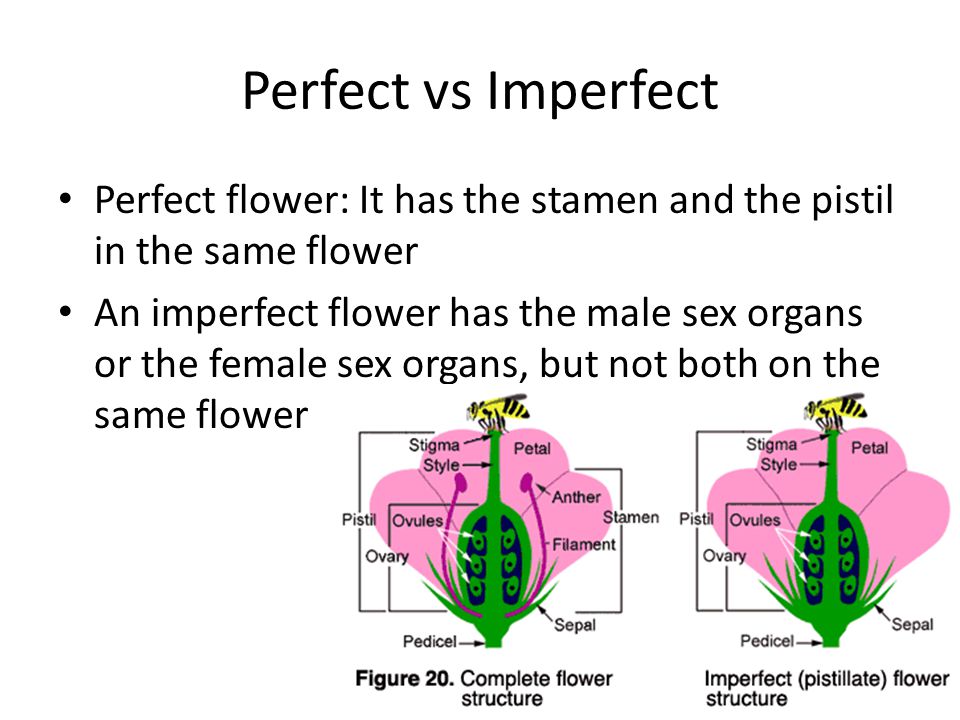
A flower that is unisexual, having either stamens or pistils but not both.
What is an imperfect flower?
A fruit developed from the ovary and its contents plus additional parts of the flower such as the receptacle, petals, and sepals.
What is an accessory fruit?
*Also acceptable: False fruit or Pseudocarp
A fleshy fruit, characteristic of the gourd family (Cucurbitaceae), that develops from a single ovary and features a firm or tough outer rind with many seeds inside.
What is a pepo?

These types of dry fruits are characteristic of the Brassicaceae (mustard family).
What are siliques and silicles?

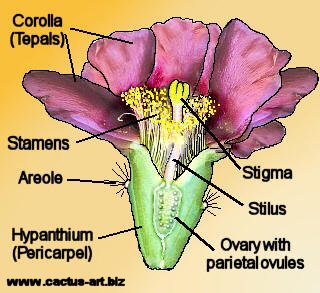
A tubular structure of a flower formed by the fusion of the basal portions of the sepals, petals, and stamens, and from which the rest of the floral parts emanate.
What is the hypanthium?
*Pericarpel or floral cup/tube also acceptable
A flower that has all four main parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
What is a complete flower?

A fruit that develops from the ovaries of multiple, individual flowers within a single inflorescence (a cluster of flowers) that fuse together into a single structure.
What is a multiple fruit?

A fleshy fruit containing a single hard "stone" or pit, which encloses the seed. This three-layered fruit structure includes an outer skin (exocarp), a fleshy edible part (mesocarp), and a hard, seed-containing shell (endocarp).
What is a drupe?

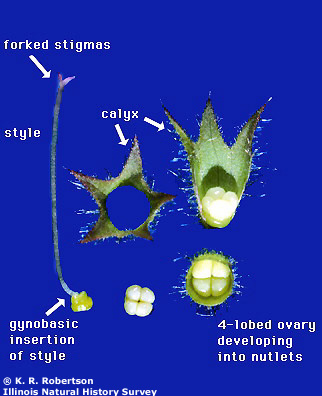
A small nut; often used to refer to one of the four parts of the mature fruit of some species of Boraginaceae, Lamiaceae, and Verbenaceae.
What is a nutlet?
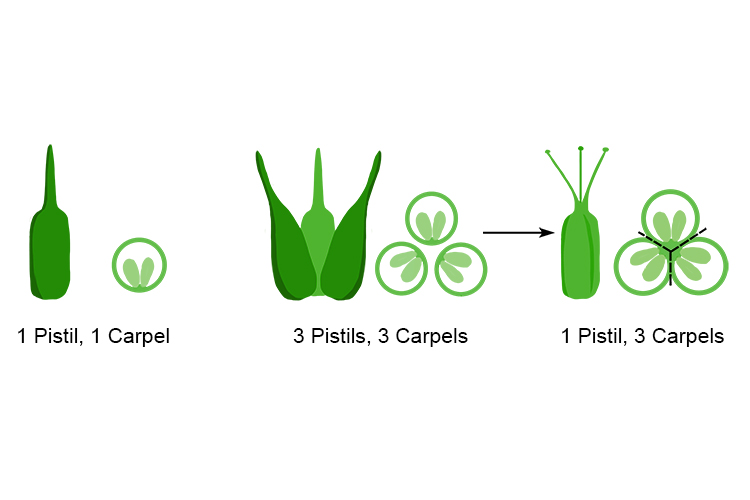
The female reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of one or more fused carpels each with a stigma, style, and ovary. Develops into a fruit and contains ovules, which can become seeds if fertilized.
What is the pistil?
A whorl of bracts (modified leaves) that surrounds and supports a flower or flower cluster.
What is an involucre?

This term used to describe fruits that develop without fertilization.
What is parthenocarpy?

A many-seeded fruit with a tough, leathery outer skin called the exocarp and a spongy mesocarp containing the edible, juicy arils (the fleshy part of the seed). The fruit develops from a multicarpellary, multilocular inferior ovary.
What is a balausta?

A type of dry fruit that splits into two or more distinct, one-seeded segments called mericarps when mature.
What is a schizocarp?
