most likely diagnosis: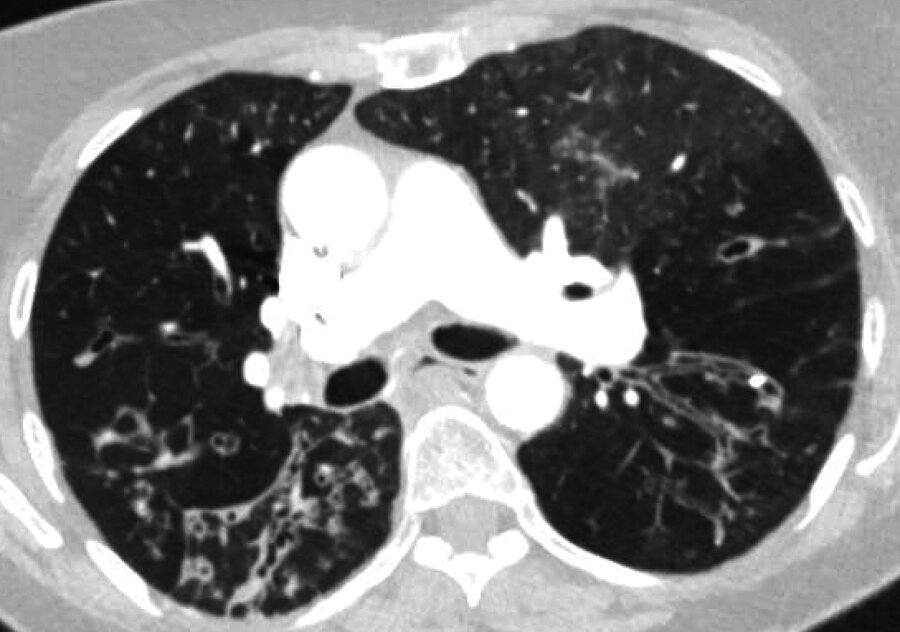
bronchiectasis
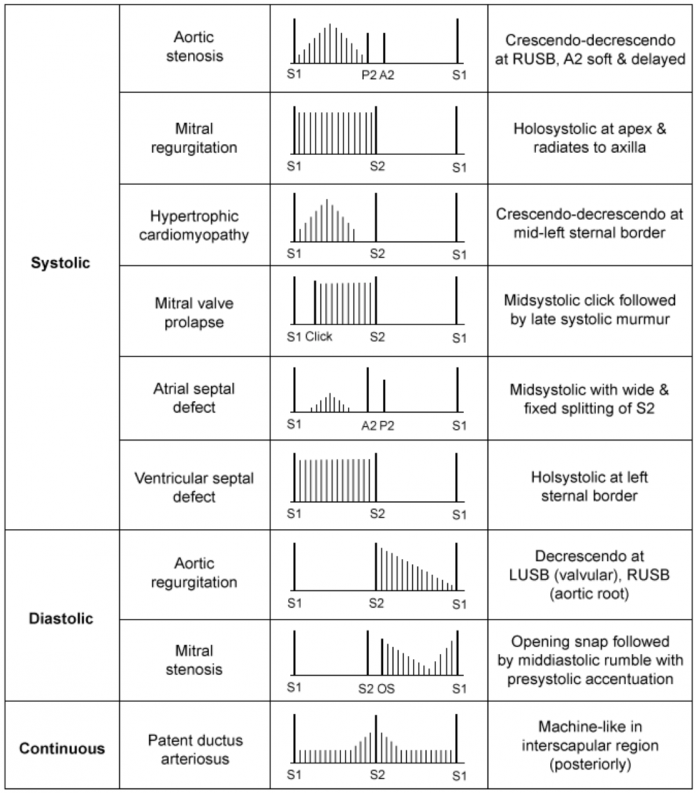
A 28-year-old man is evaluated during a routine examination. Blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 60/min. Auscultation is performed with firm pressure on the diaphragm at the upper left sternal border.
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_cv/vdx4_cv_q029
Which of the following best describes the second sound?
1) No splitting with respiration (single)
2) Persistent inspiratory/expiratory splitting
3) Splitting in expiration (paradoxical)
4) Splitting in inspiration (physiologic)
4) physiological splitting
A 51-year-old man is evaluated for syncope after prolonged standing in a warm environment.
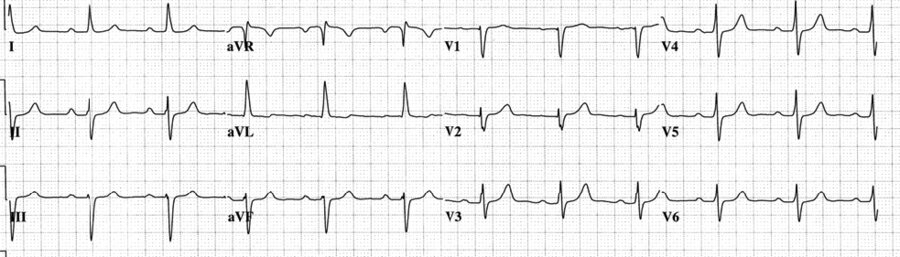
What are the ECG findings?
1st degree AV block
A 65-year-old woman is evaluated for severe pain on the right side of the upper chest of 1 week's duration and was followed by the appearance of the rash shown.
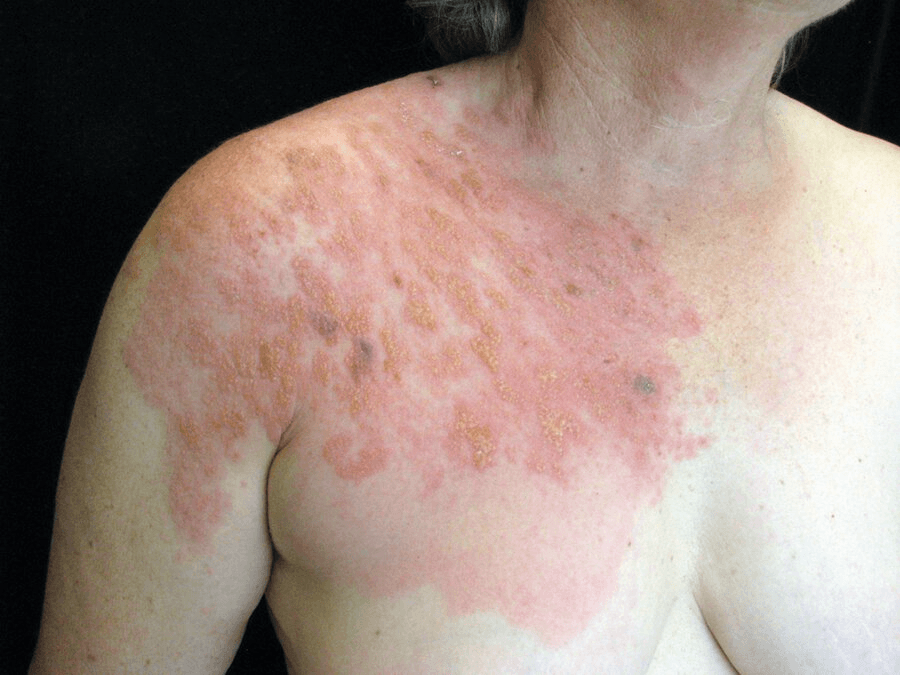
Herpes zoster.
A 52-year-old man is evaluated for chronic pain in the joints of the hands, ankles, and toes.
A radiograph of the hand is shown.
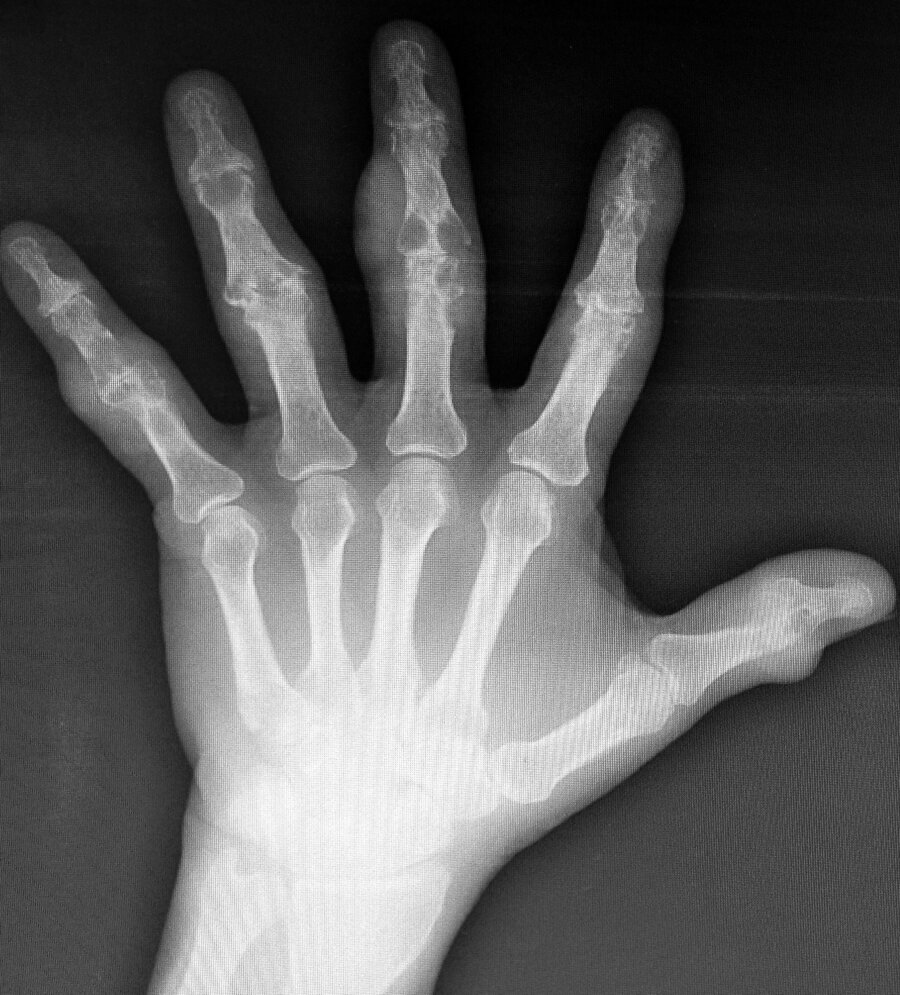
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A) basic calcium phosphate deposition
B) calcium phosphate deposition disease
C) Gout
D) osteoarthritis
Gout
A 44-year-old man is evaluated for shortness of breath. Point-of-care ultrasonography of the lungs is performed. An ultrasound video with the probe placed at the left fifth intercostal space in the posterior axillary line is shown. Diagnosis?
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_pm/vdx4_pm_q014
Pleural effusion
A 35-year-old man is evaluated for exertional dyspnea and a sensation of pounding in the neck that has progressed over the last year. Blood pressure is 150/60 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 60/min.
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_cv/vdx4_cv_q001
What is the name of the murmur?
1) Aortic Regurgitation
2) Mitral Regurgitation
3) Mitral Stenosis
4) Aortic Stenosis
Aortic Regurgitation
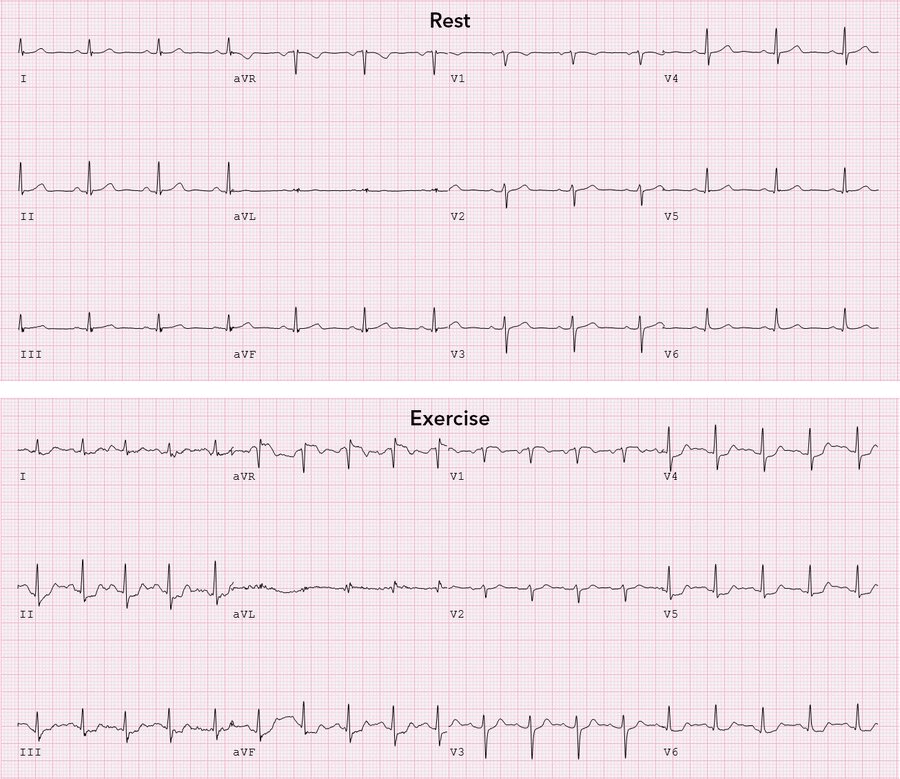
Most likely diagnosis:
1) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
2) ischemic heart disease
3) rate dependent conduction disease
4) normal
A 30-year-old man is evaluated for fever, arthralgia, myalgia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and development of the rash shown. He returned from an extended stay in the Indian subcontinent 2 weeks ago.
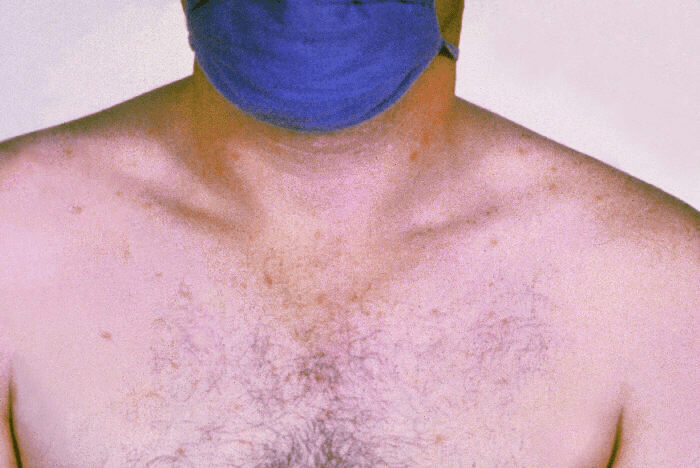
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1) dengue
2) malaria
3) enteric fever
d
enteric fever
A 45-year-old man with a history of rheumatoid arthritis is evaluated for fever and left hip pain that has become progressively severe over the past 6 weeks.
A radiograph of the hip is shown.
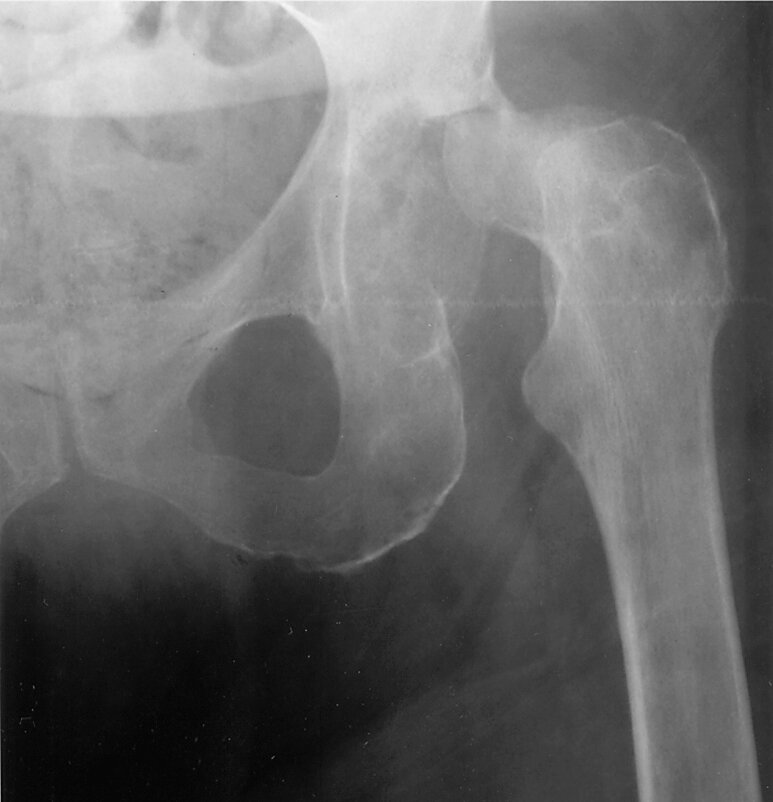
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Avascular necrosis
B) Septic Arthritis
C) Gout
D) Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease
Septic Arthritis
-cortical destruction on acetabular and femoral sides of the joint
- Radiographs of the infected joint may show periarticular osteopenia but are usually normal at presentation, but should be obtained to identify associated osteomyelitis or concurrent arthritis.
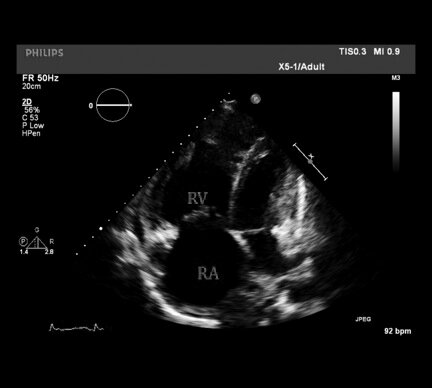
Most likely diagnosis:
1) pulmonary hypertension
2) restrictive cardiomyopathy
3) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
4) pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary Hypertension:
- RV > LV; RA > LA
-other findings can include:
right ventricular hypokinesis
septal flattening or bowing toward the left ventricle
tricuspid regurgitation
pulmonary insufficiency
midsystolic closure of the pulmonary valve
A 52-year-old woman is evaluated for exertional dyspnea and orthopnea. Blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 60/min. Auscultation over the apical impulse is performed with light pressure on the bell.
Which of the following best describes the acoustic events at the apex?
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_cv/vdx4_cv_q051
A) S1 + paradoxical splitting of S2
B) S1 + physiological splitting of S2
C) S1 + S2 + S3
D) S1 + S2 + S4
C) S1 + S2 + S3:
S3: early diastole, best heard with bell at apex, low frequency. cause? volume overload (regurgitation, shunt, late pregnancy), normal in children or highly trained athletes.
S4: low-frequency diastolic sound, late diastole
split S2: high frequency, S LICS, corresponding with asynchronous closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves.
Physiological splitting S2: single S2 during expiration, split during inspiration
Paradoxical splitting of S2 is characterized by audible splitting during expiration and a single S2 during inspiration. Associated with AS.
23 year old with recurrent syncope. Cause?
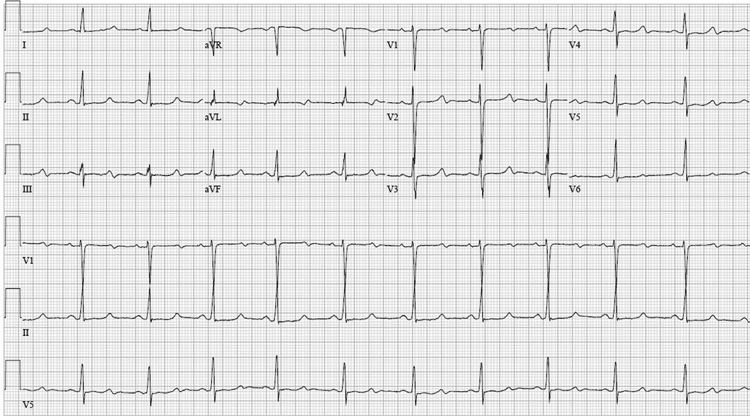
prolonged QT
A 25-year-old man is evaluated for a slightly pruritic rash that began as a single oval patch on his back.
Representative lesions on his lateral thigh are shown. Name that rash!
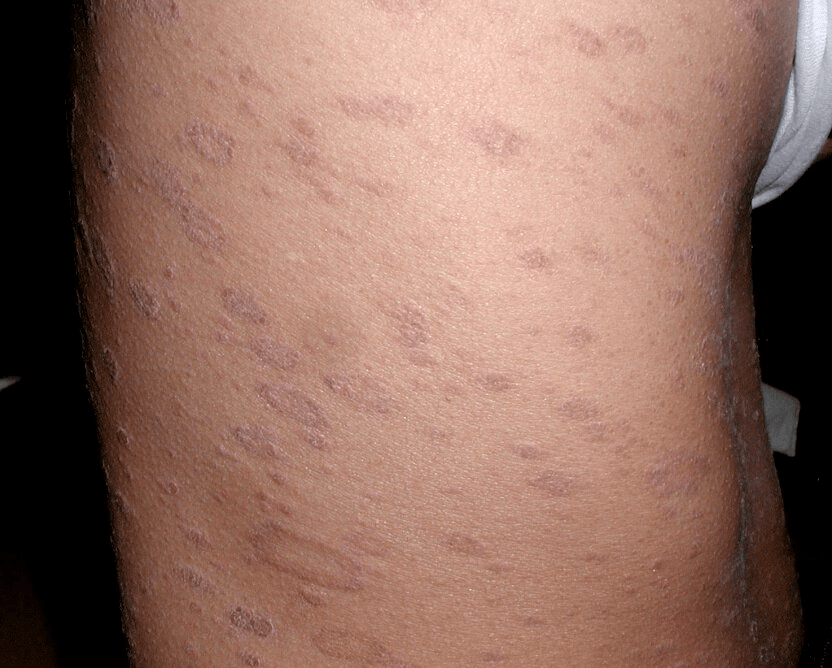
pityriasis rosea
A 26-year-old man is evaluated for the acute eruption of the palpable lesions shown.
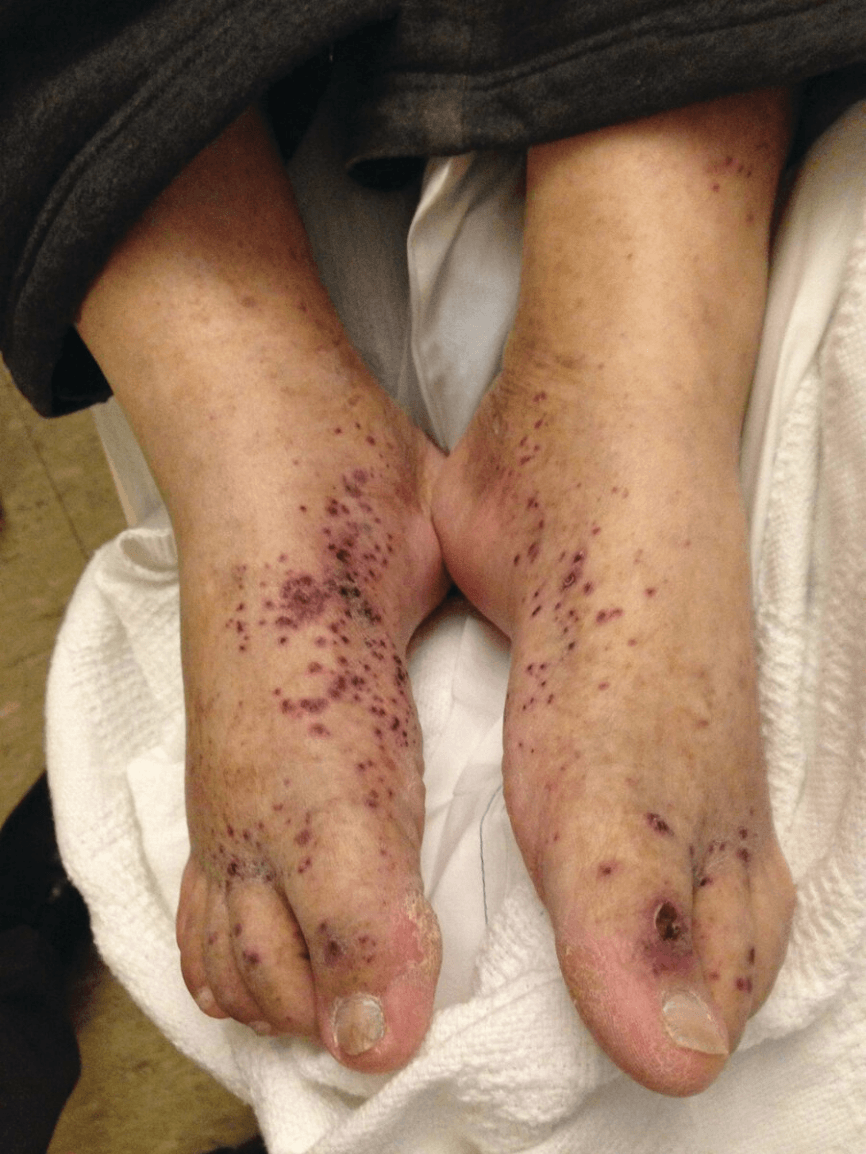
immune complex mediated vasculitis
Most likely diagnosis:
1) Disseminated histoplasmosis
2) Rheumatoid Nodules
3) Microscopic Polyangiitis
4) Miliary Tuberculosis
Rheumatoid Nodules
A 45-year-old woman is evaluated for an 18-month history of progressive fatigue and dyspnea. Blood pressure is 112/72 mm Hg, pulse rate is 76/min, and respiration rate is normal. The apical impulse is slightly sustained but not displaced. Auscultation is performed at the cardiac apex.
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_cv/vdx4_cv_q033
What is the murmur?
A) Aortic Regurgitation
B) Mitral Regurgitation
C) Mitral Stenosis
D) Pulmonary Regurgitation
Mitral Stenosis
A 34-year-old woman is evaluated for unexplained right heart enlargement and a history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Physical examination reveals a parasternal impulse, fixed splitting of S2, mitral regurgitation, and a pulmonary outflow murmur.
ECG is shown.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
ostium primum ASD findings include LAD, first degree AV block and RBBB
A 78-year-old woman is evaluated for an acute blistering skin condition that does not involve mucosal surfaces.
Representative skin findings are shown. 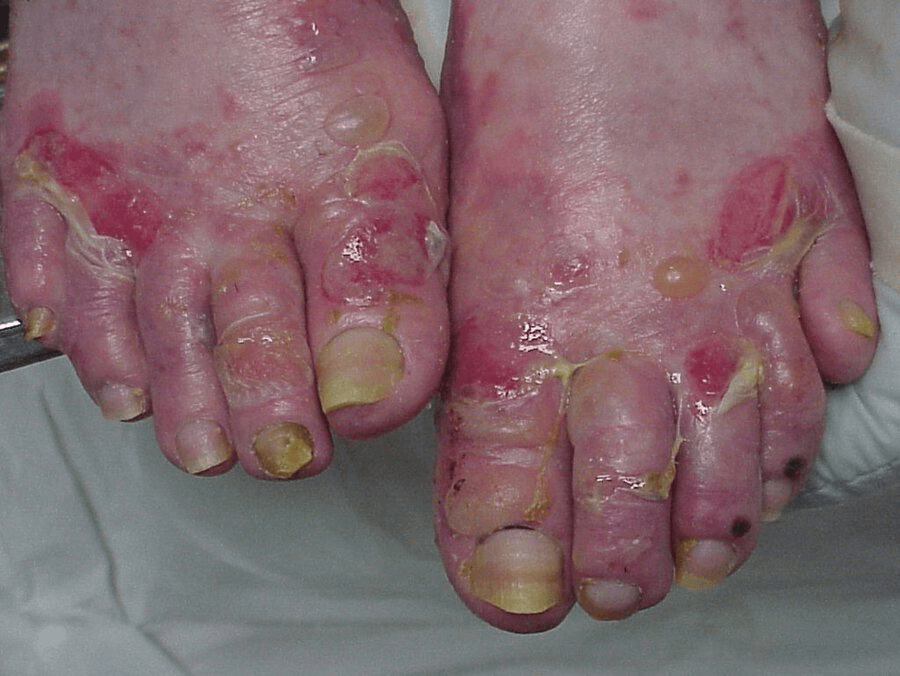
bullous pemphigoid:
- subepidermal vesicles / blisters which are tense, do not rupture easily Sites of predilection include the lower abdomen, inner thighs, groin, axillae, and flexural aspects of the arms and legs.
A 30-year-old man is evaluated for recurrent inflammatory eye disease, oral ulcers, and painful scrotal findings, as shown.
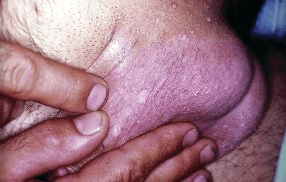
Diagnosis?
Behcet's Syndrome
A 23-year-old man is evaluated for sudden-onset chest pain and dyspnea. Focused ultrasonography is performed with the transducer placed on the lateral chest wall.
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_pm/vdx4_pm_q012
Most likely diagnosis:
1) heart failure
2) pneumothorax
3) pleural effusion
4) pneumonia
pneumothorax:
lung point sign- nearly 100% specificity for pneumothorax.
clues: intercostal space demonstrates intermittent lung sliding with periods of no lung sliding within that intercostal space corresponding to partially collapsed lung expanding to touch the parietal pleura of the chest during inspiration, then falling away during exhalation.
A 68-year-old woman is evaluated for exertional dyspnea. She was previously asymptomatic, but 4 months ago she began having shortness of breath during moderate activity. Blood pressure is 132/80 mm Hg, pulse rate is 80/min, and respiration rate is 22/min. Auscultation is performed at the upper right sternal border.
https://mksap19.acponline.org/app/question-bank/vdx/vdx_cv/vdx4_cv_q014
Diagnosis and next steps?
Aortic Stenosis, and next steps serial clinical examinations and echo examinations.
Among asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis, 75% will die or develop symptoms within 5 years. Once symptoms occur, life expectancy is generally only 1 to 2 years. Thus, serial evaluation every 6 to 12 months is recommended for patients with severe disease
Severe aortic stenosis:
Vmax > 4 m/s
mean gradient >/= 40 mm Hg
AVA </= 1.0 cm2
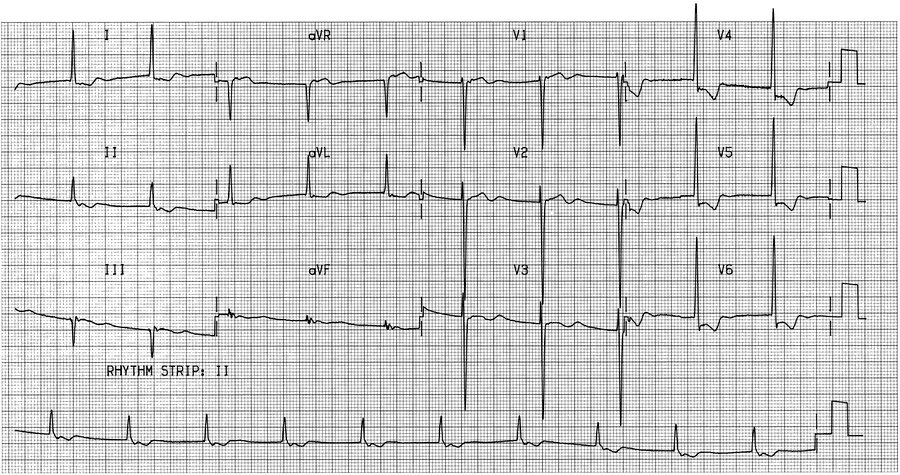
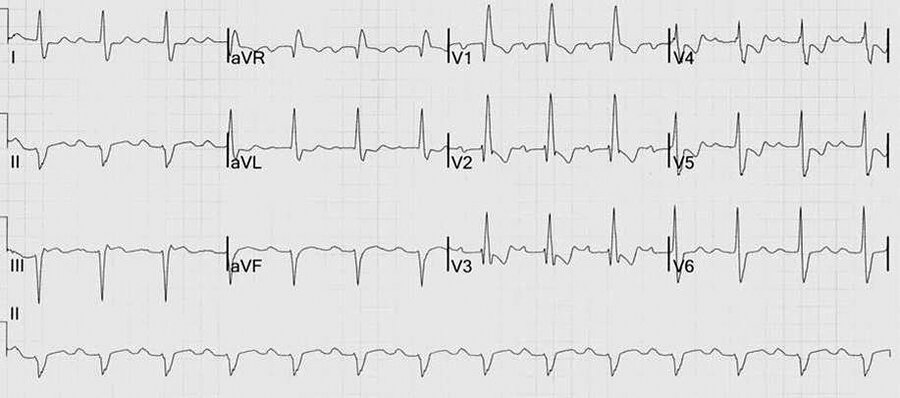
Which of the following abnormalities is demonstrated on this patient's ECG?
Junctional Rhythm
The ECG shown demonstrates a junctional rhythm, or atrioventricular nodal rhythm. Junctional rhythms are regular supraventricular rhythms in which the P wave in lead II is negative (preceding or following the QRS complex) or absent (arrows). An atrioventricular nodal escape rhythm occurs when the junctional rate is between 40/min and 60/min and the sinoatrial node is delayed or fails to function as the pacemaker. An accelerated junctional rhythm occurs when the junctional rate is between 61/min and 99/min and the junctional rate takes over the pacemaker function. Junctional tachycardia occurs when the junctional rate is faster than 99/min and takes over the pacemaker function.
A 50-year-old woman is evaluated for fever, malaise, and the acute onset of the skin rash shown, which is associated with regional lymphadenopathy.
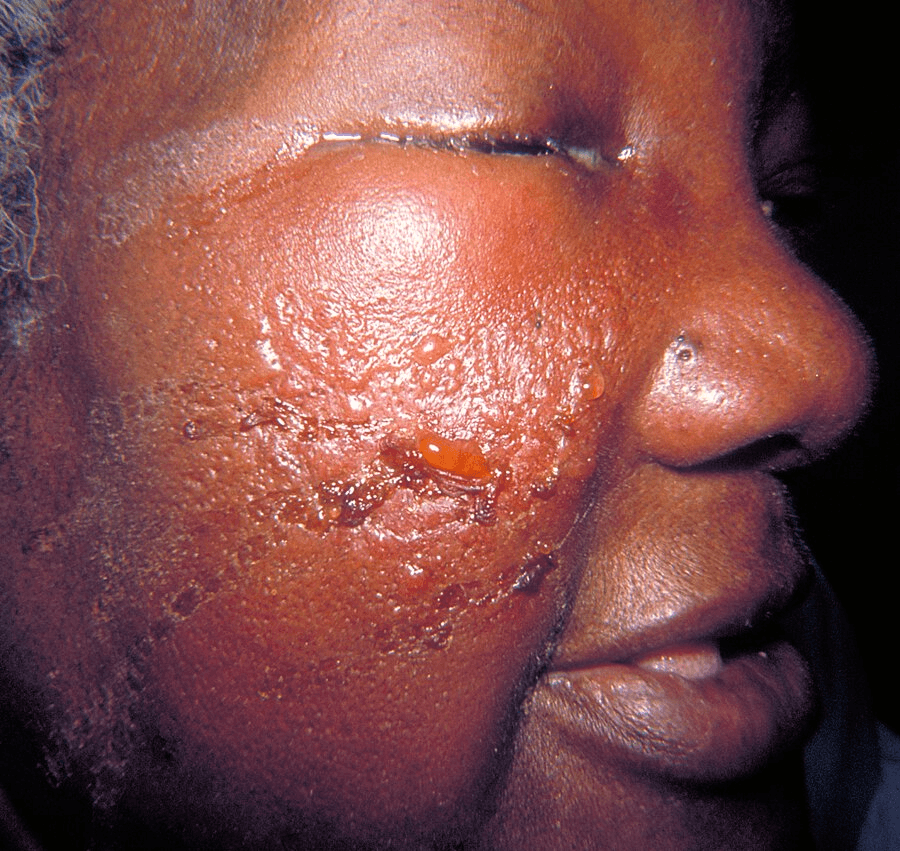
Erysipelas
severe malar and periorbital bright erythema and swelling and purulent discharge from the eye.
Erysipelas refers to infection of the epidermis, upper dermis, and superficial lymphatics and is caused by the inoculation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue with streptococcal bacteria.
Usually involving the face or lower extremities, this infection is brightly erythematous with distinct elevated borders and associated fever, lymphangitis, and regional lymphadenopathy.
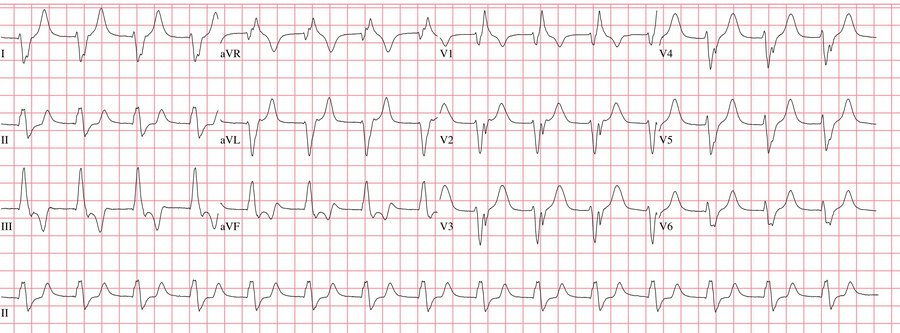
Which of the following abnormalities is demonstrated on this patient's ECG?
a) accelerated idioventricular rhythm
b) junctional rhythm
c) ventricular tachycardia
d) torsades de pointes
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm, which is an escape rhythm arising from the ventricular myocardium.
-generally benign and transient
-NOT VT b/c rate is faster
-NOT junctional bc wide qrs