Data collected through scientific investigations such as observational studies or controlled experiments.
What is empirical evidence?
What is a galaxy?
States that mass/matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter?
This is the basic unit of life.
What is a cell?
The name of the solar system model showing the planets revolving around a central sun in concentric circles.
What is the heliocentric model?
This equation is used to calculate an object's density.
What is D=M/V?
This variable in an experiment is changed on purpose by the investigating scientist. It is also graphed on the X axis when data is analyzed.
What is the independent variable?
Predicted by the color of a star.
What is temperature?
The element with 54 protons in its nucleus.
What is xenon?
This is the organelle in which cellular respiration takes place.
What is the mitochondria?
Increasing this will increase the rate of a chemical reaction.
What is temperature?
This term used for describing moon phases means mostly full of light.
What is gibbous?
This variable in an experiment is measured by the investigating scientist. It is graphed on the Y axis when data is analyzed.
What is the dependent variable?
How bright a star appears from Earth's perspective based on the star's distance from the Earth.
What is apparent magnitude?
The process that occurs when a new substance is formed that has entirely new properties than what was started with.
The process that breaks down food to provide cells energy and releases carbon dioxide.
What is cellular respiration?
What is absolute brightness (luminosity)?
During this lunar phase a lunar eclipse may occur.
What is full moon?
The materials that need to remain the same across all test groups in an experiment.
What are constants?
The picture below shows this event.
What is a solar eclipse?
Baking soda (NaHCO₃) is an example of this pure substance.
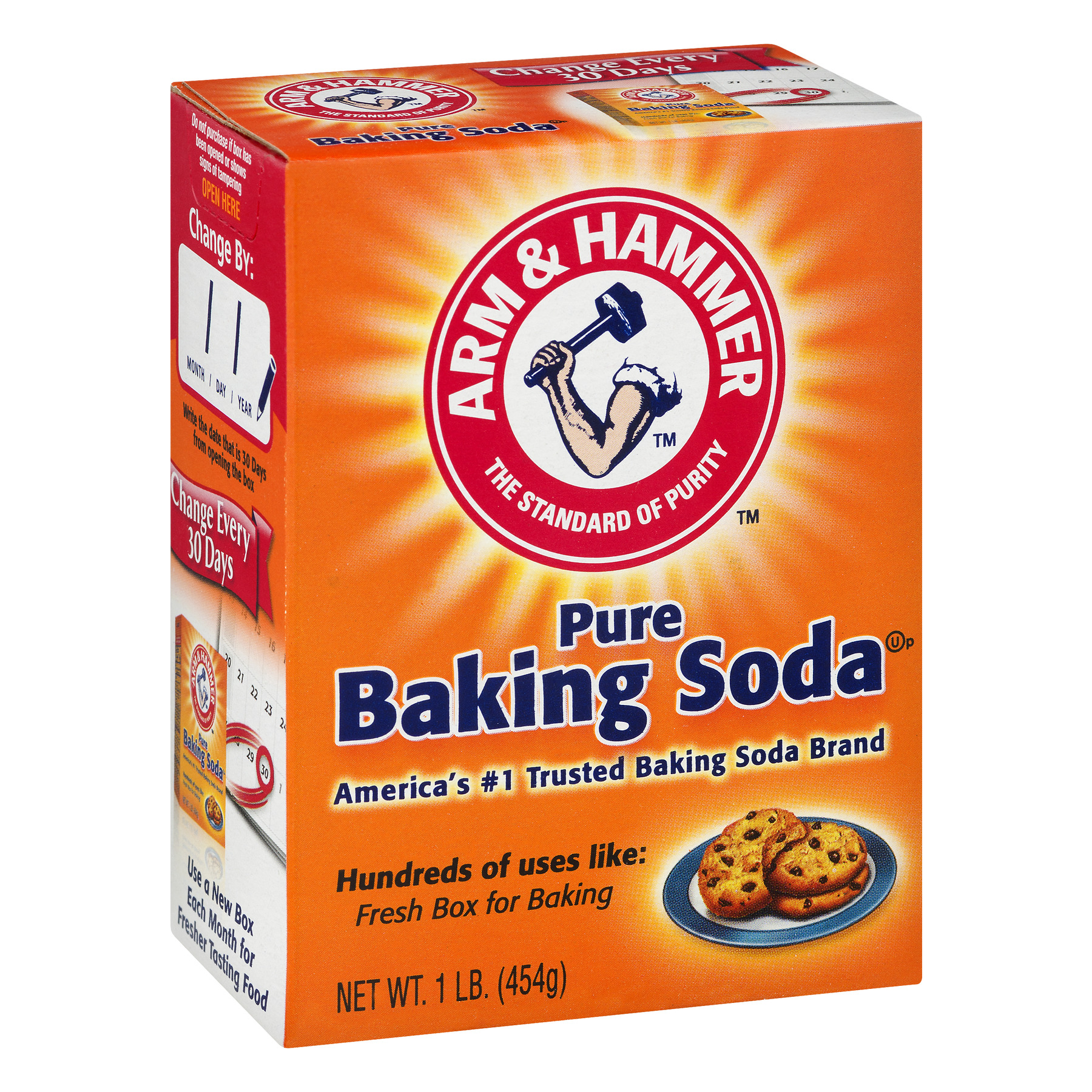

What is a compound?
This is the movement of Carbon throughout the planet.

What is the carbon cycle?
This states that the gravitational attraction between objects (such as in our Solar System) depends on their distances and their masses.
What is the Law of Universal Gravitation?
Fruit punch is an example of this type of mixture. 
What is a homogeneous mixture?
The group that does not receive the independent variable and is used as a base for comparison.
What is the control group?
The picture below shows this tidal event.
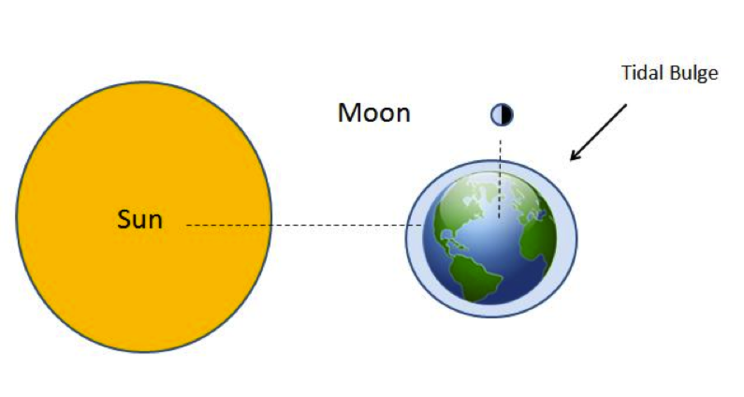
What is neap tide?
Pictured below is solid carbon dioxide. If this melts to a liquid, that is an example this type of change.
What is a physical change?
This process uses carbon dioxide, water and light to create glucose and oxygen.
What is photosynthesis?
This process uses oxygen and glucose to create carbon dioxide, energy, and water.
What is cellular respiration?
This is the reason that eclipses do not happen every month.
What is the moon's tilted orbit?