List 3 natural disasters
Volcano, earthquake, tsunami, flood, tornado, wild fire, etc.
What are the charges of protons, electrons, and neutrons?
Protons: +
Neutrons: 0
Electrons: -
What is the name of the tallest peak?
Crest
Explain conduction
Heat transferring through direct contact
What is law of superposition?
the oldest rock layers are at the bottom of a sequence, and the youngest rock layers are at the top
List the 3 types of volcanoes.
Cinder cone, stata/ composite, shield
What are valence electrons? What diagram can you use to model these?
Electrons in the outermost shell. Lewis dot diagram.
What is the name of the lowest peak?
Trough
What is thermal energy?
Heat energy.
What is cross- cutting?
a younger rock or structure will cut across an older rock or structure
What is the cause of tsunamis?
Earthquakes under water
How many electrons can fit in shell 1, 2, and 3 of a bohr's model?
1st: 2
2nd: 8
3rd: 8
What is frequency?
the number of waves that pass a fixed point in a unit of time, usually measured in hertz
What is an independent variable?
What is a dependent variable?
Something I change in the experiment
What's being measured
What is stratigraphy?
a branch of geology that involves the study of rock layers (strata) and the way they are formed
What is the difference between magma and lava?
Magma- in the ground
Lava- comes out of the volacno
What is one chemical property?
What is one physical property?
Flammability, corrosive, Toxicity, Acidity, Reactivity
Hardness, luster, Melting point, boiling point, density
What is wavelength?
the distance between two identical points on consecutive waves
List the steps to the scientific method
Ask a question,
Hypothesis,
Collect data,
Draw a conclusion,
Share your results
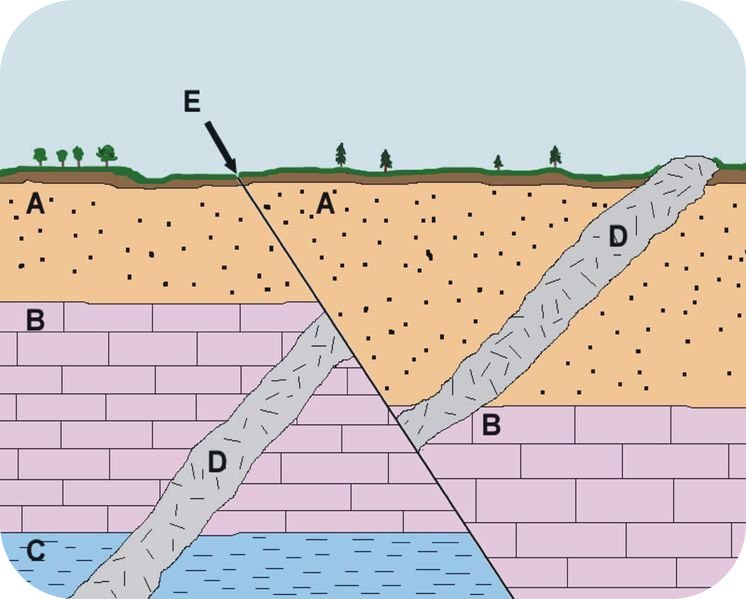
What is youngest?
A
Explain low vs high viscosity and what volcanoes have what viscosity.
Low viscosity: low resistance to flow, or in other words, flowing easily (shield)
High viscosity: high resistance to flow, thick and sticky, flows slow (composite)
What is the difference between a compound and a mixture?
A substance made of two or more elements that are chemically joined. For example, water (H2O) and table salt (NaCl) are compounds
a substance made up of two or more different substances that can be separated by physical means
Explain transverse vs longitudinal waves.
a wave in which particles of the medium vibrate at right angles, or perpendicular, to the direction that the wave travels
a wave that moves in the same direction as the vibration of the medium it's traveling through
Give an example of a hypothesis using if/then/because.
If the plant receives sunlight, then the plant will grow because of the process of photosynthesis.
What is relative dating?
a method for determining the order of past events or the age of something in relation to other objects, without providing an exact date