State the 3 factors of climate.
1. Solar energy (the greenhouse effect)
2. Latitude
3. Wind and ocean currents
What is the photic zone?
The sunlit region near the surface of the water in which photosynthesis can occur.
What are the 4 factors that affect the population size? (Hint: rates!!!)
Growth Rate (Natality), Death Rate (Mortality), Immigration, and Emigration.
What is sustainable development?
Sustainable development provides for human needs while preserving the ecosystems that produce natural resources.
Calculate the Simpson's Diversity Index for the following 2 ecosystems. Find which has a higher biodiversity.
Community 1: 0.75
Community 2: 0.48
Community 1 has higher biodiversity.
Carbon:
Carbon dioxide, calcium carbonate, carbonic acid, methane
Nitrogen:
Nitrogen gas, ammonia/ammonium, nitrite, nitrate
List the 4 main environmental factors of marine life.
Water depth, temperature and currents, nutrient availability, distance from shore.
Explain the 3 phases of logistic growth. Try to explain the reasons for each phase!
Phase I:
Population
grows rapidly.
Phase II:
Growth slows.
Phase III:
Growth stops;
population size
stabilizes at
carrying capacity.
State a pro and a con for Monoculture (a type of agricultural practice)
Monoculture enables efficient sowing, tending, and harvesting of crops using machines. However, providing food for nearly 7 billion people impacts natural resources, including depleting fresh water and leaching nutrients from fertile soil.
David selects 15 little pigs and marks them. After he releases them back, he selects a number of pigs and discovers that 2 of them are marked and 8 of them are unmarked.Using the capture-mark-recapture method, calculate the total population of pigs.
[15 x(2+8)]/2= 75 Pigs
Give an example for each of the biogeochemical processes + human activity (4 in total).
Biological: Respiration, photosynthesis, feeding
Geological: Formation of rock, volcanic eruptions
Chemical: Precipitation, lightning
Human: Burning of fossil fuels, clearing of land
State the 3 environmental functions of wetlands.
1. Purify water by filtering pollutants
2. Prevent flooding by controlling water amount
3. Estuary (special kind of wetland): rich nursing grounds for commercial usage
What aspects of population do researchers investigate?
Populations’ geographic range, density and distribution, growth rate, and age structure.
What are 2 methods to reduce soil erosion?
Sample: 1. Altering the shape of the land is a way to limit erosion. (Contour Planting, Terracing) 2. Leaving stems and roots of the previous year’s crop in the soil can help hold soil in place between plantings 3. Crop rotation
In Random Quadrat Sampling, if Giannis counts 15 plants in 0.5 m^2, how many plants can he expect in the entire field with dimensions 600cm x 15m?
2700 plants.
Explain the competitive exclusion principle.
No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in the same habitat at the same time. If they do, one will eventually outcompete and exclude the other species.
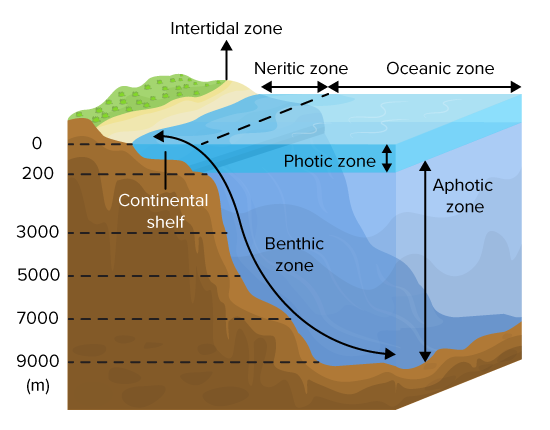
Draw a diagram of the cross section of the ocean.
(Include: photic zone, aphotic zone, benthic zone, intertidal region, coastal ocean, open ocean)
Give 3 examples of Density-Dependent limiting factors and 3 examples of Density-Independent limiting factors.
Sample:
Density-Dependent: competition, predation, herbivory, parasitism,
disease, and stress from overcrowding.
Density-Independent: hurricanes, droughts, or floods,
and natural disasters such as wildfires.
Explain Biological Magnification.
Biological magnification occurs if a pollutant, such as DDT, mercury, or a PCB, is picked up by an organism and is not broken down or eliminated from its body. The concentration of pollutants increase exponentially as it goes up the trophic levels.
An ecosystem has a total of 5 species. There is a total of 200 organisms. There is 48 Organism A, 16% of total is Organism B, 56 of Organism C, 7% is Organism D, and the rest is all Organism E.
What is the Simpson's Diversity Index of this ecosystem? If an ecosystem is considered highly diverse if its index is 0.7 or greater, is this one diverse?
There is 48 A, 32 B, 56 C, 14 D, 50 E.
D=0.77
Yes, it is highly diverse.
Describe the process of primary succession.
Lichens (pioneer species) arrive, decomposes and produce nutrient-rich soil. Mosses grow then small plants start to grow. As bushes and trees provide habitat, primary consumers arrive, then secondary and tertiary ones. The area then finally reaches climax community.
Explain why studies on organisms from the deep seas are difficult to carry out. (Hint: think about the different conditions!!!)
The water pressure is very high at deeper parts of the ocean, thus the internal pressure of organisms is large to withstand this. When these are brought up to sea level, they often become deformed or even burst apart, thus studies are difficult to carry out.
Explain the 3 stages of demographic transition. Include the reason behind all of these transitions.
Stage I: The birthrate and
death rate are
equally high.
Stage II: The death rate begins
to fall, but birthrates
remain high for a time.
Stage III: The birthrate falls to
meet the death rate.
State the differences between Ecosystem Diversity, Species Diversity, and Genetic Diversity.
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere. The number of different species in the biosphere, or in a particular area, is called species diversity. Genetic diversity can refer to the sum total of all different forms of genetic information carried by a particular species, or by all organisms on Earth.
Liam is studying the population of a specific type of tree in a forest. He randomly selects 0.25 hectare plots (1 hectare = 10,000 m²) and counts 120 trees within one of the plots. The total area of the forest is 5 km².
Using his sample data, estimate the total number of trees in the entire forest.
240,000 trees