The use and development of special lenses and lens systems to view objects that can't be seen with the naked eye.
Microscopy
Organisms that cannot survive for long in the presence of oxygen
Obligate anaerobes
You want to examine an organelle in a cell. Would you use a light microscope, TEM or STM?
A STM's magnification looks for macromolecules, and an organelle is bigger than that.
A TEM has magnification that allow you to examine organelles.
Both of these have magnifications too large for an entire eukaryotic cell.
You would use a TEM for the organelle
Transmission Electron Microscope (I got thrown off since these thing were used to see the first atoms.) Jesse 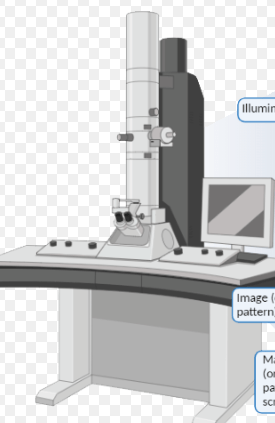
Why are cyanobacteria important for life?
They produce oxygen through photosynthesis.
What macromolecules make up a virus?
Which type enters the cell to cause an infection?
Viruses are made of proteins and nucleic acids.
Nucleic Acids must get into the cell to cause an infection.
Defined Nucleic Acid: Nucleic acids are large biomolecules essential for all living cells, with the primary function of storing and expressing genetic information. The two main types are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which carries the genetic code, and ribonucleic acid (RNA) which has various roles in protein synthesis and gene expression.
Providing conditions that enable growth of microbes (or any type of cell, tissue, or organ)
Culturing
Organisms that can perform aerobic respiration but can switch to fermentation when little or no oxygen is present.
Facultative anaerobes
You want do examine an entire eukaryotic cell? What type of microscope? Light, TEM or STM?
Light microscope for an entire eukaryotic cell.
This is what a light microscope does well.
A bacterium that is part of normal flora becomes toxic but is the same strain. Most likely, what made it become toxic?
It got into the wrong place in the body.
What do ssDNA, dsDNA, ssRNa and ds RNA mean?
ssDNA is single-strand
dsDNA is double-strand
ssRNA is single-stranded
dsRNA is double-stranded
A liquid culture that contains the nutrients the microbe needs (the organism can live anywhere in the culture, but often settle to the bottom.)
Broth Culture
The study of blood serum and immune responses
Serology
When a gram stain is applied, what colors will you see and what do we call the bacteria with each color?
Blue - Gram-positive bacteria
For the following groups, indicate whether they are gram-positive, or gram-negative.
gammaproteobacteria?
firmicutes?
nonproteobacteria?
actinobacteria?
All proteobacteria & nonproteobacterisa are gram negative.
gammaproteobacteria -
firmicutes +
nonproteobacteria -
actinobacteria +
If a virus infects someone but doesn't produce symptoms for many years, did it initially enter the lytic cycle or lysogenic cycle?
The lytic cycle is a viral replication process where a virus infects a host cell, hijacks its machinery to create many new viruses
The lysogenic cycle is a viral replication process where the viral DNA integrates into the host cell's genome, allowing the virus to replicate passively alongside the host without causing immediate harm, essentially becoming dormant until triggered to reactivate.
A solid culture that contain the nutrients the microbe needs (The organisms live on or near the surface of the culture)
Agar culture
Strain
What do we call it when we add a sample of bacteria to a culture?
Inoculation
How many different types of bacteria are needed to take nitrogen from the air and convert it into nitrate, which some plants need to survive?
Three,
Rhizobium make ammonia
Nitrobacter turns that into nitrite
and then Nitrosomas turns nitrite into nitrate
Are all viruses pathogens?
No, Most are but the book discusses one that allows plants to live where they otherwise couldn't live.
Organism that live in especially harsh conditions: very high temps, very acidic, high salt, etc.
Extremophiles
The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into a nitrogen-containing molecule that organisms can use
Nitrogen fixation
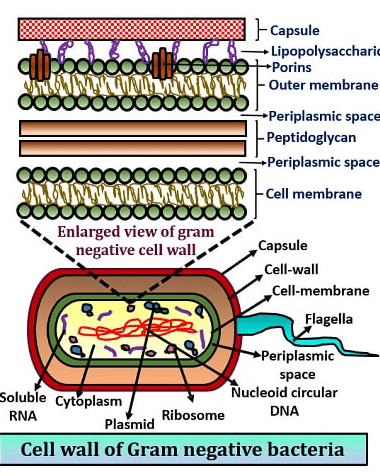
What is the main thing used to distinguish between domains Archaea and Bacteria?
The presence of a chemical: Peptidoglycan.
Archaea do not have it.
a polymer that forms a rigid, mesh-like layer in the cell walls of most bacteria, providing structural support and maintaining cell shape. It is composed of sugars cross-linked by short peptides, and its thickness is a key factor in the classification of bacteria as Gram-positive or Gram-negative
List the following in the order of size, starting from smallest: bacteria, prions, virus
Prions, viruses, bacteria
Prions are molecules, viruses are made of at least two types of macromolecules, while bacteria are made of many, many macromolecules.
A tough structure that protects a dormant bacterium and allows it to become feely living once the external conditions become suitable for life.
Endospore
Preproduction of viruses using the host cell's biomachinery, resulting in lysis of the host cell to release the virions.
Lytic cycle
What are the four groups of extremophiles and what is the characteristic of each?
Halophiles - very salty
thermophiles - hot
acidophiles - acid
Methanogens - produce methane

yes
The microbes that live on or inside a healthy human body.
Normal flora
Viral nucleic acid is inserted into the host genome and replicates as the host replicate, sometimes called temperate infection
Lysogenic cycle
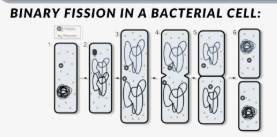
What is the main method of reproduction among bacteria?
Binary fission.
asexual reproduction method in which a single parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells
67^67 hehehehehehehehe or you could do what is 67 plus 69^2/64
2.22337e+122 or 141.390625
Organisms that must have oxygen in order to survive
Obligate aerobes
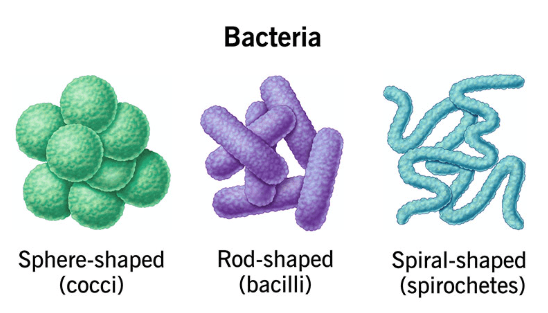
If you look at Lactobacillus acidophilus under a microscope, what would their shape be?
Agrococcus terrus?
Herbaspirillum huttiense?
Lactobacillus acidophilus - rod shaped
Agrococcus terrus - sphere shaped
Herbaspirillum huttiense - spiral shaped
what word starts with the letter I and ends with the letter I and is one letter.
I
What is (0^0+4-3)2^5
64