This particle determines the atomic number of an element.
What is a proton?
Instead of being broken down, in this type of reaction amino acids combine to form proteins; it is considered endergonic.
What is an anabolic (synthesis) reaction?
This property of water explains why it requires large amounts of heat to change temperature.
What is high heat capacity?
These are the building blocks of proteins.
What are amino acids?
This gel-like substance inside the cell surrounds the organelles and provides a medium for chemical reactions.
What is the cytosol?
An element with atomic number 16 has this many electrons in a neutral atom.
What is 16?
This energy barrier must be overcome before a reaction proceeds, and enzymes lower it.
What is activation energy?
Water molecules cling to each other through this property, which helps explain surface tension.
What is cohesion?
This polysaccharide is the storage form of glucose in animals, especially in liver and muscle.
What is glycogen?
Tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions are examples of these specialized structures that connect neighboring cells.
What are cell junctions?
These bonds are not true bonds
What is a hydrogen bond?
This process makes ATP directly during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle by transferring a phosphate group.
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
A solution with pH 3 has this many times more H⁺ than a solution with pH 5.
What is 100 times more?
When proteins lose their structure and function due to heat or pH, this process occurs.
what is denaturing?
This organelle is the "powerhouse of the cell," producing ATP through cellular respiration.
What is the mitochondrion?
This type of bond forms when electrons are shared unequally, producing partial charges
What is a polar covalent bond?
Rather than being reduced, in cellular respiration this molecule is oxidized to form carbon dioxide.
What is glucose?
A solution containing 4 millimoles of phosphate ions (P³⁻) has this many milliequivalents.
What is 12 mEq?
This disaccharide, made of glucose and galactose, is larger than glucose but much smaller than starch or glycogen.
What is lactose?
This process moves water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration.
what is osmosis?
The aggregation of two or more polypeptide chains in a protein represents this level of structure.
What is quaternary structure?
This process in the mitochondria produces the greatest yield of ATP, powered by the electron transport chain.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
20 g of NaOH (MW = 40 g/mol) dissolved in 500 mL solution. Find the molarity.
1.0M
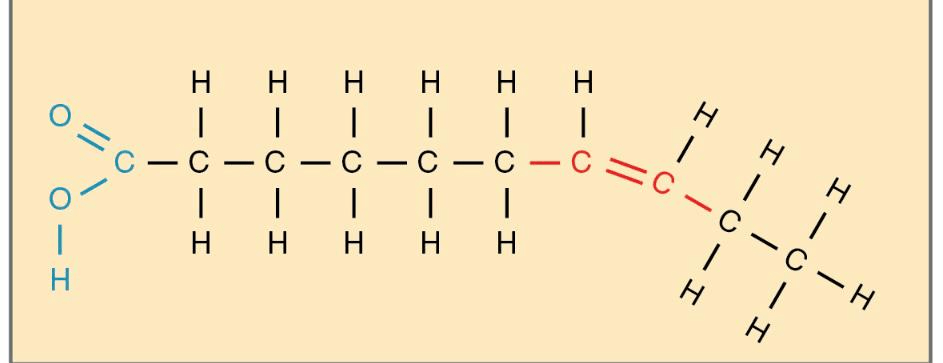
what is unsaturated fatty acid?
This describes the plasma membrane as a flexible layer with proteins floating in a sea of phospholipids.
What is the fluid mosaic model?