This principle states that all living things are composed of cells, and the cell is the basic unit of life.
What is the cell theory?
The random movement of particles from high to low concentration.
What is diffusion?
The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
What is osmosis?
This nucleic acid is single-stranded, uses the base uracil instead of thymine, and helps carry out the instructions stored in DNA.
what is RNA?
This reaction removes a water molecule to join two monomers into a polymer
What is dehydration synthesis/condensation?
The flexible barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell.
what is the plasma membrane?
This process moves water and solutes across a membrane due to hydrostatic pressure.
What is filtration?
The electrical charge difference across the membrane of a resting cell.
What is the resting membrane potential?
Formed when two monosaccharides join by dehydration synthesis; sucrose and lactose belong to this group.
What is a disaccharide?
This type of reaction, also called catabolic, breaks larger molecules into smaller ones and usually releases energy. Its opposite, also called anabolic, builds larger molecules from smaller ones and usually requires energy.
What are decomposition reactions and synthesis reactions?
This structure provides shape and support for the cell and includes microtubules and microfilaments.
What is the cytoskeleton?
This process moves molecules down their gradient using carrier proteins but no ATP.
What is facilitated diffusion?
This pump maintains sodium and potassium gradients essential for nerve impulses.
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
This type of compound will bind (accept) a proton. while the other will donate a proton
What is a base and an acid?
This process forms ATP by directly transferring a phosphate to ADP during reactions like glycolysis, while this process generates most ATP by using the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
What are substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation?
One of these organelles contains digestive enzymes to break down waste and old cell parts, while the other contains enzymes that detoxify harmful substances like hydrogen peroxide. Name both.
What are lysosomes and peroxisomes?
Think of a cell as a shipping company—packages are sent out in vesicles through this process.
What is exocytosis?
The form of endocytosis that brings in fluid and dissolved substances.
What is pinocytosis?
what is this structure?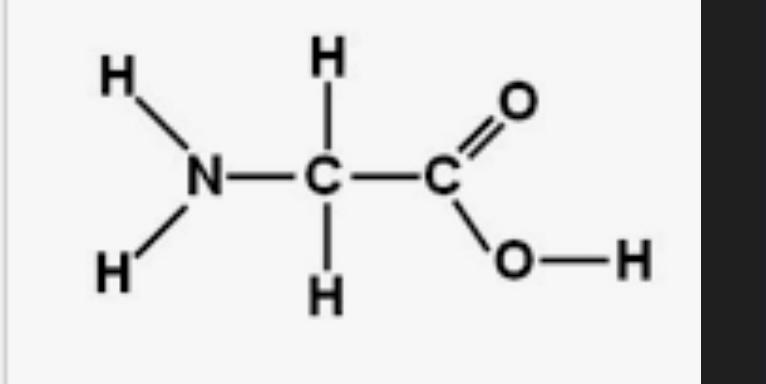
what is amino acid?
the specific region on the enzyme where the substrate binds and the reaction occurs
what is active site?
These are the three specialized junctions that connect neighboring cells. Name them and explain the role each plays.
What are tight junctions (seal between cells), desmosomes (anchor cells for strength), and gap junctions (allow communication between cells)?
Name the two types of active transport, and explain how they differ in their energy source.
What are primary active transport (direct use of ATP) and secondary active transport (indirect use of ion gradients)?
These cell-surface receptors activate G proteins that trigger intracellular signaling cascades.
What are G-protein coupled receptors?
the four levels of protein structure. explain
Primary structure → the linear sequence of amino acids. Secondary structure → local folding into α-helices or β-pleated sheets, stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Tertiary structure → the overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain, stabilized by interactions like disulfide bonds, hydrophobic forces, etc. Quaternary structure → the arrangement/association of two or more polypeptide chains (like in hemoglobin).
Primary = sequence
Secondary = coils/sheets
Tertiary = 3D folding
A 1 L solution of 0.9% NaCl has ____ grams of NaCl and is ____ mOsm.
What are 9 grams and 308 mOsm?