This is a semipermeable membrane in the brain that protects the brain form foreign objects
What is the blood - brain barrier?
This is cranial nerve III and controls voluntary movement of the eyeballs, including pupil constriction.
What is the Oculomotor nerve?
This lobe interprets impulses arising from the retina.
What is the occipital lobe?
This division of the ANS causes a stress response.
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
This picture represents either the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system.
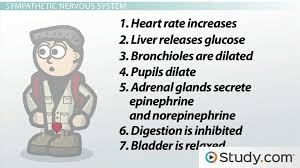
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
This neuron fiber carries impulses toward the cell body
What is a dendrite?
There are three cranial nerves that control the eyeball. Cranial nerve III controls contraction of the eye muscles, Cranial nerve IV regulates voluntary muscles of the eyelid and eyeball. The last cranial nerve is a motor nerve and controls eye movement.
What is Cranial nerve VI the Abducens nerve?
Messages from the internal ear and from sensory receptors in tendons and muscles helps maintain this function.
What is balance?
This division of the ANS reverses the stress response.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
These 2 neurotransmitters are secreted by the ANS.
What are acetylcholine and norepinephrine?
This neuro fiber carries impulses away from the cell body.
What is an axon?
Damage to this nerve causes sagging facial muscles.
What is cranial nerve VII, the facial nerve?
When this area of the brain is damaged, a person can understand what is being said but has difficulty expressing themselves.
What is Broca's area?
The physiologic effects seen in this picture results from this division of the ANS being stimulated.

What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
This system promotes the "flight or fight" response.
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
These are the 3 basic parts of a neuron.
What are the cell body, dendrites, and and axon?
This cranial nerve is the longest and supplies organs in the head, neck, thoracic and abdominal; cavities.
What is cranial nerve X, the vagus nerve?
When this area of the brain is damaged a person will have difficulty understanding the meaning of speech.
What is the Wernicke area?
In the ANS, these fibers secrete acetylcholine
What are cholinergic fibers?
In the ANS this type of adrenergic receptor is excited by norepinephrine (NE).
What is alpha adrenergic receptors?
The myelin sheath is made up of Schwann cells that encase the axons in the neuron and acts to insulate the axon in the peripheral nervous system. Along the myelin sheath there are tiny gaps in the axon that are important in speeding nerve impulse conduction. These gaps are called
What are Nodes of Ranvier?
When this cranial nerve is damaged, there is impaired movement of the head, neck and shoulders.
What is cranial nerve XI the spinal accessory nerve?
This area is responsible for learning and emotions such as anger, fear, sorrow, pleasure, and sexual feelings
What is the Limbic system?
In the ANS, these fibers secrete norepinephrine.
What are Adrenergic fibers?
This group of drugs called beta blockers bind to beta receptors to block which neurotransmitter.
What is norepinephrine?