The amount of air inhaled and exhaled during a normal breath.
What is Tidal Volume?
This structure consists of two sheets of connective tissue and several large muscles.
What is the Abdominal Wall?
Respiratory structure is also known as the "voice box".
What is the Larynx?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/larynx/tZGht0xtLKMYmmgX4SQ_Larynx.png)
Structure that performs gas exchange in the lungs.
What is the Alveoli?
A dome-shaped muscle that is the primary driver of inhalation.
What is the Diaphragm? 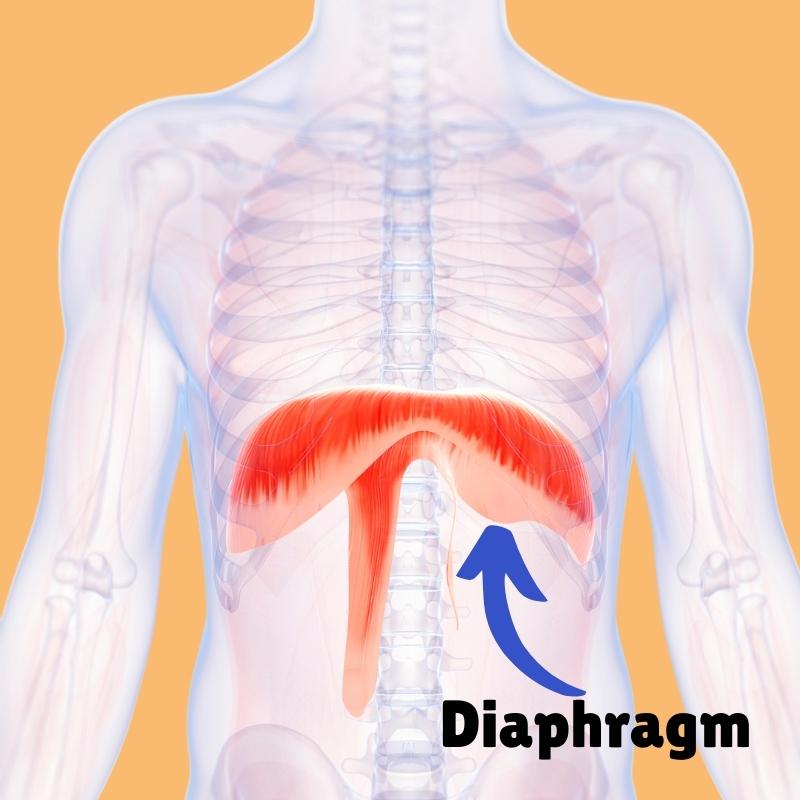
The maximum amount of air the lungs can hold.
What is Total Lung Capacity?
These are cone-shaped, porous, and spongy organs that contain elastic fibers, encased by the visceral and parietal pleura.
What are the Lungs?
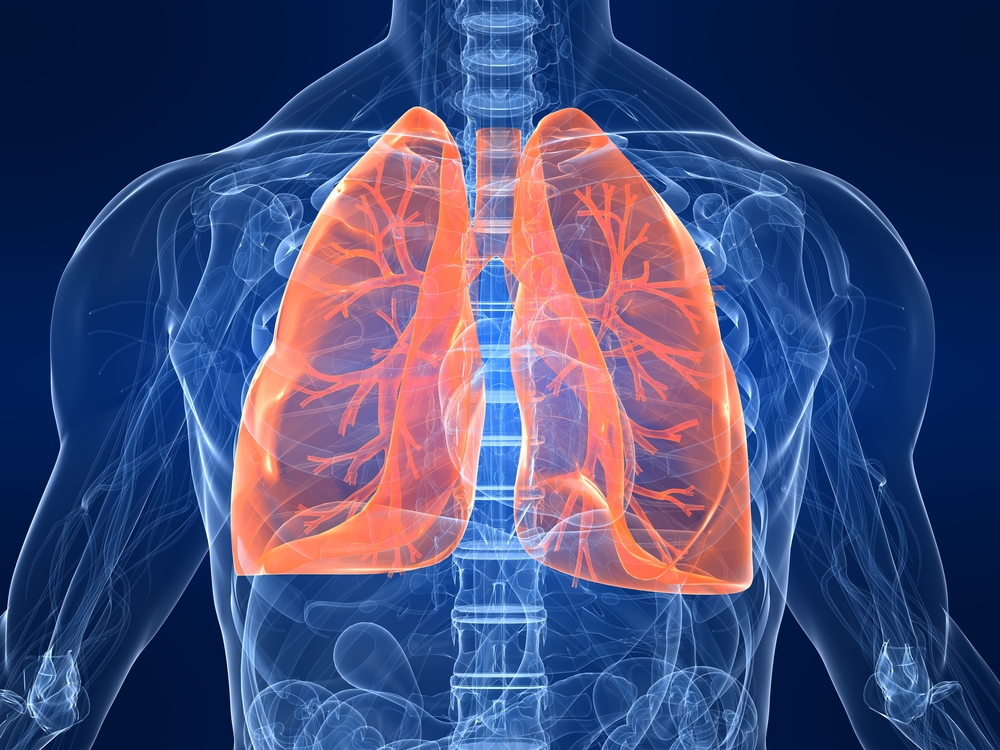
Controls airflow and breath support for phonation.
What is the role of the diaphragm in speech production?
Gas that is absorbed into the blood during inhalation.
What is Oxygen?
Muscles are found between the ribs and help with breathing by moving the ribcage.
What are the Intercostal Muscles?
The air remaining in the lungs after a full exhalation.
What is Residual Volume?
Layer of fluid that links the pulmonary apparatus and chest wall.
What is the Pleaural Linkage?
Structure that helps amplify and shape the sound of your voice.
What is the Nasal Cavity?
Gas that is expelled from the body during exhalation.
What is Carbon Dioxide?
The four abdominal muscles.
What are Rectus, Transversus Abdominis, External and Internal Oblique?

The amount of air your lungs can hold after taking a deep breath in.
What is Inspiratory Reserve Volume?
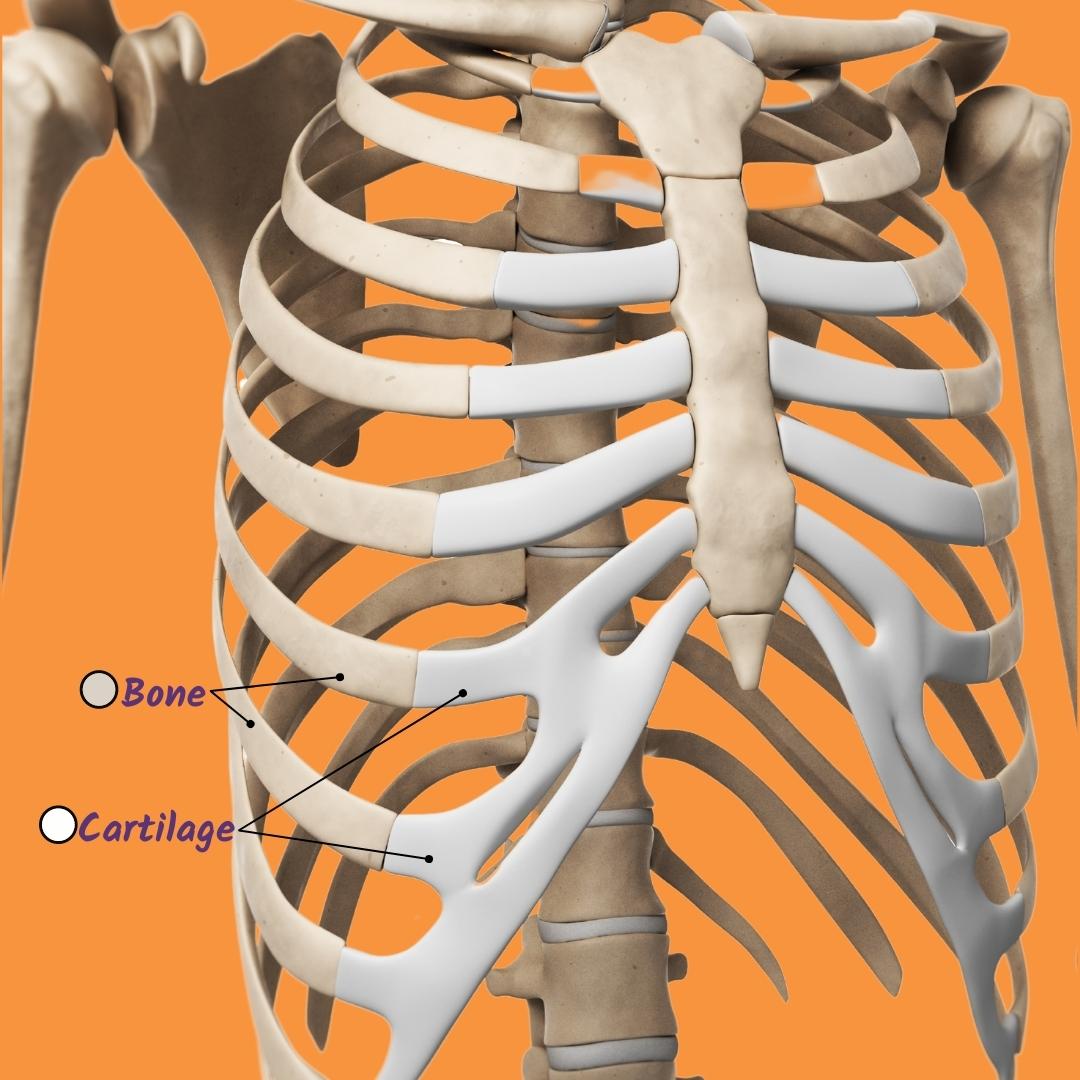
Structure that comprise most of the skeletal framework.
What are the Ribs?
The process of modifying airflow to create different speech sounds.
What is Articulation?
The tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, allowing air to pass into the lungs.
What is the Trachea?

The large neck muscle helps lift the sternum and clavicle during deep inhalation.
What is the Sternocleidomastoid?
The process by which oxygen moves from the lungs into the blood and carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the lungs
What is Gas Exchange?
Structure formed by 34 irregularly shaped bones.
What is the Vertebral Column?
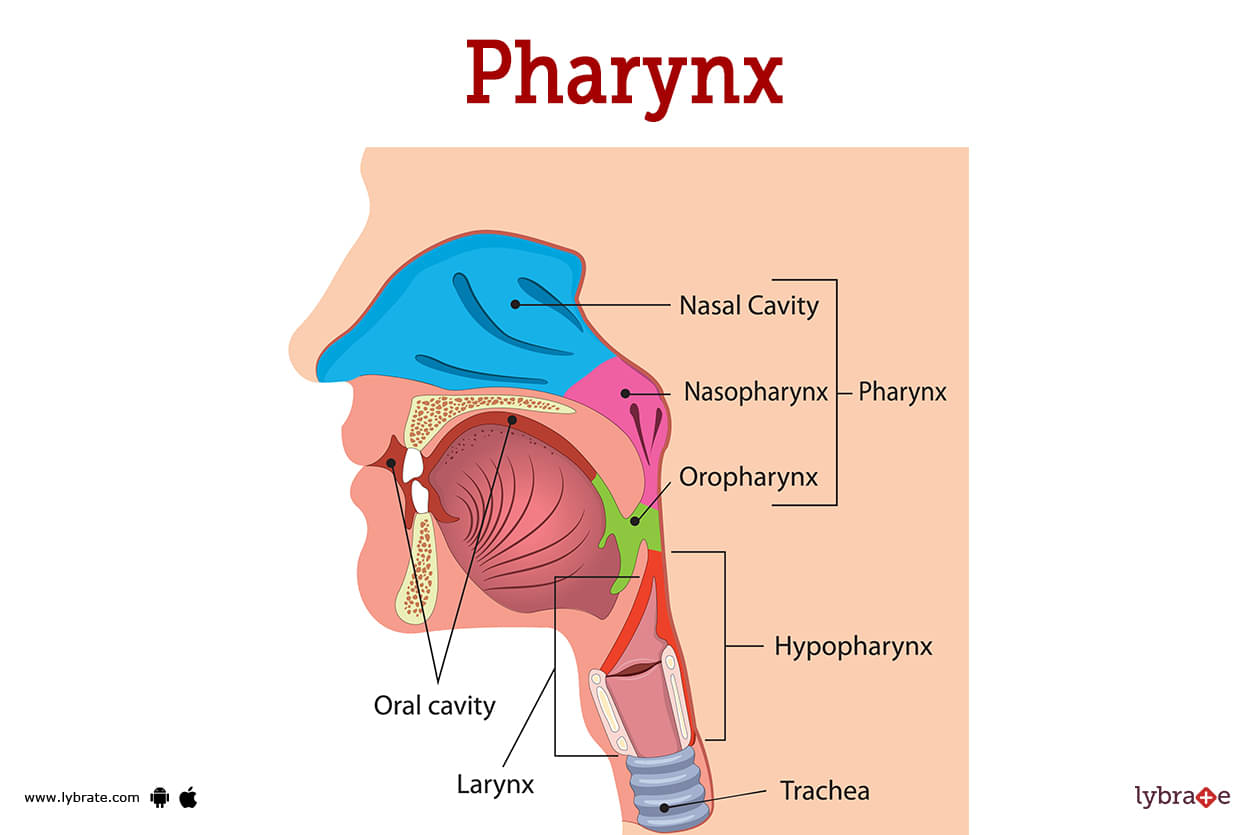
Structure acts as a passageway for air and food, playing a role in speech.
What is the Pharynx?
Structures that are formed when the trachea branches into two main passages that lead to each lung.
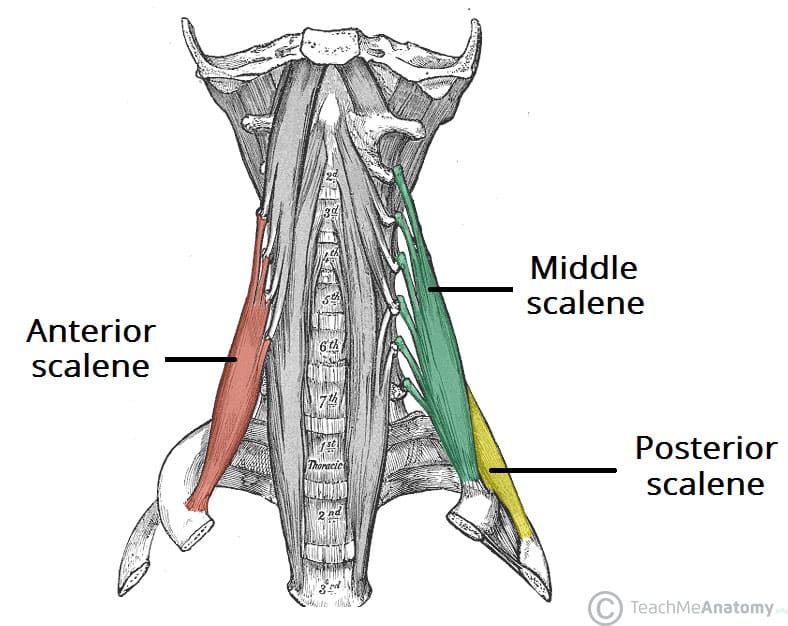
Smaller muscles in the neck help elevate the first two ribs during forced inspiration
What are the Scalene Muscles?