When using the gas laws, temperature must always be expressed in this unit.
Kelvin
This quantity has a value of zero for any pure element in its standard state.
standard enthalpy of formation
(\Delta H_\text{f} ^\circ)
This principle states that the enthalpy change for a given reaction is constant regardless of the pathway taken.
Hess's Law
This term describes an atom’s capacity to attract electrons.
electronegativity
Expanded octets are possible beginning in this row of the periodic table.
row 3
A sample of gas is simultaneously heated and compressed. Does its pressure increase, decrease, or stay the same? (Or is it impossible to tell without more information?) Justify your answer either conceptually or mathematically.
Increase. Faster motion (heating) combined with less space (compression) leads to higher pressure. Alternately, noting that T2 > T1 and V1 > V2, we find P2 > P1 from the following:
(P_1V_1)/T_1 = (P_2V_2)/T_2 -> P_2 = (P_1V_1T_2)/(T_1V_2)
This quantity tells us how much heat is required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by 1 °C.
specific heat capacity
[DAILY DOUBLE] A system absorbs 353 J of heat and does 324 J of mechanical work. What is the resulting change in its internal energy?
29 J
Sometimes, multiple valid Lewis structures can be drawn for a particular compound. If the structures are equivalent (same arrangement of atoms, same number/type of bonds), they are called what?
resonance structures
A compound’s electronic and molecular geometries will be the same if there are none of these on the central atom.
lone pairs
This is the volume occupied by one mole of any ideal gas at STP.
22.4 L
This is the formation equation for liquid water.
\text{H}_2 (g) + 1/2 \text{O}_2 (g) -> \text{H}_2\text{O} (l)
In Lab 7, you calculated both q and ΔHrxn for a given chemical reaction. Briefly explain the difference between these two quantities.
Both measure heat, but q depends on the mass of substance(s) you used in the experiment, while ΔHrxn is defined for the molar amounts in the balanced equation.
Name TWO things that can help you identify the central atom in a molecule.
options: first in formula, only one of its kind, largest in size, least electronegative
This type of molecular structure has angles of 120° between the equatorial atoms and 90° between the axial and equatorial atoms.
trigonal bipyramidal
In a given mixture of N2 and O2, the partial pressure of N2 is 600 torr and the partial pressure of O2 is 200 torr. What is the mole fraction of O2 in this mixture?
0.25
In this block, you have learned four ways to find a reaction's ΔH. List all four.
calorimetry, standard enthalpies of formation, Hess's law, and bond enthalpies
Consider the following thermochemical equation:
2\text{A}+3\text{B}->\text{C}, \DeltaH=-50 \text{ kJ}
If 3 moles of A react with excess B, how many kilojoules of heat are released in this process?
75 kJ
If non-equivalent Lewis structures can be drawn for a given compound, the best one can be determined by calculating the formal charge on each atom. Which TWO things should you be looking out for when selecting the best Lewis structure?
(1) All formal charges should be relatively close to zero. (2) If there are any negative formal charges, they should be on the most electronegative atom(s).
The central atom in a given molecule is surrounded by four bonds and two lone pairs. Identify its electronic and molecular geometries.
octahedral electronic geometry, square planar molecular geometry
Solid CO2 is also called "dry ice" because it goes straight from solid to gas. Suppose you seal exactly 2 grams of dry ice into a balloon at 0.9 atm and 298 K. How big will the balloon get? Express your answer in liters.
1.23 L
A 110-g sample of a metal (specific heat capacity = 0.200 J/g·°C) is heated to 82.4 °C and then placed in a container of water at 22.3 °C. The final temperature of the water and metal is 24.9 °C. What is the mass of the water in the container, assuming all of the heat lost by the metal is gained by the water?
116 g
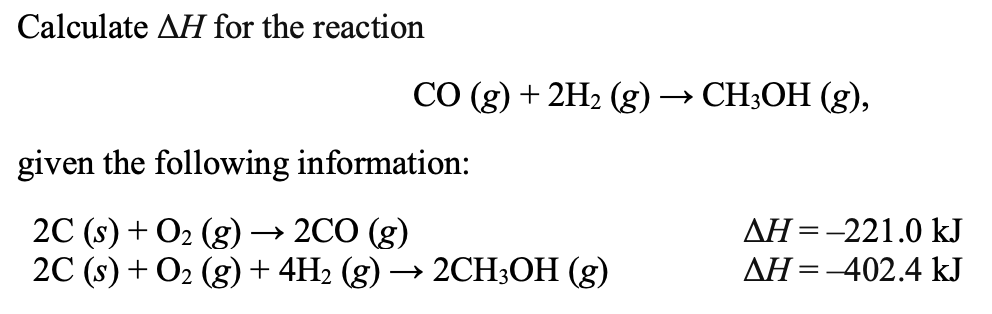
–90.7 kJ
The central atom in a given molecule is surrounded by a double bond, a single bond, and a lone pair. Identify its electronic and molecular geometries.
trigonal planar electronic geometry, V-shaped/bent molecular geometry
Draw the Lewis structure for H2CO (carbon is the central atom). Provide its electronic and molecular geometries, and state whether it is polar or nonpolar.
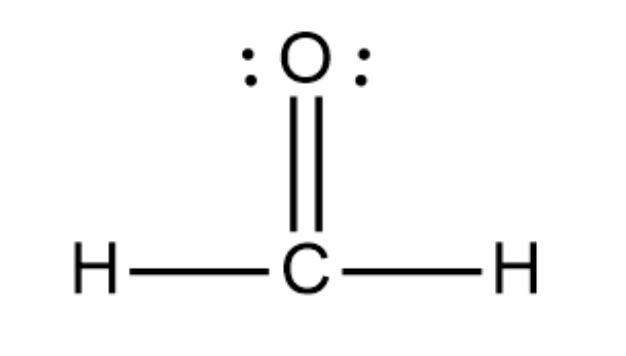
Its electronic and molecular geometries are both trigonal planar. It is polar.