Maneuver is used for a shoulder dystocia?
What is McRoberts maneuver and suprapubic pressure
Normal Newborn
HR:
RR:
Temp:
What is:
110-160 beats per minute
30-60 breaths per minute
36.5-37.5 C
The GOLD standard of treatment for GDM
What is Insulin
Gene(s) linked to Breast Cancer
What is BRCA1 and BRCA2
Synthetic form of endogenous oxytocin
What is Pitocin
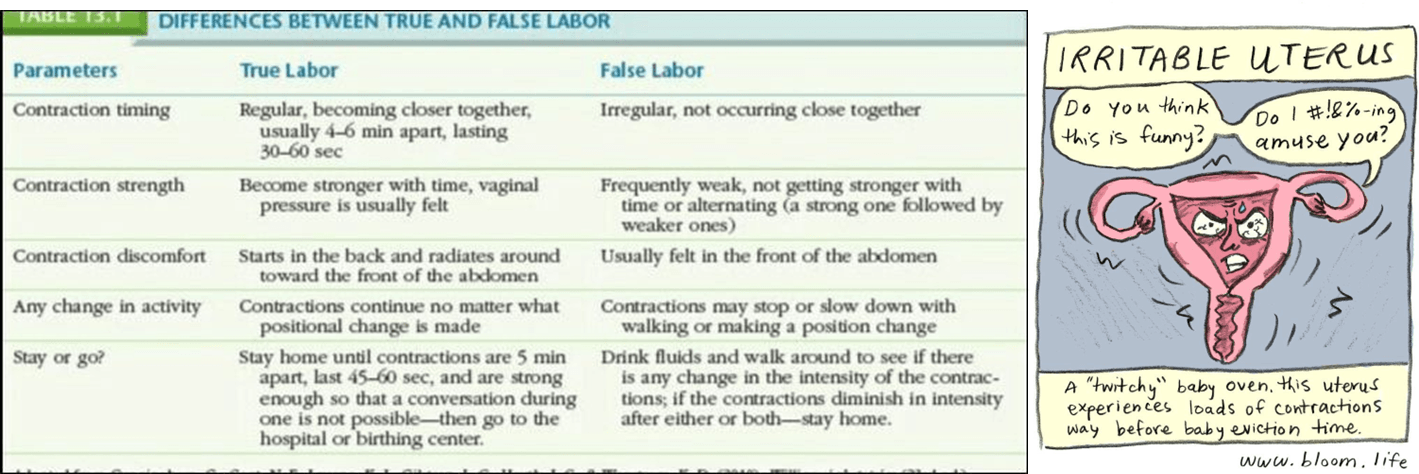
Describe true labor V. false labor
Name 3 reasons a newborn may experience hypoglycemia
What is:
SGA
LGA
Cold stress
GDM mother
Improper feeding/Latch
Preterm/Late Preterm
Used to detect chromosomal abnormalities and several hereditary metabolic defects
A birth control method that requires monthly checks for string length
What is an IUD
Given IM to mom to stimulate fetal lung maturity
What is Betametasone?
An area mom would feel excess pain or pressure for a baby in the OP position.
What is lower back/laboring through her back
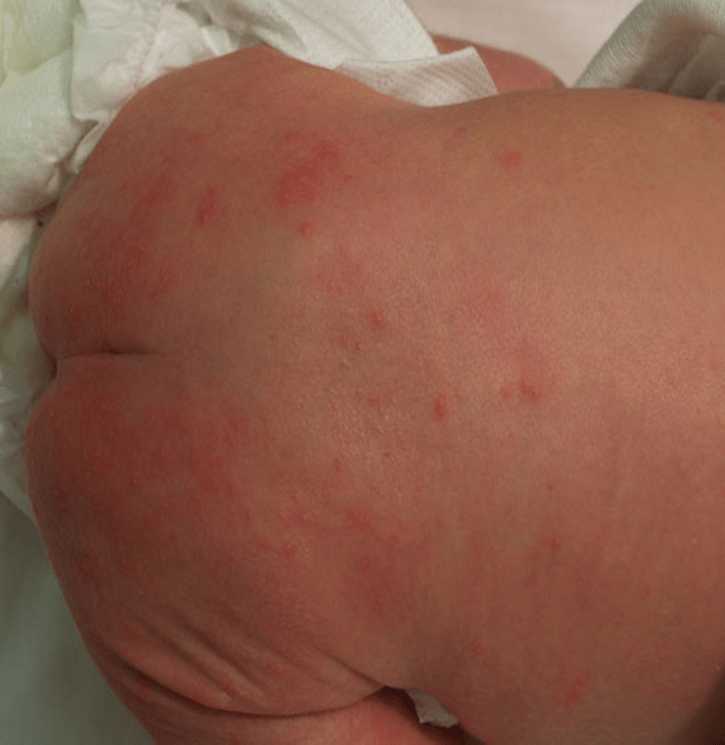
What is Erythema Toxicum
aka normal newborn rash
Braxton Hicks contractions (16–28 wks)
Positive pregnancy test (4–12 wks)
Abdominal enlargement (14 wks)
Ballottement (16–28 wks)
Goodell’s sign (5 wks)
Chadwick’s sign (6–8 wks)
Hegar’s sign (6–12 wks)
What are Probable Signs of Pregnancy
A birth control method contraindicated in women who smoke or with uncontrolled hypertension
What medication used to control PPH is contraindicated in a patient with a h/o asthma?
What is Hemabate?
Name FIVE symptoms of preterm labor
Change or increase in vaginal discharge
Pelvic pressure
Low, dull backache
Menstrual-like cramps
Urinary tract infection symptoms
Feeling of pelvic pressure or fullness
Gastrointestinal upset
Intestinal cramping
- General sense of discomfort or unease
Heaviness or aching in the thighs
Uterine contractions
More than six contractions per hour x 2 or more hours
Shortened cervix on ultrasound/ “funneling”
Name 2 pathologic signs of jaundice
What is:
Appears within 24 hours of birth-Requires intervention
Mother/newborn blood group incompatibility
Polycythemia
Systemic Acidosis
Cephalohematoma
Infections
The two layers of the membrane surrounding the developing fetus
What are the Chorion and the Amnion?
Chorion: the layer closest to the intrauterine wall that gives rise to the placenta and continues as the outer membrane surrounding the amnion Amnion: the inner of the two membranes that form the sac containing the fetus and the amniotic fluid
Characterized by steady decline in number of immature ova, estrogen levels and testosterone levels. Involves the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian-uterine axis and has physiologic changes in reproductive organs and multiple body systems
What is Menopause
Characterized by elevated BP and/or maternal organ dysfunction
What is a pharmacologic tx? What is reversal agent?
What is PreE w/ severe features?
What is magnesium sulfate?
What is calcium gluconate?
Name the stages of Labor
What is
Stage 1- 0 cm to 10 cm dilated
Stage 2- Birth of the infant
Stage 3- Delivery of the placenta
Stage 4- Recovery- Begins after placenta is delivered to 4 hours after birth
Heat loss in Newborns:
Name and describe 2 of the 4 types
What is:
Conduction: when the newborn is placed naked on a cooler surface, such as table, scale, cold bed., there is a transfer of heat from the newborn to that surface.
Convection: when the newborn is exposed to cool surrounding air or to a draft from open doors, windows he/she loses heat to surrounding air or liquid.
Evaporation: the infant often loses heat when amniotic fluid on his/her skin at birth evaporates.
Radiation: when the newborn is near cool objects, walls, tables, cabinets, without actually being in contact with them. This is the primary cause of heat loss after birth.
Physiologic Anemia of Pregnancy
What is an increase in blood volume that occurs at a larger proportion than the increase of RBC (Lower hematocrit and hemoglobin)
Treatment: Iron supplementation
Name four medical treatments for PCOS
What is:
Oral Contraceptives
Hirsutism Treatments
Metformin for hyperinsulinemia
Thiazolidinedione (Avandia) to decrease insulin resistance
Clomid to treat infertility
Statins for hyperlipidemia
Four T's of PPH
What is:
- Tone: Uterine atony
- Trauma: Genital tract trauma
- Tissue: Retained products of conception
- Thrombin: Coagulopathy