Name all 4 IMF's and in order from strongest to weakest
-Ion Dipole
-Hydrogen Bonding
-Dipole Dipole
-London Dispersion Forces
What is Henry's Law equation and what does each part mean?
Sg=kPg
Sg=solubility
k=Henrys constant
Pg=partial pressure
Define Solute, Solvent, and Solution.
Bonus: explain the connection between IMFs and what solvent dissolves which solute
Solute- whats being dissolved
Solvent- whats doing the dissolving
Solution- the combination of the soute and solvent
Bonus: solvents dissolve solutes with similar IMF
polar dissolves polar and ionic, nonpolar dissolves non polar
Which of the following occurs to an aqueous solution upon the addition of a solute?
I. The vapor pressure increases.
II. The freezing point increases.
III. The boiling point increases
a) 1,2,& 3
b) 2 only
c) 3 only
d) 1 and 3
c) 3 only
Label each point on the phase diagram:

A- Solid-Liquid point
B- Solid-Gas point
C- Solid
D- Liquid
E- Gas
F- Triple Point
G- Supercritical Point
Define Viscocity, Surface tension, and Capillary Action
Viscocity- resistence to flow/ how thick it is
Surface tension- force that pulls liquids inward
Capillary Action- ability of a liquid to flow against gravity and up the capillary
Fill in this table
3 Masses 2 Moles 1 Volume
a) d) f)
b) e)
c)
a)mass of solute
b)mass of solvent
c)mass of solution
d)moles of solute
e)moles of solvent
f)volume of solution
What does unsaturated, satured, and supersaturated mean?
Unsaturated= below max of solute that can be dissolved
Satuated= at the max amount of solute that can be dissolved in the solvent
Supersaturated= more than the maximum amount of solute dissolved in the solvent (Unstable)
What is the vant Hoff i factor for Al(NO3)3
4
Label each section such as A-B, B-C, etc..
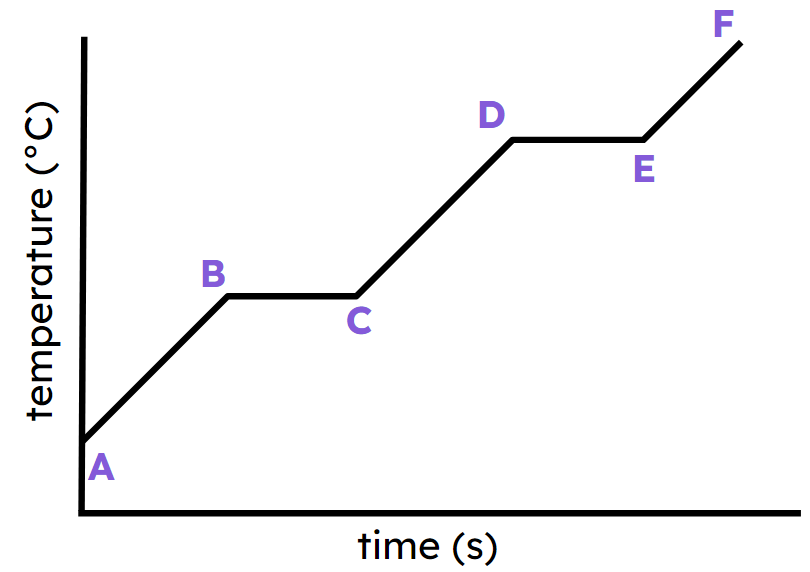
A-B) heating solid
B-C) solid to liquid
C-D) heating liquid
D-E) liquid to gas
E-F) heating gas
Name the three reasons a molecule would be polar
Hint: one of the reasons you have to list the 6 elements bonded to C or H that would make it polar
1. theres an element bonded to a different element
(element bonded to itself is nonpolar)
2. C or H is bonded to:
-O, -N, -F, -Cl, -Br, -I
3.if the molecule is not symmetrical
Formula for Molarity, molality, mass %, mole fraction, and density
M= moles of solute/liters of solution
m= moles of solute/kg of solvent
mass %= moles of solute/total mass of solution
fraction= moles of solute/total moles of solution
density= mass of solution/volume of solution
Define Miscible and Immiscible
Miscible- two liquids that are completely soluble in one another (simmilar IMF)
Immiscible- two liquids that will not dissolve in one another (different IMF)
Which of the following aqueous solutions would have the lowest freezing point?
a. 0.10 m C6H12O6
b. 0.10 m NaCl
c. 0.10 m BaCl2
d. 0.10 m Al2(SO4)3
d. 0.10 m Al2(SO4)3
What fraction of each atom is in each unit of a cell for:
Corner, edge, face, and body atoms
Corner: 1/8
Edge: 1/4
Face: 1/2
Body: 1
Name the IMF's:
HF
HCl
CH3OH
CH3CH3
KCl in H 2 O
CaCl2 in CH3CH2OH
-H bond
-Dipole Dipole
-H bond
-LDF
-Ion dipole
-Ion dipole
What are the formulas used for heating and cooling curves?
Hint: horizontal portion has 4 different variations
Sloped:
q=MCdeltaT
Horizontal:
q=mdeltaHfus
q=ndeltaHfus
q=mdeltaHvap
q=ndeltaHvap
Define the folowing:
Freezing Point Depression
Boiling Point Elevation
Vapor Pressure Lowering
FPD: need colder tempertures to freeze
BPE: need higher temperture to boil something
VPL: when VP of a solvent lowers when a non volatile solute is added to it
Under which conditions would you expect to find the largest concentration of carbon dioxide in water in a
soda bottle? (The pressure refers to the partial pressure of carbon dioxide over the solution in the bottle.)
a. 5 °C and 5 atm c. 85 °C and 5 atm
b. 5 °C and 1 atm d. 85 °C and 1 atm
a. 5 °C and 5 atm
Why is delta Hvaporization so much bigger than delta Hfusion?
delta Hvaporization has to break all the IMF's present while deltaHfusion only has to break some
How do IMF's affect capillary action, surface tension, viscosity, vapor pressure, and boiling point?
hint: strong imf's=?
-Stronger IMF's= greater surface tension
-Strong IMF's= taller column of liquid
-Strong IMF's= lower vapor pressure
-Strong IMF= higher boiling point
What are the freezing point depression and the boiling point elevation formulas?
hint: theres two formulas for each so four total
FPD
-Tf solution =Tf solvent - delta Tf
-delta Tf= i Kf m
BPE
-Tb solution= Tb solvent+ delta Tb
-delta Tb = i Kb m
Finish the scentence:
Solids:
High temp= ____ solubility
High pressure= ____ solubility
Gas:
High temp= _____ solubility
High pressure= _____ solubility
Liquid:
High VP= _____ BP
Solid
High Temp= High Solutbility
Pressure doesn't affect solid solubility
Gas
High Temp= Low Solubility
High Pressure= High Solubility
Liquid
High VP=Low BP
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 85.0 g of HCl in 275 mL of solution? Molar mass of HCl is
36.46 g/mol.
a. 7.23 M d. 8.81 M
b. 7.92 M e. 9.25 M
c. 8.47 M
c. 8.47 M
Name the following transitions:
Solid to Liquid
Liquid to Solid
Solid to Gas
Gas to Solid
Liquid to Gas
Gas to Liquid
Soild to Liquid: Melting
Liquid to Solid: Freezing
Solid to Gas: Sumblimation
Gas to Solid: Deposition
Liquid to Gas: Vaporization
Gas to Liquid: Condensation