magic
magic
Name this condition 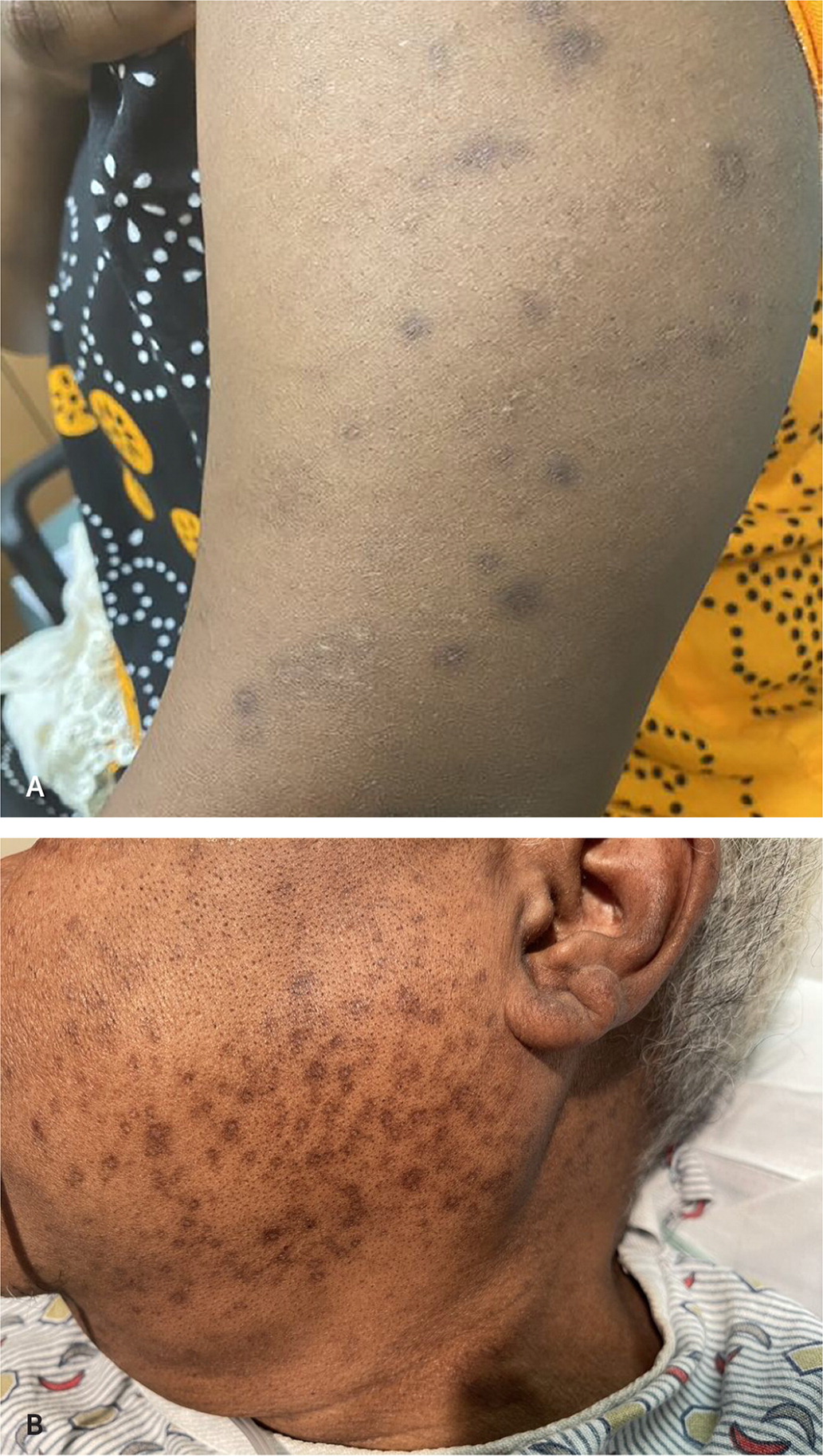
Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation - a reactive hyper melanosis that occurs after endogenous inflammation or external injury
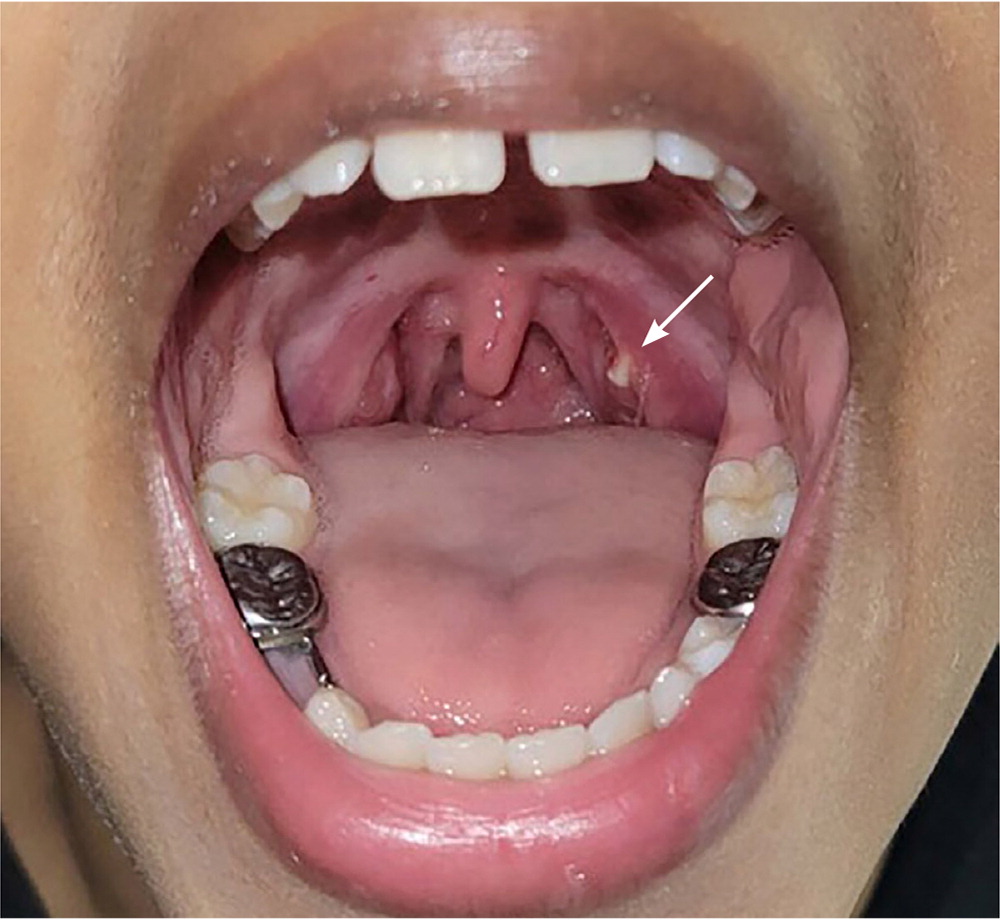
Tonsilloliths can be asymptomatic when small and appear as mineralized, white or yellow collections in the deep tonsillar crypts. Symptoms include recurrent sore throat, halitosis, sensation of a foreign body in the throat, odynophagia, and hoarseness.
Patient presents with pain in hands, worse in the morning and improves during the day for the past 3 months. Exam reveals swelling in the MCP and PIP joints. CRP and ESR mildly elevated. Rheumatoid factor positive.
XRay findings:
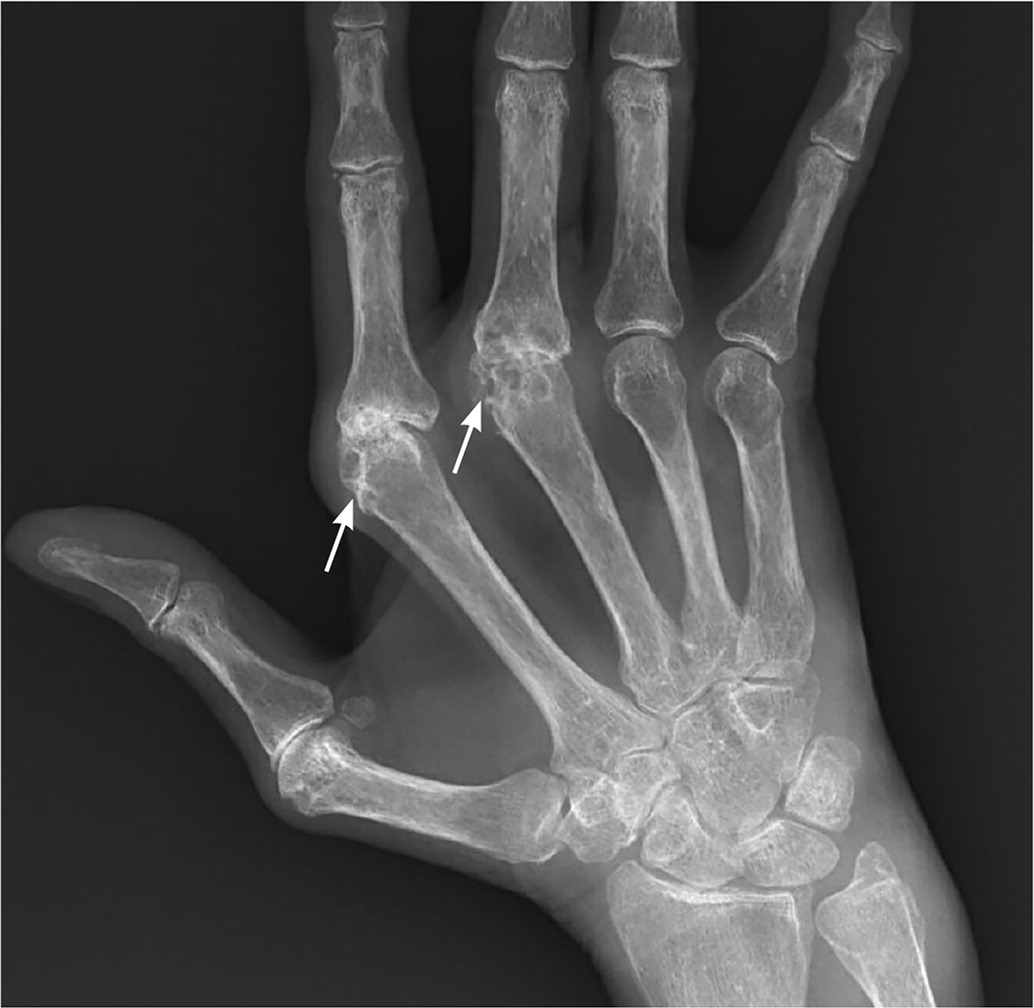
RA
Preferred medication treatments of acute or chronic hyperkalemia
Patiromer (Veltassa) and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma)
First line treatment for temporomandibular disorders
Define the condition in this image:
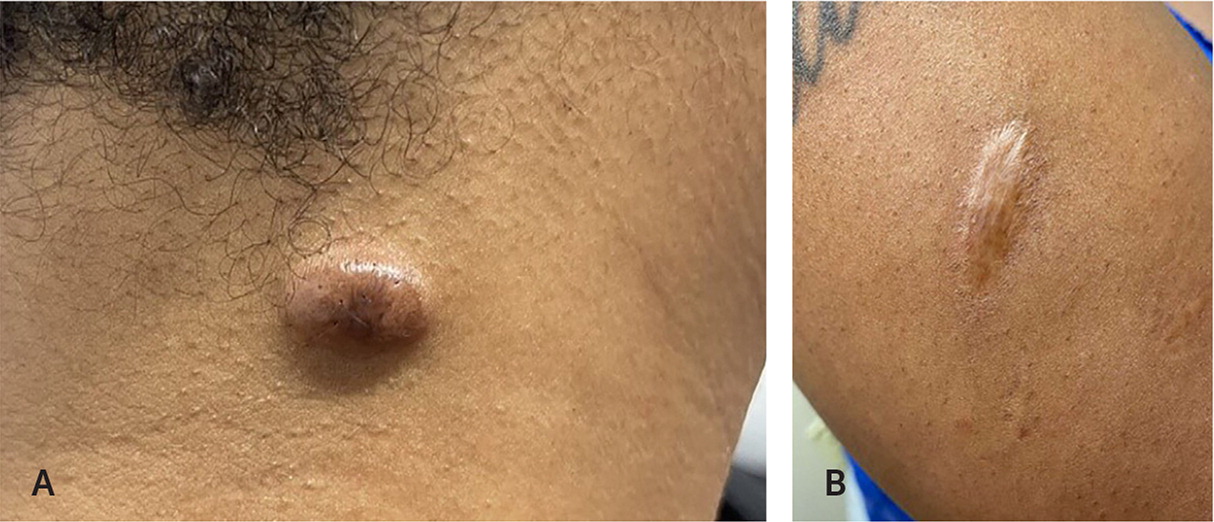
Keloids - firm, rubbery proliferative nodules that occur 1 to 12 months after injury
They extend beyond the boundary of the original injury and do not regress spontaneously
Treatment for bacterial GAS tonsillitis
Penicillin V 500mg BID or TID x 10d
Amoxicillin 500mg BID (50mg/kg daily in kids) x 10d
Penicillin G 1.2 million units IM x1
Cephalosporins for mild to moderate penicillin allergy
Macrolides for severe penicillin allergy
Redness
Swelling
Warmth with prolonged morning stiffness
Pain at night
Stiffness with rest
Indications for IV potassium ( as opposed to PO) replacement - name 2
Severe hypokalemia (<2.5 mEq)
ECG abnormalities (peaked T waves)
neuromuscular symptoms (or other physical sx)
Unable to tolerate PO
Testing for mono
CBC with diff
Rapid heterophile antibody test (monospot)
Name and treatment
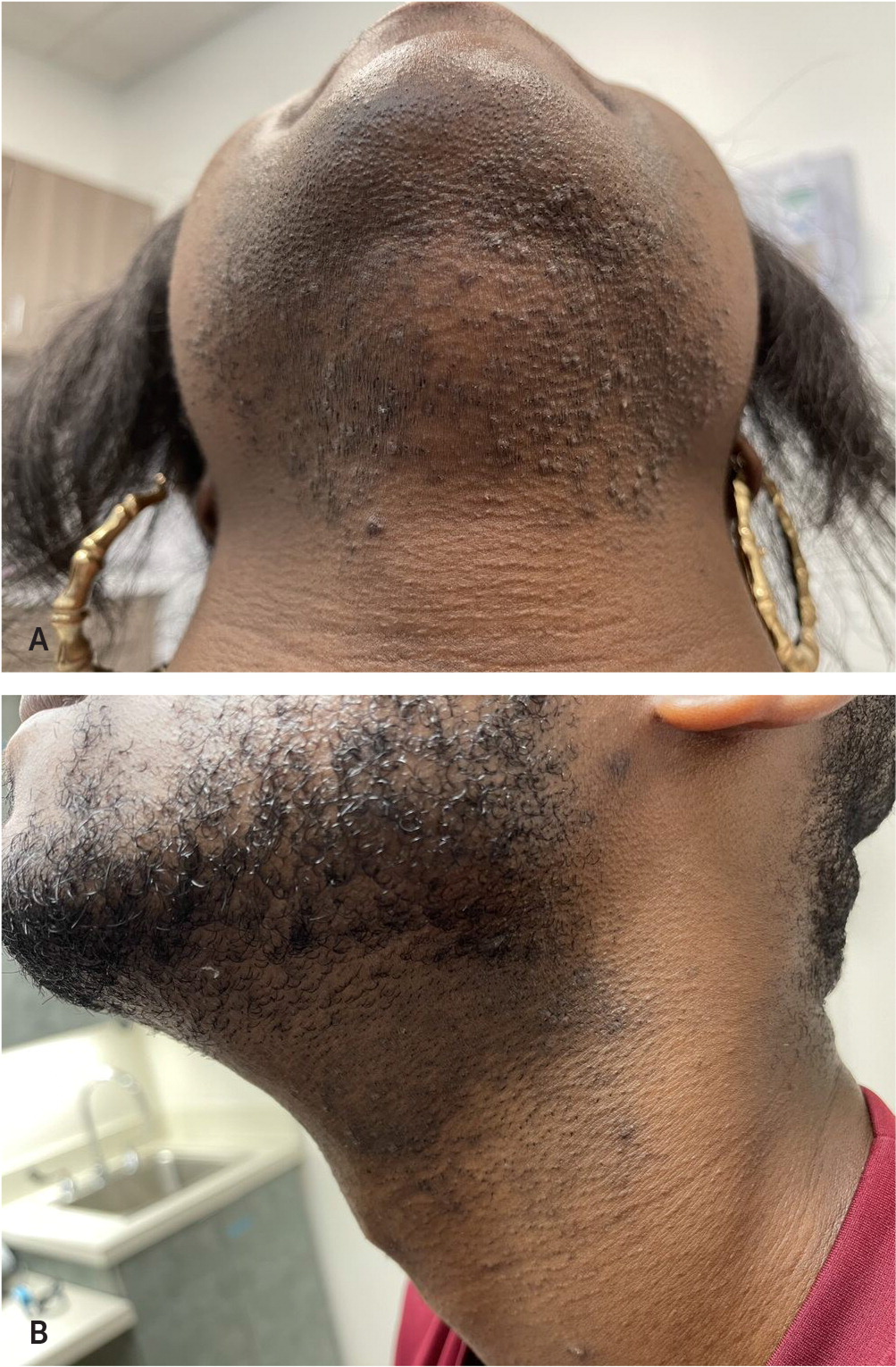
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae aka "ingrown hairs" - erythematous or hyperpigmented, firm papules and pustules in a beard distribution. It is caused by follicular penetration of recently shaved curly hair.
Treatment: avoiding shaving for 8 weeks. Possible meds include benzoyl peroxide, clindamycin gel, tretinoin cream
70-95%
Differential diagnosis for ACUTE inflammatory polyarthritis (name 5) - <6 weeks
Gonorrhea, infectious endocarditis, Lyme disease, meningitis, rheumatic fever
Gout, pseudogout
Polymyalgia rheumatica, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, SLE
Sarcoidosis
HIV, parvovirus B19, viral hepatitis
High to low: Wide QRS, bradyarrhythmias, prolonged PR interval, peaked T wave, U waves, prolonged QT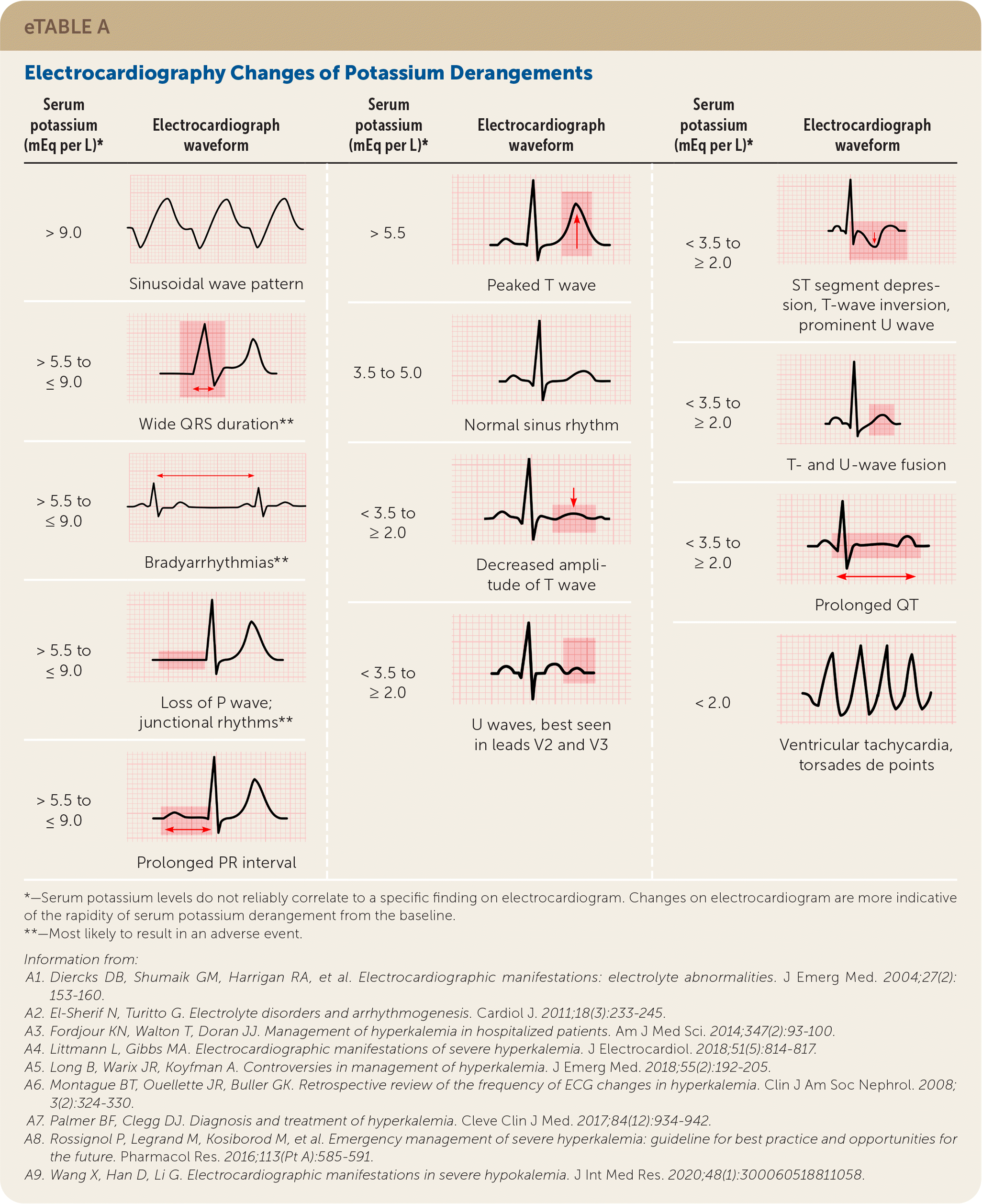
What restriction is associated with mono?
No sports/exercise for 3 weeks due to risk for splenic rupture.
Most splenic rupture occurs 21 days after symptom onset.
Treatment for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation
Standard therapy = topical lightening agent hydroquinone 4% 1-2x / day for 3 months
Other options: adapalene 0.3% gel & tretinoin 0.1% cream (for acne associated)
List the centor criteria
+1 for 3-14 years, -1 for >44 years
tonsillar swelling or exudates +1
Tenders/swollen anterior cervical lymph nodes +1
Fever +1
Cough absent +1
*consider test for score of 2 or more. IDSA recommends treatment only for positive testing.
Differential diagnoses for CHRONIC inflammatory polyarthritis (name 3) - 6 weeks or more
Pseudogout, gout, IBD associated arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, sjogrens, SLE
Name 4 causes for hypokalemia
Medical: type 1 or 2 renal tubular acidosis, hypomagnesemia, chronic/acute diarrhea, bowel prep, vomiting, refeeding syndrome, alkalosis, thyrotoxicosis, hypothermia, anorexia, starvation, TPN
Medications: thiazide or loop diuretics, mineralocorticoids, exogenous steroids, laxatives/enemas, insulin, beta agonists, caffeine
Symptoms associated with mono (name 5)
Pharyngitis, fever, fatigue, tonsillar enlargement or exudate, lymphadenopathy, and/or palatal petechiae
Name and treatment
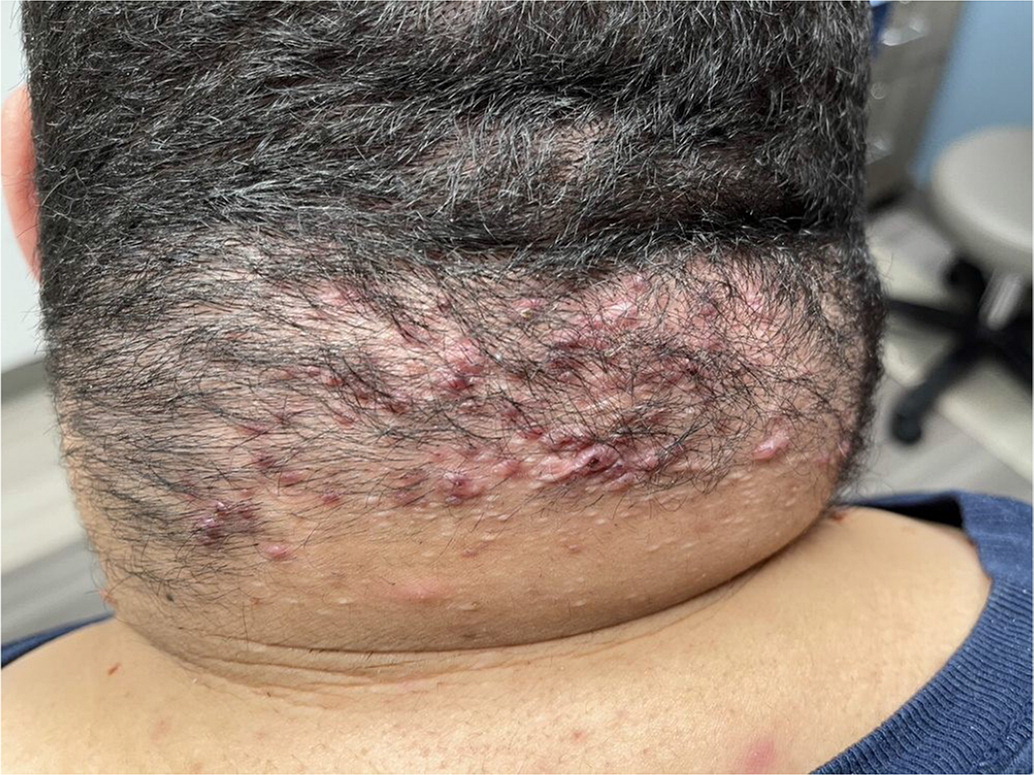
Acne keloidalis nuchae - a chronic inflammatory condition leading to scarring of the hair follicles, development of keloid-like papules and plaques, and cicatricial alopecia of the nuchal and occipital scalp
Tx: triamcinolone with topical retinoids or clindamycin 1% (mild). intralesional triamcinolone (moderate). surgical excision (severe).
Derm- phototherapy and laser therapy
Complications of bacterial tonsillitis (name 2)
Abscess
Rheumatic fever (group A strep) - a nonsuppurative sequela that occurs two to four weeks following group A Streptococcus (GAS) pharyngitis and may consist of arthritis, carditis, chorea, erythema marginatum, and subcutaneous nodules. Damage to cardiac valves may be chronic and progressive, resulting in cardiac decompensation. Usually in children 5-15 years. Seldom occurs before age of 2-3 years or in adults.
Acute glomerulonephritis
Scarlet fever (diffuse erythematous skin eruption)
Work up for inflammatory arthropathies
ESR & CRP
RA & CCP ab testing
ANA
Joint aspiration if applicable
X-ray
Define the different stages of CKD (1-5) based on GFR and associated recommended potassium intake
1: eGFR 90 or higher - 3510 mg
2: eGFR 60-89 - 3510 mg
3: eGFR 30-59 - 3510 mg unless severe hyperK
4: eGFR 15-29 - <3000 mg
5: eGFR <15 - <3000 mg
Presenting symptoms of temporomandibular disorder (name 5)
headache, bruxism (teeth grinding), pain at the TMJ, otalgia, jaw popping/clicking, tinnitus, dizziness, decreased hearing, or hyperacuity to sound