Indication for Referral of a Distal Phalanx fracture/mallet finger
2. Inability to flex or extended joint/loss of distal sensation
3. Non union
Routine Labs?
NO! unless moderate to high risk surgery and/or other clinical concerns based on individual patient history
outpatients with comorbidities and inpatients with non severe CAP
A combination of a beta-lactam or third-generation cephalosporin plus a macrolide, or monotherapy with a respiratory fluoroquinolone is recommended. Patients should be treated for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas infection only if they present with risk factors for those pathogens
Concerning soft tissue characteristics
Masses that are deep to the fascia, are 5 cm in diameter or larger, grow rapidly, or present suddenly without explanation
Most widely used clinical tool to determine severity of injury and prognosis of a stroke

In the absence of above concerns, splinting the DIP joint in full extension for four to six weeks is usually sufficient.
Most common in-hospital surgical procedures
Orthopedic, tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy
Abx treatment in outpatients with CAP without comorbidities
amoxicillin, doxycycline, or a macrolide is recommended (the latter only in areas where pneumococcal resistance to macrolides is less than 25%)
Superficial mass that is freely mobile with a doughy consistency
Lipoma
Encephalopathies, infection, electrolyte disturbances, psychogenic conditions, and toxicities are all examples of....
Stroke Mimics... aka certain conditions that can present similarly to stroke
Management of "Mallet Finger"
In the absence of indications for referral, mallet finger (with or without an avulsion fracture) can be effectively treated with strict immobilization. The DIP joint should be splinted in full extension to slight hyperextension for eight week
HEMSTOP (Hematoma, hEmorrhage, Menorrhagia, Surgery, Tooth extraction, Obstetrics, Parents)
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine regiment
All adults 65 years or older or those 19 to 64 with underlying conditions should receive the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine alone or the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine followed by 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine one year later.
10 year old with painful cervical (Neck) mass
Rhabdomyosarcoma! Ultrasound first line imaging study, referral to orthopedic oncology
What diagnosis should be considered in patients with sudden onset of a severe atraumatic headache that is described as the worst headache of their life
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
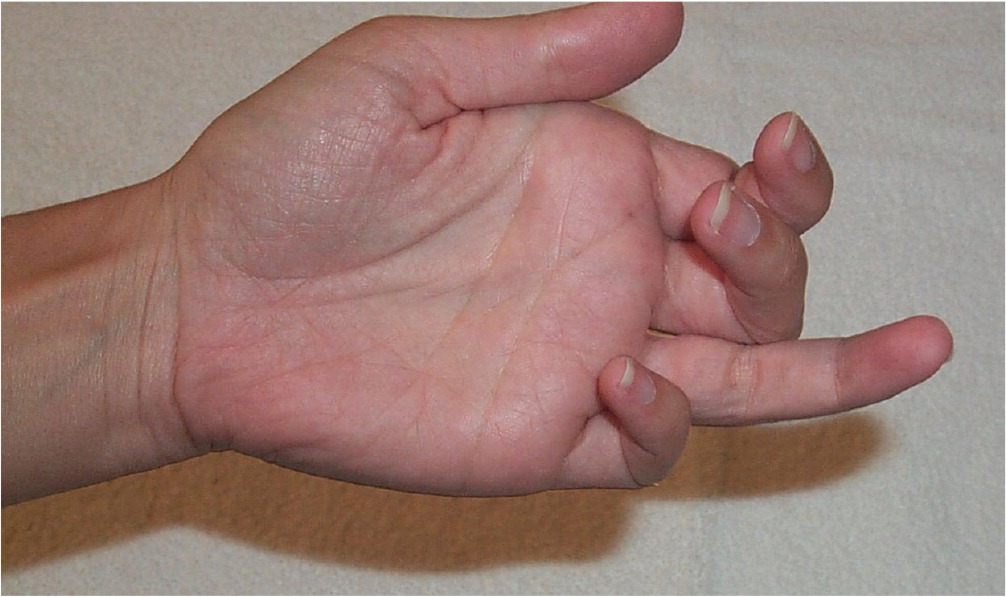
Flexor digitorum profundus avulsion fracture (jersey finger). Require expedited referral to an orthopedic specialist because flexor digitorum profundus avulsion fractures can benefit from surgery within seven to 10 days.
What is the Choose Wisely Campaign

CRB-65
-Confusion
-RR >30
-BP <90
-65 and older
Moderate (1 or 2) ---> Hospitalize in most cases
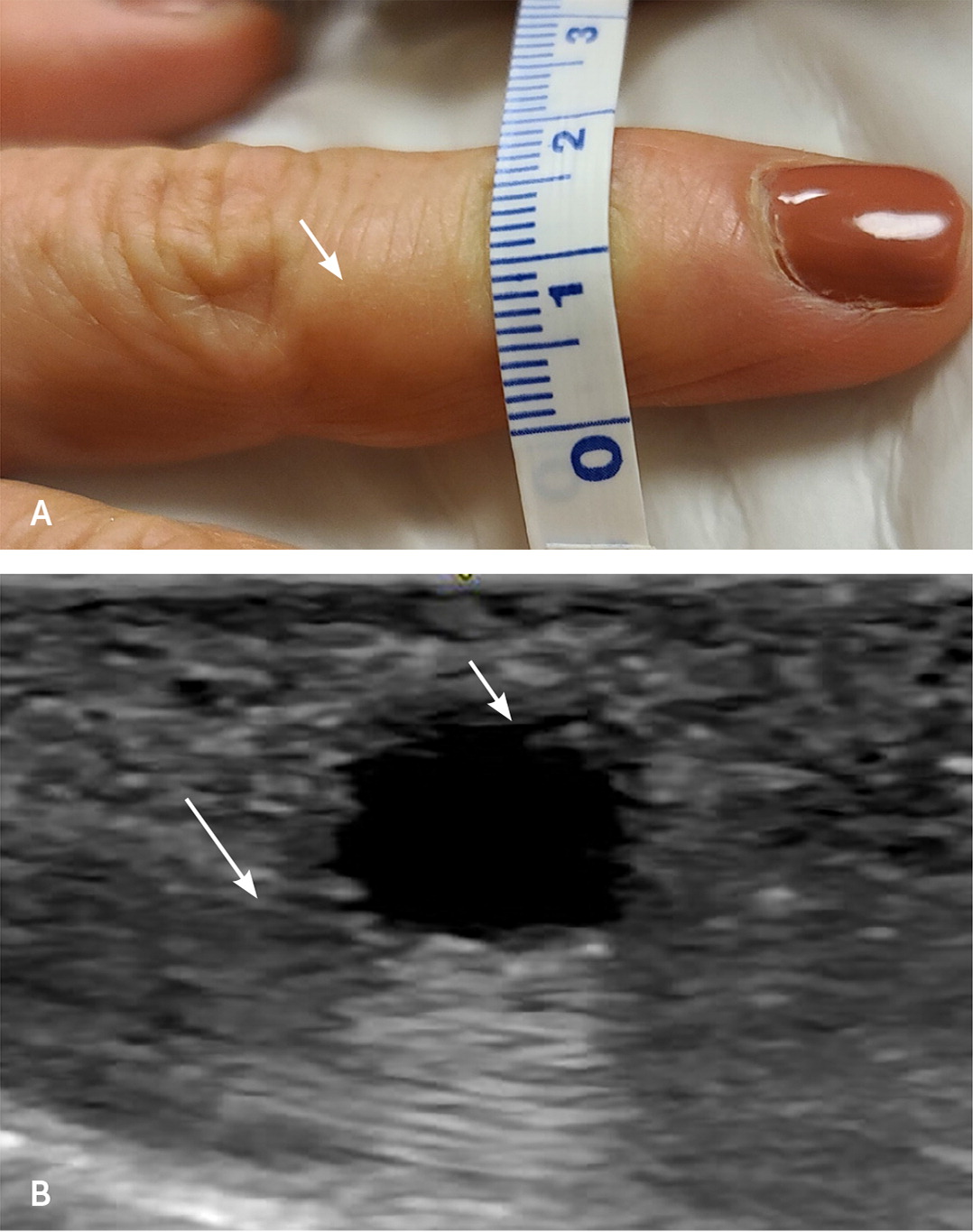
Ganglion cysts arise from joint, ligament, or tendon injuries. The capsule contains hyaluronic acid and mucopolysaccharides, which are highly viscous, Symptoms can include pain, swelling, and stiffness of the joint. These can be Observed, aspiration can be performed, or excision.
What test is required before administration of rtPA
Glucose! Elevated blood glucose at the time of acute stroke increases the risk of hemorrhagic transformation with tPA treatment and it is associated with poor clinical outcomes, longer in-hospital stay, increased cost, and mortality.
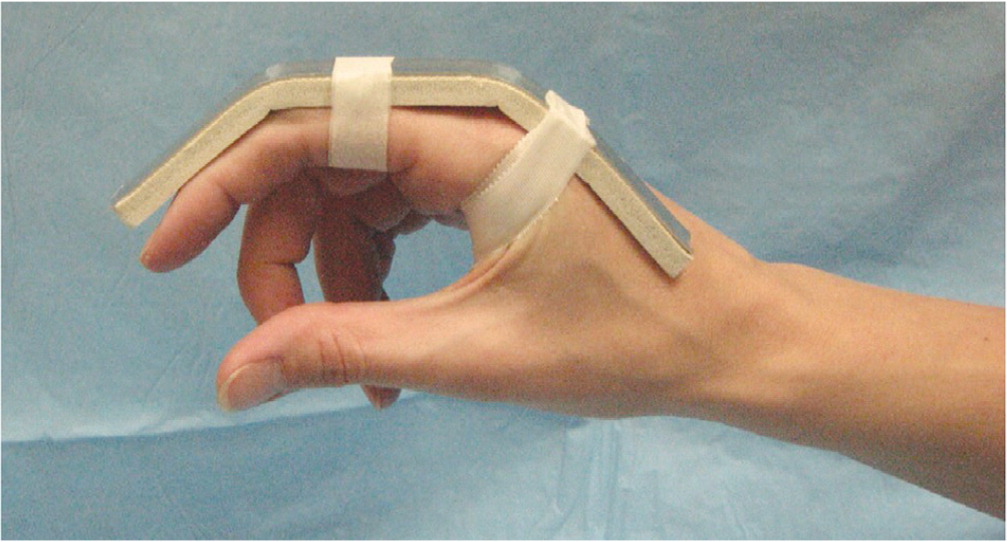
Dorsal dislocations of the PIP joint should be treated using an extension-block splint, with the finger slightly flexed at 20 to 30 degrees for two to three weeks, then progressive flexion as tolerated.
Medications to continue perioperatively
Antiepileptics, Asthma Inhalers, H2/PPI, Steroids
Severe CAP workup includes...
-Testing for Legionella species should be reserved for cases of severe CAP or in areas where a known outbreak of Legionella infection has occurred
-Diagnostic cultures and antigen testing should be obtained only in patients with severe CAP
-Procalcitonin measurement is not recommended by the IDSA and has not been found to reduce antibiotic use among patients admitted to the emergency department
Commonly affects quadriceps femoris and brachialis muscle, usually self limiting.
This Trial showed a significant reduction in recurrent ischemic strokes with patent foramen ovale closures
RESPECT Trial. NEJM 2017. Among adults who had had a cryptogenic ischemic stroke, closure of a PFO was associated with a lower rate of recurrent ischemic strokes than medical therapy alone during extended follow-up.