Putting prevention into practice
What is the recommended drug to treat R.A for patients with low disease activity?
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, hydroxychloroquine is recommended for initial treatment in those with low disease activity.Hydroxychloroquine is better tolerated and has a better risk profile than the others.
Doses are 200 mg to 400 mg daily can be OD, or BID
Low disease activity define Clinical Disase Acivity index of 2.9 to 10.
TRUE OR FALSE
USPSTF recomends the use of ASA in the prevention of CVD in patients of 60 years and older with ASCDV risk of 10% or greater?
For patients 60 years or older, the USPSTF recommends against initiating low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of CVD events
TRUE OR FALSE
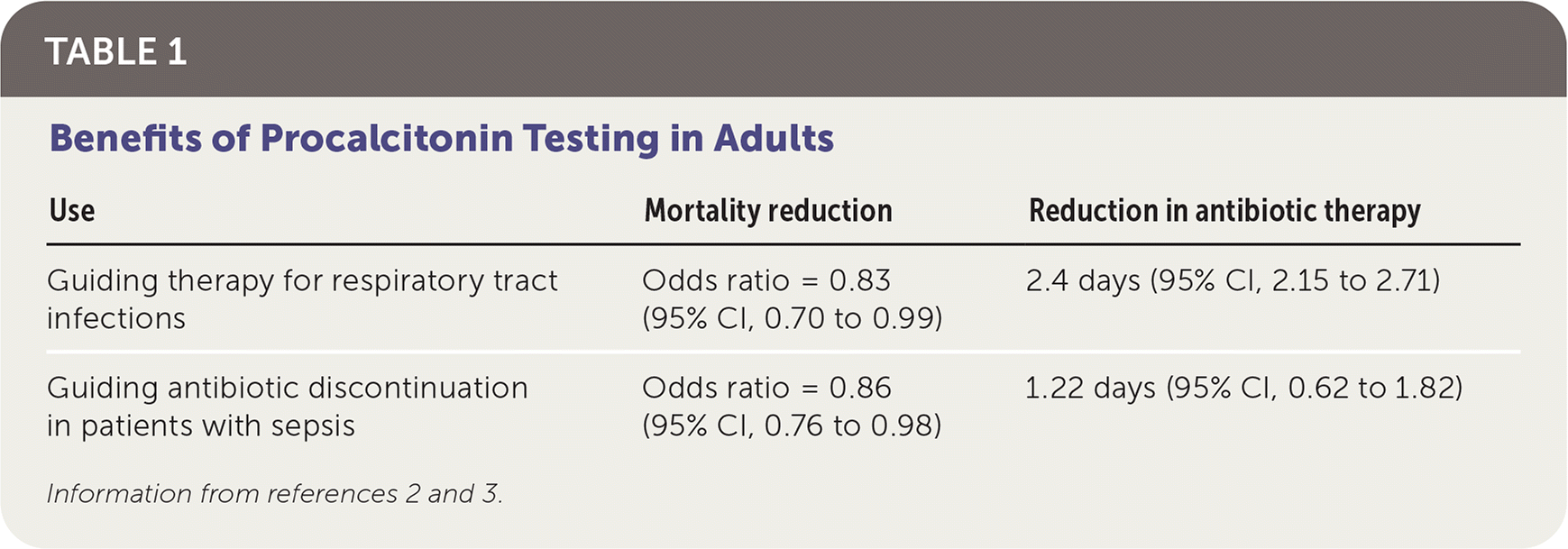
Can Procalcitonin testing can reduce mortality and unnecessary antibiotic use in hospitalized adults with respiratory tract infections ?
TRUE
When used in conjunction with an algorithm and clinical judgment, procalcitonin testing can reduce mortality and unnecessary antibiotic use in hospitalized adults with respiratory tract infections
When is iron chelation therapy recommended in patients with thalassemia?
Iron chelation therapy corrects iron overload caused by hemolytic anemia, increased intestinal iron absorption, and repeated transfusions. It is recommended in transfusion-dependent thalassemia when ferritin levels exceed 1,000 ng per mL (1,000 mcg per L) and non–transfusion-dependent thalassemia when ferritin levels exceed 800 ng per mL (800 mcg per L).
Alpha- and Beta-thalassemia: Rapid Evidence Review; March 2022
What exercises are recommended to treat posterior tibial tendinopathy?
Patients who have posterior tibial tendinopathy present with medial ankle pain, pes planovalgus deformity, and a positive too many toes sign. Eccentric exercises (i.e., contraction where the muscle lengthens under load or tension) are recommended over concentric exercises (i.e., contraction with muscle shortening) for posterior tibial tendinopathy. See Figure 3 and the video in the article for more details.
Tendinopathies of the Foot and Ankle; May 2022
For Moderate disease activity CDAI
what is the best initial treatment?

TRUE OR FALSE
USPSTF recomends the use of ASA in the prevention of CVD in patients 40-59 years with ASCDV risk of 10% or greater?
For adults 40 to 59 years of age with a 10% or greater 10-year CVD risk, the USPSTF found with moderate certainty that the use of aspirin for primary prevention of CVD events has a small net benefit. The USPSTF recommends that the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin in these patients should be an individual one, based on the patient's risk for CVD and bleeding and willingness to take a daily medication
Other causes of elevated procalcitonin are
Major trauma, cardiac arrest/shock, surgery, pancreatitis, and other systemic inflammatory processes
When should nonpregnant people be retested after treatment for chlamydia or gonorrhea?
Nonpregnant people treated for chlamydial or gonococcal infections should be tested for reinfection three months after treatment.
Chlamydial and Gonococcal Infections: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment; April 2022
What is the best approach to determine the severity, prognosis, and treatment options for alcoholic hepatitis?
Use laboratory-based prognostic tools, including the Maddrey Discriminant Function, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, and Lille Model scores, to determine severity and prognosis of alcoholic hepatitis and treatment options.
Alcoholic Hepatitis: Diagnosis and Management; April 2022
For patients without adequate symptom control on methotrexate alone, what will be the best approach?
A combination of methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine, is as effective as adding a bDMARD or tsDMARD.
According to the USPSTF recommendation statement, at what age it be appropriate for someone who uses aspirin as a primary prevention for CVD and who meets eligibility criteria to consider stopping aspirin use
Around 75 year of age
False negative procalcitonin can be found in ?
procalcitonin may not rise in localized pulmonary infections such as abscesses or empyemas.
Are SSRIs or SNRIs more effective for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms of menopause?
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are effective at relieving vasomotor symptoms of menopause. No studies have directly compared the two drug classes. SNRIs are associated with more adverse effects. Venlafaxine is preferred in women with breast cancer because SSRIs may interfere with tamoxifen metabolism.
SSRIs vs. SNRIs for Vasomotor Symptoms of Menopause; April 2022
TRUE OR FALSE
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends against the use of Oral Antihistamine/Analgesic/Decongestant Combinations for the Common Coldin children younger than four years?
TRUE
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration advises against the use of over-the-counter cough and cold medications in children younger than two years and recommends caution when using in children two years or older.3 However, the American Academy of Pediatrics advises against the use of these medications in children younger than four years.4 An American College of Chest Physicians consensus expert panel in 2017 recommended against the use of cough medications in adults and children until more convincing evidence is available.5
When to disontinue or reduce the doses?
Because stopping all DMARDs is associated with a moderate to high risk of a symptom flare-up and potential for irreversible damage, a minimum of one DMARD is recommended in all patients
For patients with symptoms at the targeted level for less than six months, continuing all DMARDs at their current dose is recommended. Because the risk of a flare-up is highest when lowering the dose or stopping DMARDs, any dose reductions should be gradual
How long should patients with provoked venous thromboembolism be treated with anticoagulation therapy?
Patients with venous thromboembolism due to a transient risk factor (provoked) can stop anticoagulation after three months of treatment.
Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism; April 2022
TRUE or FALSE
Can procalcitonin test reduce the use of antibiotics in outpatient, ED, and inpatient settings?
Procalcitonin guidance was associated with a 2.4-day reduction in antibiotic use
Schuetz P, Wirz Y, Sager R, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic treatment on mortality in acute respiratory infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):95-107.
Is cilostazol therapy safe and effective for improving walking distance in patients with intermittent claudication due to peripheral artery disease (PAD)?
Cilostazol (Pletal) improves initial and absolute walking distances in patients with intermittent claudication secondary to PAD and appears to be equivalent in effect to pentoxifylline (Trental). Adverse effects of cilostazol include headache, diarrhea, dizziness, and palpitations.
Cilostazol for Intermittent Claudication Caused by Peripheral Artery Disease; April 2022
Dutch history and dipstick score
When to avoid bDMARDs, tsDMARDs, and glucocorticoids ?
In patients who have had a serious infection within the previous 12 months, bDMARDs, tsDMARDs, and glucocorticoids should be avoided.
What treatment options are available for restless legs syndrome?
Nonpharmacologic interventions are first-line treatment for restless legs syndrome, followed by the use of alpha-2-delta ligands (i.e., gabapentin [Neurontin], pregabalin [Lyrica]). Dopamine agonists (e.g., ropinirole [Requip], pramipexole [Mirapex], rotigotine [Neupro]) should be used if there is an inadequate response.
Common Sleep Disorders in Adults: Diagnosis and Management; April 2022
When is safe to discontinue antibiotics based on procalcitonin levels?
Different organisms may cause different procalcitonin elevations. One study of hospitalized adults with CAP demonstrated that typical bacteria cause a larger rise in procalcitonin (2.5 ng per mL) than atypical bacteria (0.2 ng per mL).8 Expert consensus has suggested that a procalcitonin level of less than 0.25 ng per mL in addition to clinical judgment can be used to support discontinuing antibiotics
Do patient education interventions improve A1C values in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Patient education interventions, specifically those including face-to-face interactions with trained educators or nurses, improve A1C values in patients by 0.3% to 1.4% compared with usual diabetes care.
Patient Education Interventions Improve A1C Values; April 2022
Thank you for participating
BONUS POINT :)