When someone other than the seller incurs a cost from a product
What is a negative externality
This is the type of good that is more likely to have the free-rider effect
What is a non-excludable good (if also non-rival it is called a pure public good)
The sole owner of a business was forced to close a business, but not until after he sold his car and house to pay the debts of the firm. This is because the business was a
What is sole-proprietorship
This is the only group that is allowed to originate laws that collect government revenue
What is the house of representatives
The Sherman act is the act that limits restraints of trade. In other words, a firm could not be the only seller also known as this
What is a monopoly
This is an example of a __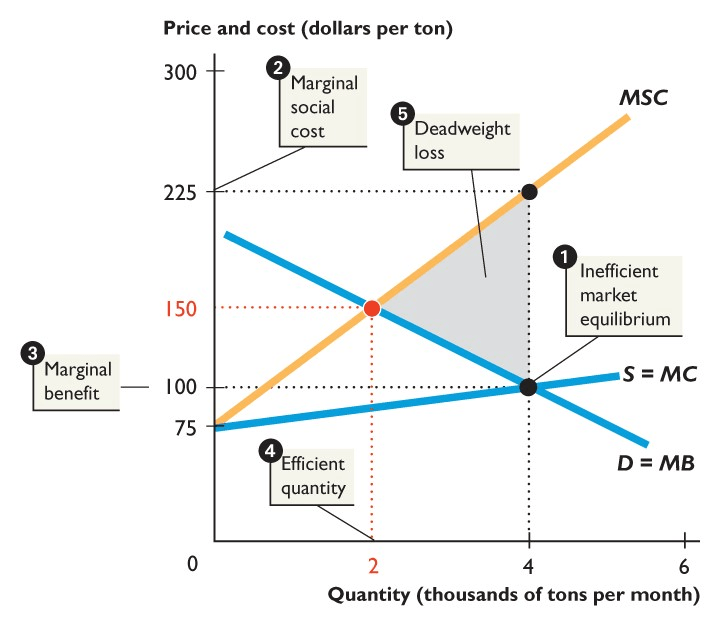
What is a negative externality
This is the role of government which uses fiscal and monetary policy
What is the stabilization of prices, output and employment
What is the stock price that they paid when they bought the business
This is how ambassadors, judges of the supreme court and officers (cabinet) of the US government are appointed
What is nominated by President and approved by the Senate
In 1914, the Clayton Act expanded regulation of large firms to prohibit unfair trade practices. In this way, the Clayton Act was designed to benefit _____
Who are rival firms and consumers
Does the market make too many or too few of goods with positive externalities
What is too few
This is the name of the term for when government takes money or benefits from some and gives it to others
What is redistribution
Many accounting, medical and legal businesses are partnerships. Do partnerships typically have limited or personal liability?
What is personal liability
The federal court system is limited to these types of cases
What are cases that involve more than 1 state (plus cases involving ambassadors, foreign trade, maritime law and cases from another country)
Beginning in 1979, the U.S. reduced the use of public provision of goods, regulation of businesses and restrictions on trade. What was this called
What is Deregulation or What is Neoliberalism
What is ( tax, law, fine, requiring clean up)
What is industrial policy
The Anglo-Saxon economies are primarily market based. We call this (in french)
What is Laissez Faire
If the constitution doesn't give the right to the federal government, who has the right?
This is the duo - one the President of the U.S. and the other the Prime Minister of the U.K. - who advocated the deregulation of business and a smaller government in 1980's
Who are Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher
Watch this This is the drawback to firms to pollute more than allowed in a cap and trade program.
What is an added cost from polluting (note that this is a market solution to a negative externality)
Government also sets up the rules to increase competition and by which businesses must operate in order to enhance public well-being. This is referred to as the _____ of business
What is regulation
The US economy is based primarily on this type of ownership
What is private property ownership
What is as punishment for a crime where the party has been duly convicted
This is an example of government regulation of labor markets
What are overtime laws, underage worker laws, the minimum wage, Osha requirements, labor unions