The four most common elements in the human body are...
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
True or False: The atoms in a molecule of water are bound together through hydrogen bonds.
False. The atoms in a molecule of water are bound together through polar covalent bonds.
The amount of energy that needs to be absorbed to start a chemical reaction
activation energy (Ea)
Most enzymes are...
proteins
4
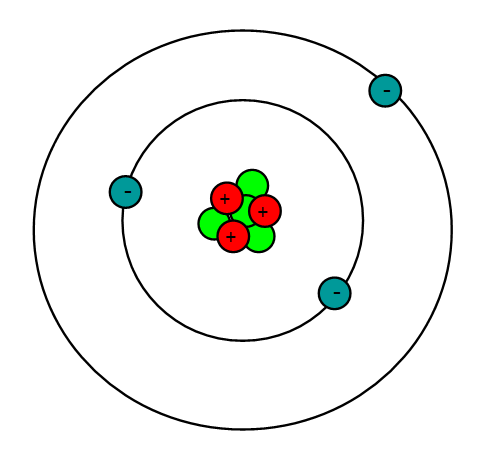
When forming a bond, this atom is more likely to gain electron(s)/lose electron(s) making this a __________ charged ion.
lose electrons
positively
These prevent rapid, drastic changes in the pH of a body fluid by converting strong acids and bases into weak acids and bases.
Buffers
What is a dehydration synthesis reaction?
the creation of larger molecules from smaller ones when a water molecule is released
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the
active site
_____ fats contain "kinks" in their structure due to the presence of one or more double bonds. These fats are _____ at room temperature.
1) Unsaturated fats
2) liquid
The bond that forms between two or more atoms that share a pair of electrons
covalent bond
Compare the hydrogen ion concentration between the two substances:
—Substance A: pH 2
—Substance B: pH 5
What type of chemical reaction does this graph represent?
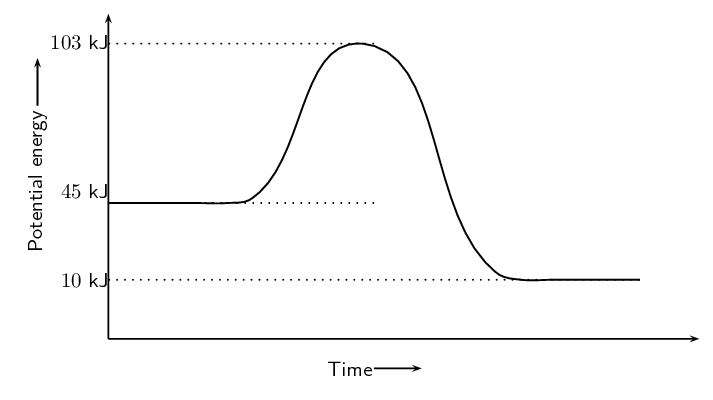
The graph represents an exothermic reaction because the reactants have high bond energies than the products.
Describe a catalyst's effect on activation energy and rate of chemical reaction.
DECREASES activation energy and INCREASES rate of chemical reaction
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
What determines an atom's bonding properties?
List the 3 properties of water we discussed in class.
High Specific Heat – Water resists changes in temperature. Compared to other compounds, water must absorb more heat energy to change in temperature.
Cohesion: the attraction among molecules of a substance; water molecules stick together; produces surface tension
Adhesion: the attraction between molecules of different substances; water molecules stick to other things
When does a chemical reaction reach equilibrium?
when a reaction takes place at equal rates in both directions
Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds within the enzyme, impeding its ability to function properly. This is called _____.
denaturation
List the four biomolecules and each of their monomers.
carbohydrates = monosaccharides
lipids = glycerol and fatty acids
proteins = amino acids
nucleic acids = nucleotides
Give an example of each of the following:
element, molecule, compound
element: a substance made up of one type of atom and cannot be broken into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means
molecule: two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
compound: a substance made of atoms of different elements bonded together in a certain ratio
The atoms in ammonia (NH3) are bound together through equal sharing of electrons. Using this information, answer the following question:
Would ammonia dissolve in oil?
What type of chemical reaction is this?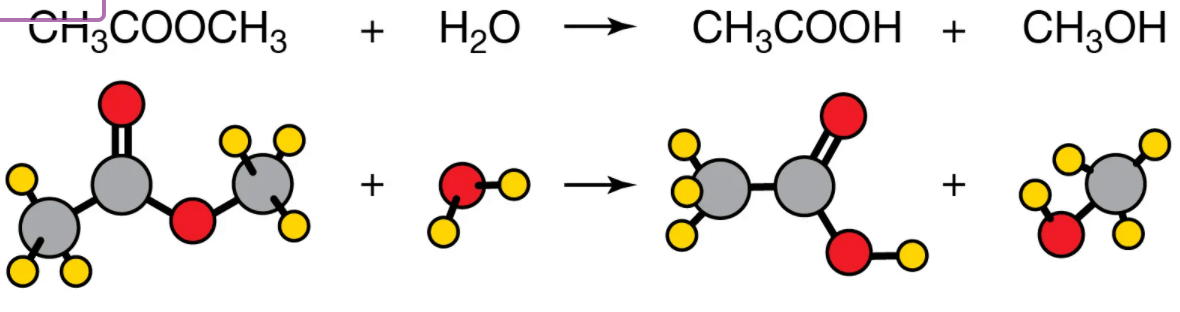
hydrolysis reaction
When a piece of liver is dropped into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the peroxide bubbles vigorously as a result of what reaction?
a) peroxide being broken into water and oxygen
b) peroxide is destroying germs in the liver
c) more peroxide is being created by the liver
d) liver and peroxide are joining together to make a new protein
A
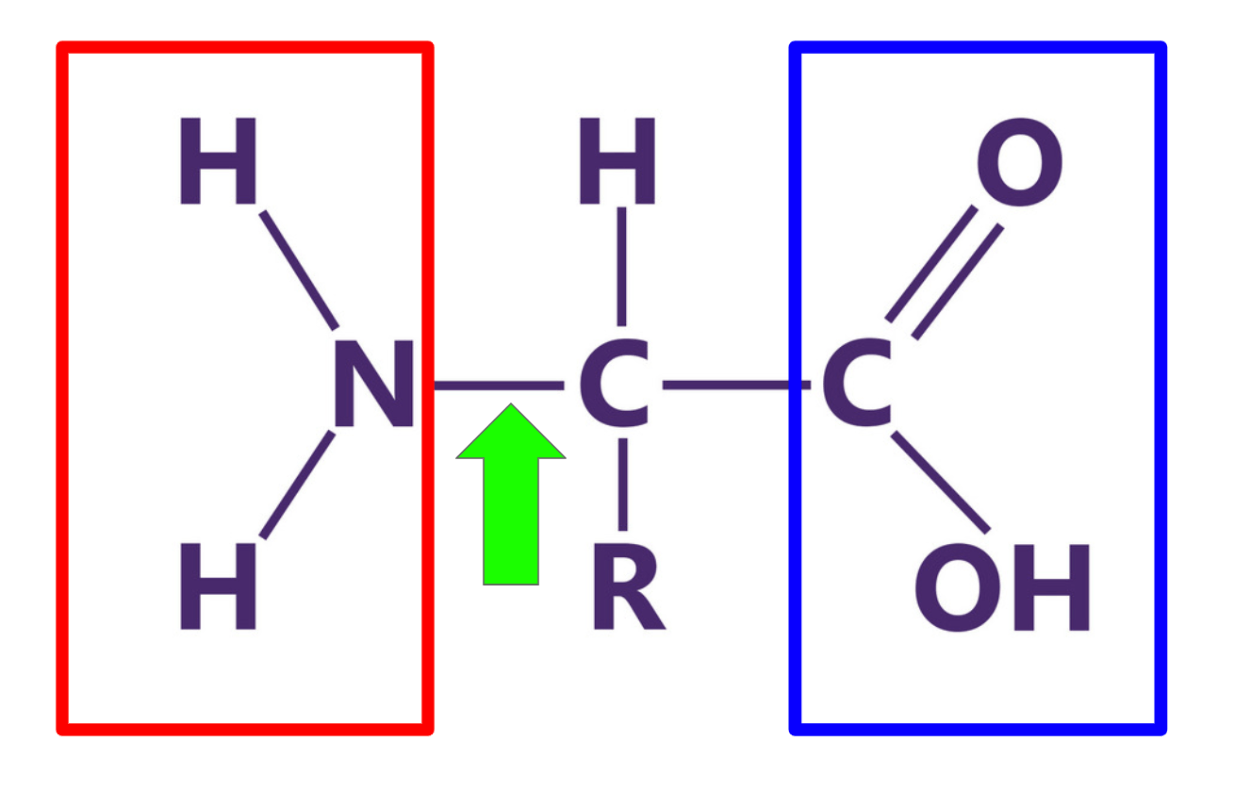 What is this structure? Label each of the highlighted components.
What is this structure? Label each of the highlighted components.
A protein composed of amino acids.
red = amino group
green = peptide bond
blue = carboxyl group