It is the inflammation of the liver cells.
What is hepatitis?
It is the removal of all or part of the pancreas.
What is Pancreatectomy?
This is the most common substance found in gallstones.
What is cholesterol?
This is the route of transmission for Hepatitis A & E.
What is the Fecal-oral route?
These are red lesions, vascular in nature with branches radiating on the nose, cheeks, upper thorax, shoulders found in patients with cirrhosis.
What are Spider angiomas?
It is the scarring and hardening of the liver from chronic or prolonged inflammation.
What is cirrhosis?
This progressive, destructive disease of the pancreas results in the development of calcification and necrosis, possibly resulting in hemorrhagic pancreatitis, and has a mortality as high as 50%.
What is chronic pancreatitis?
It is the removal of the gallbladder through a small abdominal incision.
What is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
This is the route of transmission for hepatitis C.
What is blood?
These medications are intended to lower the ammonia level.
What are lactulose and non-absorbable antibiotics (Refaximin)?
It is the yellowing of the sclera and skin from excess bilirubin.
What is jaundice?
These are the positions of comfort in clients with pain due to pancreatitis.
What are fetal, side-lying, the head of the bed elevated, sitting up or leaning forward
This rare but fatal surgical complication can occur if adequate amounts of bile are not drained from the surgical site.
What is bile peritonitis?
This is the most definitive approach used to identify the intensity of the infection and the degree of liver damage.
What is liver biopsy?
The signs indicate worsening of encephalopathy.
What are aaterixis and fetor hepaticus?
It is characterized by changes in neurological status from excessive ammonia.
What is encephalopathy?
This complication occurs in clients with pancreatitis as they lose up to 6 L of fluid from third spacing caused by retroperitoneal loss of protein-rich fluid from proteolytic digestion.
What is hypovolemia?
This is a surgical drain that allows the bile to drain freely from the gallbladder following surgery.
What is a T-tube?
This instruction to the client is crucial in the successful and safe completion of the liver biopsy procedure.
What is "exhale and hold breath for at least 10 seconds while the needle is inserted" ?
This complication of liver disease results from the development of collateral circulation in the upper stomach and esophagus stemming from portal hypertension.
What are esophageal varices?
It is the foil breath exhibited by clients with liver disease.
What is fetor hepaticus?
In clients with pancreatitis effusion and atelectasis mostly affect this lung.
What is the left lung?
It is the inability to take a deep breath when fingers are pressed under the liver margin.
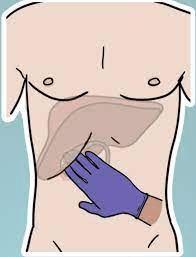
What is Murphy's sign?
After a liver biopsy, this position is maintained for several hours to prevent complications.
What is right side-lying position?
These are health promotion and disease prevention recommendation for pancreatitis.
What are avoid excessive alcohol consumption and a diet low in fat?
It is a manifestation of liver disease characterized by increased pressure in the portal circulation.
What is portal hypertension?
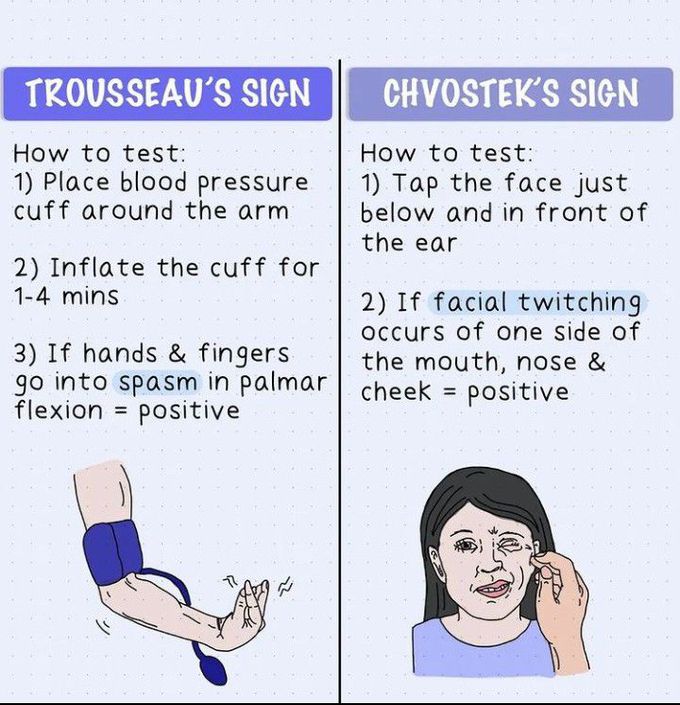
These signs are indicative of this electrolyte imbalance in patients with pancreatitis.
What is hypocalcemia?
Intense pain (increased heart rate, pallor, diaphoresis) with nausea and vomiting after ingestion of high-fat food in patients with cholecystitis is caused by this reaction.
What is biliary colic?
This is recommended for postexposure protection against hepatitis A for those older than 40 yr, children younger than 12 months, those with chronic liver disease, immunosupressed or people allergic to vaccination.
What is Immunogobulin?
This is the typical location for pain associated with pancreatitis.
What is epigastric, radiating to the back, left flank, or left shoulder that is worse when lying down or while eating?
It is the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity from decreased albumin level.
What is ascites?
This complication of pancreatitis is due to the destruction of the pancreatic beta cells.
What is type 1 diabetes mellitus?
This reaction can occur with the accumulation of bile salts in the skin.
What is pruritus?
This lab value increases within 24 hours and remains increased for 2-3 days in clients with pancreatitis.
What is serum amylase?
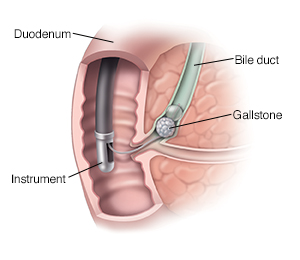
This procedure is performed to view the biliary tract to assist in removing stones, to collect specimens for biopsy and for placement of a stent.
What is an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)?
This is the most common type of hepatitis?
What is viral hepatitis?
This assessment finding is indicative of pancreatitis.
What is Cullen's sign?
This pain medication is contraindicated in older adults due to seizure as a possible adverse effect.
What is meperidine (Demerol) ?
This lab value increases slowly and can remain increased for days longer than amylase in clients with pancreatitis.
What is serum lipase?
This procedure involves inserting a stent (tube) to connect the portal veins to adjacent blood vessels that have lower pressure in patients with portal hypertension.
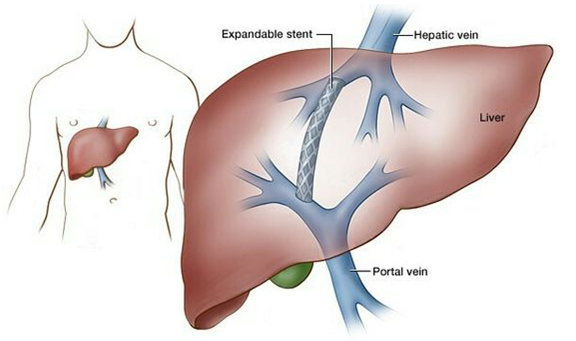
What is transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)?
After nausea have subsided these dietary adjustments are needed for patients with liver disease.
What is high calorie, high carbohydrate, moderate fat, and moderate protein diet (given in small frequent portions)?
This assessment finding is indicative of pancreatitis.

What is Turner's sign?
It is the inflammation of the gallbladder.
What is cholecystitis?
This medication aids with the digestion of fats and proteins when taken with meals and snacks in patients with impaired production of pancreatic enzyme.
What is pancrelipase (Viokase) ?
This procedure is performed in patients with ascites, during which a needle is inserted into the peritoneal cavity to obtain ascitic fluid. [
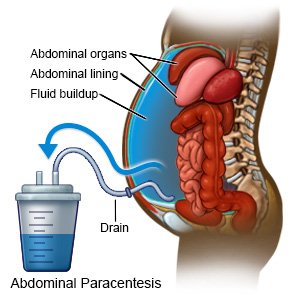
What is paracentesis?
These are the four types of cirrhosis.
What are postnecrotic, Laennec's, biliary, and cardiac.
This coagulation defect is one serious complication of pancreatitis.
What is disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC)?
This non-invasive procedure will dissolve cholesterol-based stones in clients with gallstones who are non-surgical candidates.
What is Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) ?
These are coarse tremors characterized by rapid, nonrhythmic extension and flexion of the wrists and fingers often seen in liver disease.
What is Asterixis (liver flapping tremor)?
These are dietary instructions given to clients with gallbladder disease.
What are:
Encourage a low-fat diet (reduce dairy products and avoid fried foods, chocolate, nuts, gravies).
Small, frequent meals may be more easily tolerated.
Avoid gas-forming foods (beans, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli).
Promote weight reduction.
Instruct client to take fat-soluble vitamins or bile salts as prescribed to enhance absorption and aid with digestion.
?