This chemical compound is the "acid" component of most acid base disorders.
What is carbon dioxide?
Respiratory acidosis may be caused by _______ (increased or decreased) respiratory rate.
What is "decreased"?
This is the primary treatment for respiratory acidosis.
What is invasive or non-invasive mechanical ventilation?
An elderly man is admitted with septic shock. Shortly after admission, blood tests reveal the following:
pH 7.18, PaCO2 16, HCO3- 7
What disorder does this man have?
What is metabolic acidosis?
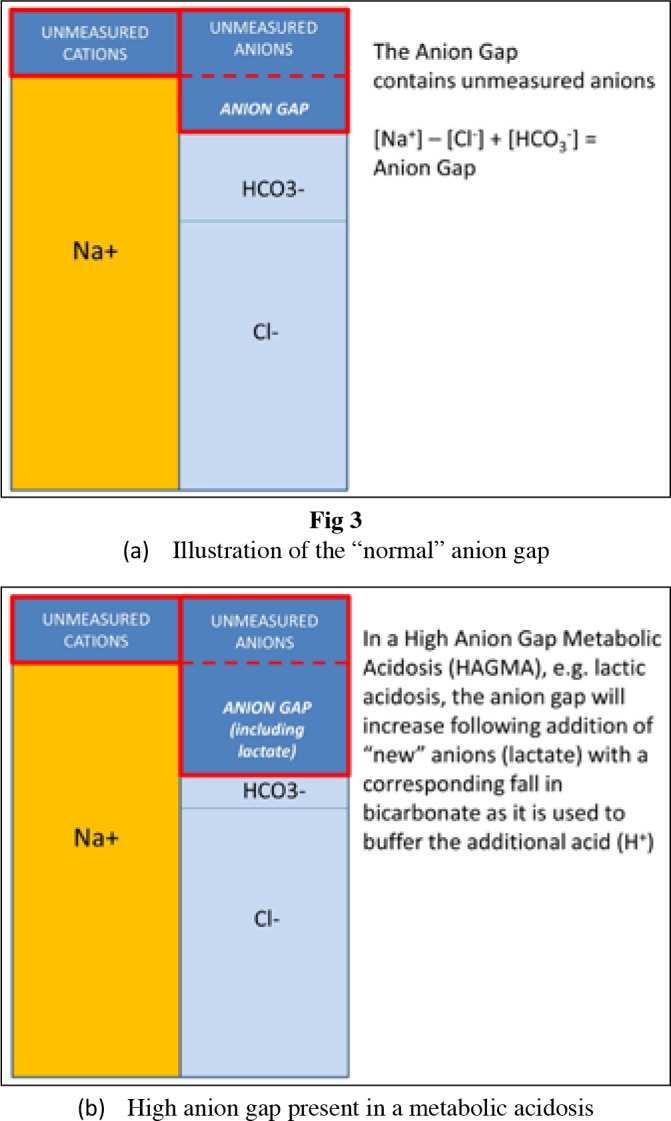
Please draw a visual representation of an anion gap and how it's calculated.
This chemical compound is the "base" component of most acid base disorders.
What is bicarbonate?
This is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis.
What is anxiety or panic attacks?
What drug can be used to treat metabolic alkalosis?
What is acetazolamide?
An elderly man developed hypotension, thirst, and profuse diarrhea due to Salmonella infection. Shortly after admission, blood tests reveal the following:
pH 7.25, PaCO2 31, HCO3- 17
What is this disorder? What is the likely cause?
What is metabolic acidosis?
What is diarrhea and intestinal bicarbonate loss?
This common IV fluid can worsen hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
This disorder is characterized by a low pH and a low bicarbonate level.
What is a metabolic acidosis?
Name three causes of metabolic acidosis.
DKA, lactic acidosis, renal failure, diarrhea, drugs (must be specific)
This drug may be beneficial to prolong time to renal replacement therapy in patients with metabolic acidosis or with a pH of < 7 in DKA per guidelines (although RCT's show no benefit).
What is sodium bicarbonate?
A woman is being treated for CHF in the ICU. After several days of treatment, the following results are returned:
pH 7.55, PaCO2 43, HCO3- 42
What disorder does she have? What is the likely culprit?
What is metabolic alkalosis?
What are loop diuretics?
This lab trend is often a better marker of resolution than pH in metabolic acidosis.
What is lactic acid?
This disorder is characterized by a high pH and low carbon dioxide.
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Name a drug class used for treating heart failure that is associated with causing metabolic alkalosis.
Extra 100 points: Explain the mechanism.
What are loop diuretics?
Also known as a "contraction alkalosis"
Loop diuretics work by inhibiting reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the ascending loop of Henle. As chloride is excreted, the body wants to maintain a normal anion gap and will increase the other anion, which is bicarbonate. Increased bicarbonate leads to a metabolic alkalosis.
This therapy may be required for severe metabolic acidosis refractory to medical management.
What is renal replacement therapy?
An elderly woman with COPD is admitted with increasing confusion. Shortly after admission, blood tests reveal the following:
pH 7.21, PaCO2 83, HCO3- 35 mmol/L
What disorder does she have? What is the likely culprit?
What is respiratory acidosis?
What is COPD exacerbation?
A toxic alcohol ingestion will present acutely with an elevated _______ gap. Eventually, as the alcohol is metabolized, that gap will close and the _____ gap will open.
What is osmolar gap and anion gap?
Extra 100 points: Write the equation to calculate osmolarity and osmolar gap.
Describe the primary buffer system in our body.
Extra 200 points: Write out the carbonic acid equation.
This system comprises a weak acid (carbonic acid, H2CO3) and its conjugate base (the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-), which exist in a dynamic equilibrium. As hydrogen ions are produced, they are consumed by bicarbonate ions thus neutralizing the acidity. As they are neutralized, they are converted to carbonic acid and subsequently water + carbon dioxide. Our kidneys are responsible for maintaining adequate bicarbonate stores and our lungs are responsible for excreting or retaining carbon dioxide.
![]()
MUDPILES is an acronym used for causes of a high anion gap metabolic acidosis. Please list what MUDPILES stands for.
Methanol toxicity
Uremia
Diabetes
Paraldehyde
Iron/Isoniazid toxicity
Lactate
Ethylene glycol toxicity
Salicylate toxicity
This non-pharmacologic intervention can help prevent iatrogenic respiratory alkalosis in ventilated patients.
What is reducing minute ventilation (lower respiratory rate or tidal volume)?
A 67-year-old man with a history of COPD, heart failure, and type 2 diabetes is admitted to the ICU for septic shock due to pneumonia. He is intubated and mechanically ventilated. Initial labs and ABG are as follows:
pH: 7.32, PaCO₂: 28 mm Hg, HCO₃⁻: 14 mEq/L, Lactate: 6.1 mmol/L
What acid–base disorder(s) is likely present?
What are mixed anion gap metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis?
This clinical scenario commonly produces a mixed metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. (There are two answers. You get bonus points if you get both.)
What is sepsis?
Bonus 100 points: What is salicylate toxicity?