Diagnosis for a young man with substernal chest pain, deep T-wave inversions in V2-V4, and a harsh systolic murmur that increases with Valsalva maneuver
HCM
-> Echo, Beta blocker
Preferred first diagnostic test for achalasia
Barium swallow: the preferred screening test when diagnosis is suspected clinically; shows “bird’s beak” narrowing of the GE junction
Test of choice to diagnose Thalassemia or other hemoglobinopathy as cause of hemolytic anemia
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
This is a viral infection of the finger often mistaken for bacterial infection
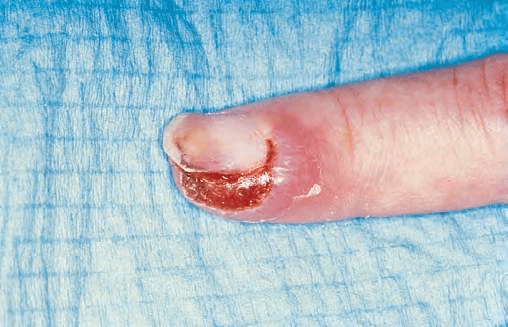
Herpetic whitlow

Renal tubular acidosis associated with hyperkalemia
Type 4 RTA – hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism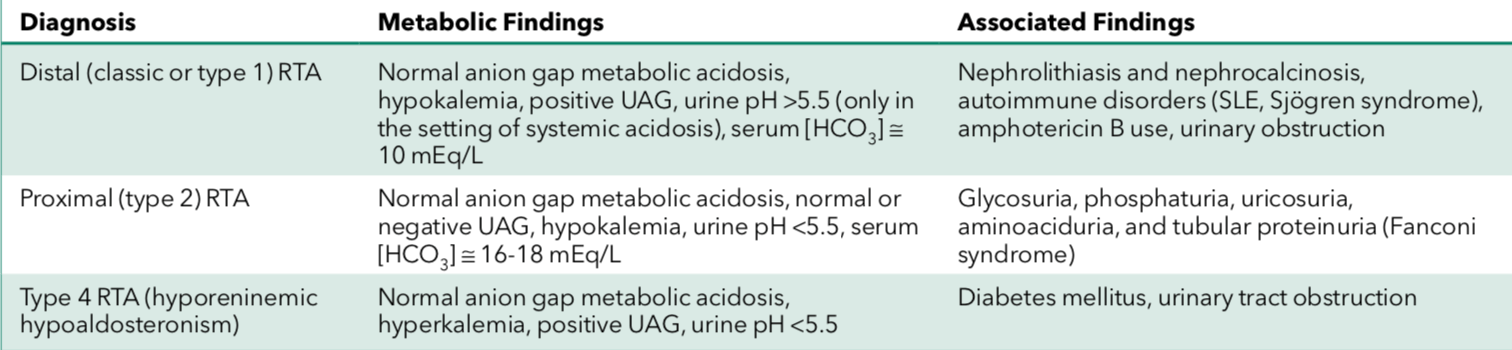
This procedure is indicated acutely for STEMI in the presence of thrombolytic PCI failure or mechanical complications (papillary muscle rupture, VSD, free wall rupture).
CABG
Men over 50 years old with GERD symptoms for over five years (plus additional risk factors) should be screened for this disease.
Barrett Esophagus / Esophageal Cancer
Screen men aged >50 years with GERD symptoms for more than 5 years and additional risk factors (nocturnal reflux symptoms, hiatal hernia, elevated BMI, tobacco use, and intra-abdominal distribution of fat) to detect esophageal adenocarcinoma and BE.
Disease most associated with translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22 [t(9;22), the Philadelphia chromosome].
CML is characterized by myeloid proliferation associated with translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22 [t(9;22), the Philadelphia chromosome].
Patients usually present in the chronic phase. CML may transform into acute leukemia. The trans- formation may be recognized as an accelerated phase or as blast crisis (AML).
Size of positive tuberculin test in patient who immigrated from a country with high TB prevalence within the last 5 years.
10 mm induration or greater.
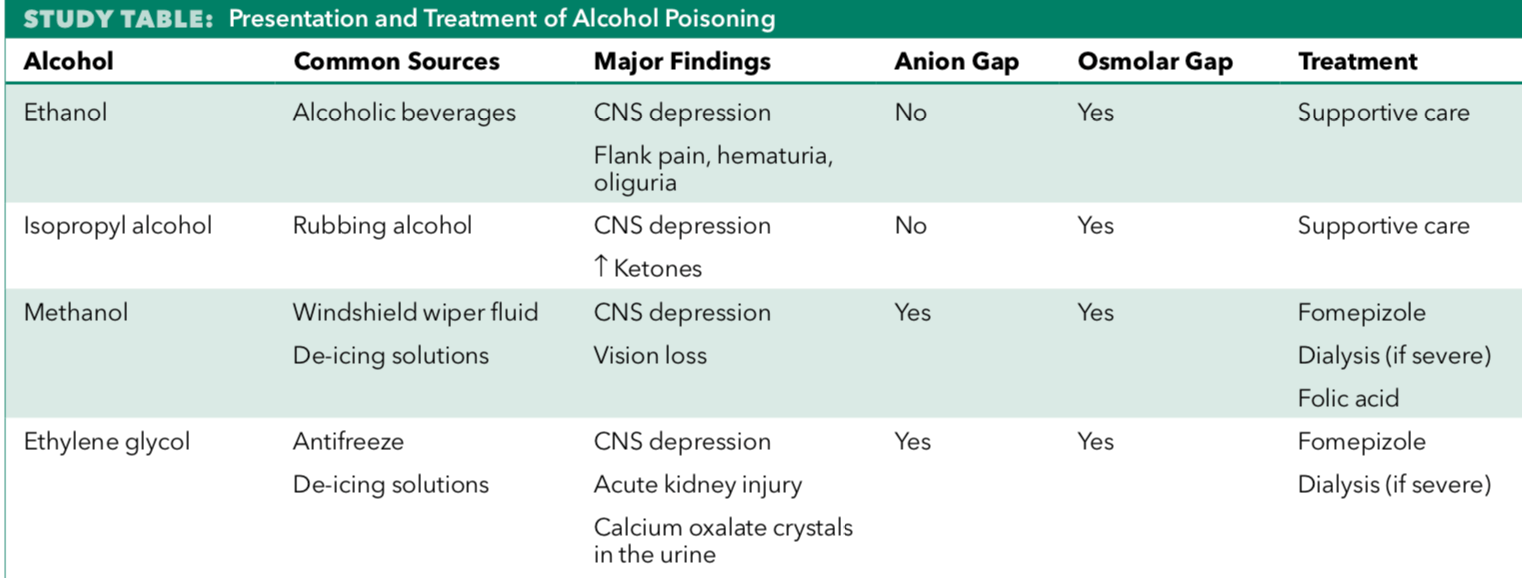
Type of alcohol poisoning associated with acute kidney injury and calcium oxalate crystals in the urine.
Ethylene glycol
Heart sound most associated with diagnosis of congestive heart failure.
S3 (11-fold higher likelihood of diagnosis)
"S3 floppy, S4 stiff"
Dystonia and Parkinsonism are serious complications of this drug, often used to increase gastric motility.
Dystonia and parkinsonian-like tardive dyskinesia are serious complications of metoclopramide; the drug must be stopped at the first sign of these disorders, which may be irreversible.
This drug, plus phlebotomy, is often treatment of choice for patients with Polycythemia Vera at high risk for thrombosis.
Hydroxyurea in addition to phlebotomy is often the treatment of choice for patients at high risk for thrombosis (e.g., >60 years, previous thrombosis, leukocytosis).
Diagnosis for chronic nodular infection of distal extremities with exposure to fish tanks or marine environments.
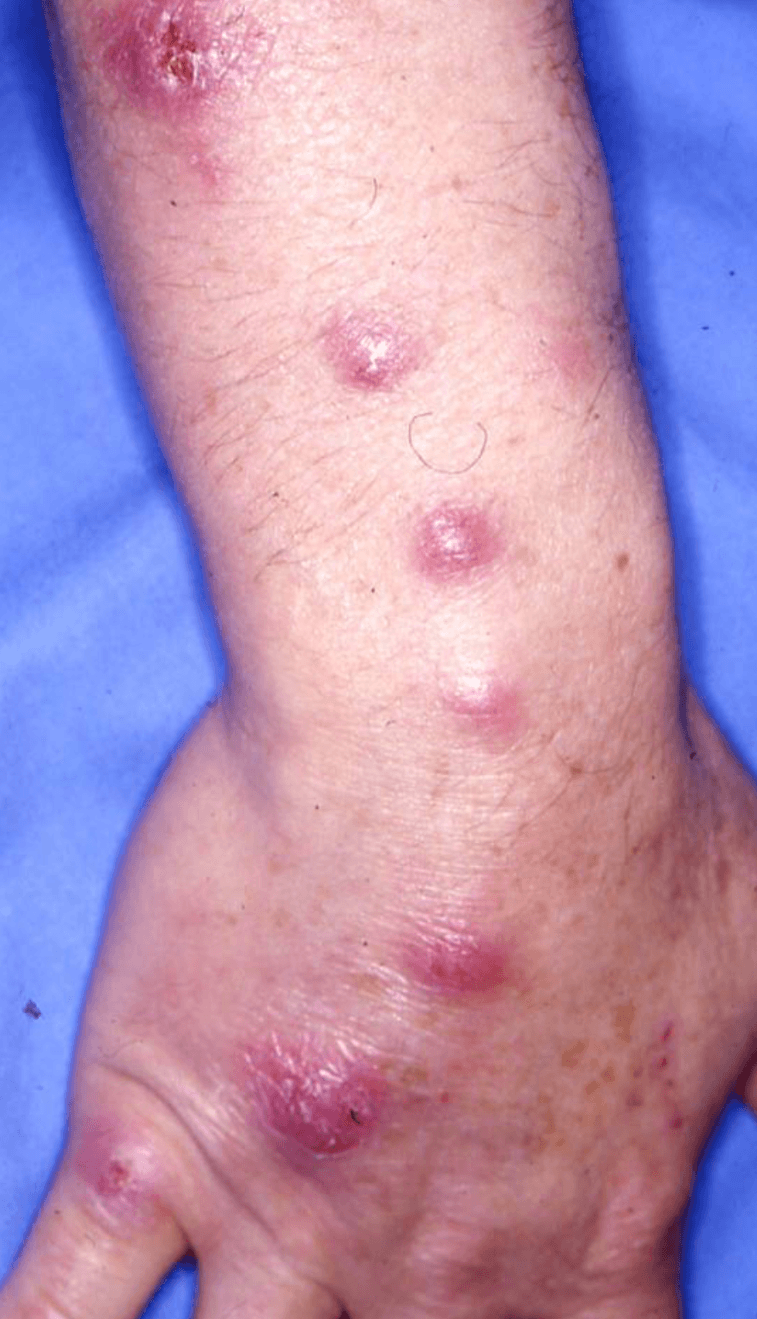
Mycobacterium marinum
Type of AKI associated with a urine sodium of less than 20 meq/L
Pre-renal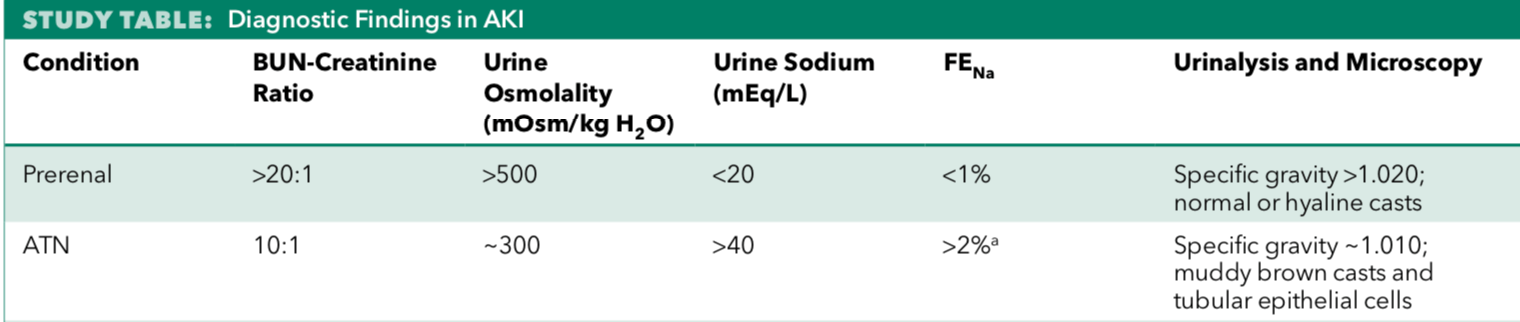
CHF medication that can be used as a substitute for an ACE inhibitor or ARB in HFrEF (NYHA class II or III) in patients who have tolerated ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy
Valsartan-sacubitril
Young adults with chronic pancreatitis should be tested for this genetic disease.
Young adults with chronic pancreatitis require sweat chloride testing for CF.
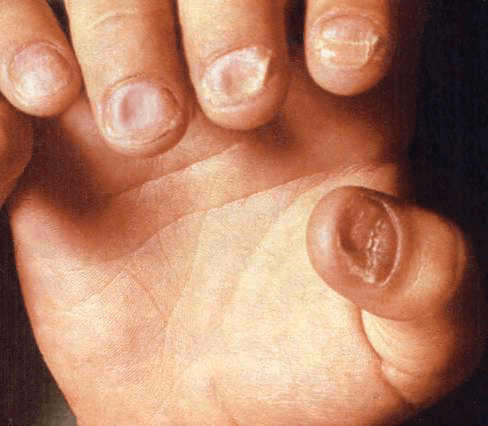
Hematologic finding associated with this sign on exam.
Koilonychia associated with iron deficiency anemia
Fungal infection occurring almost exclusively in patients who engage in landscaping or gardening.
Sporotrichosis (Sporothrix schenckii)
Papule appears days to weeks later at inoculation site, with similar lesions occurring along lymphatic channels proximal to inoculation site. 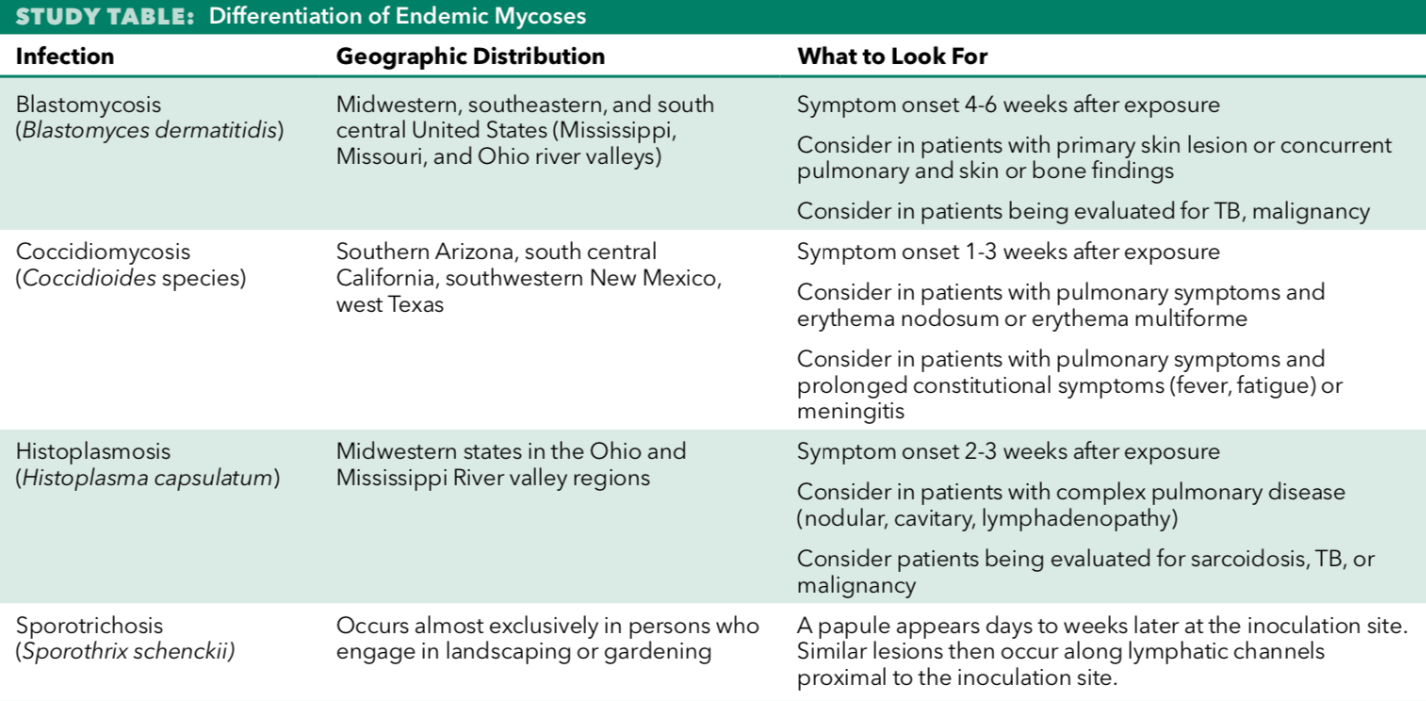
Electrolyte abnormality that's also associated with hypocalcemia and hypokalemia
Hypomagnesemia
-Can be due to GI losses, renal losses, medications, hungry bone syndrome following parathyroidectomy.
Peripartum cardiomyopathy is characterized by the presence of HF with an LVEF <45% diagnosed between 1 month before and this many months after delivery.
5 months
Diagnosis of a patient who recently traveled to India or Puerto Rico, with malabsorption, weight loss, malaise, folate or vitamin B12 deficiency, steatorrhea
Diagnose tropical sprue.
Order a small bowel biopsy.
Treat with a sulfonamide or tetracycline and folic acid.
Avoid this treatment in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, as it can worsen microvascular occlusion and hasten clinical decline.
Platelet transfusion
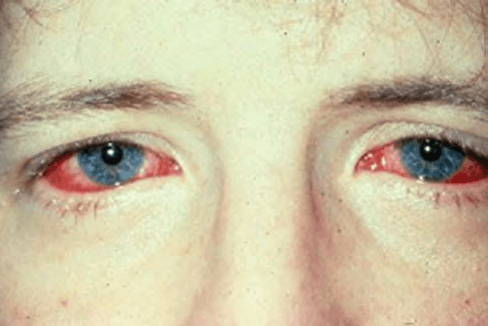
Diagnosis for this patient, who recently traveled to a tropical area and presents with abrupt onset of fever, rigors, myalgia, and headache.
Leptospirosis
Kidney failure, uveitis, respiratory failure, myocarditis, and rhabdomyolysis can occur. A key physical sign is conjunctival suffusion, infrequently found in other infectious diseases. The diagnosis is usually made by serologic confirmation.
Most cases are self-limited, but doxycycline and penicillin may be helpful in severe disease or shortening the duration of mild disease.
Cause of secondary hypertension in a patient cramping, nocturne, thirst, a normal physical exam, and labs showing hypokalemia.
Primary hyperaldosteronism
Muscle cramping, nocturia, thirst; physical examination normal; hypokalemia and elevated plasma aldosterone-plasma renin activity ratio