Question 1: The lowest daily average air pressure recorded during the first 5 days of the study was:
A. 762.0 mm Hg B. 745.2 mm Hg
C. 21.14 mm Hg D. 18.03 mm Hg
B. 745.2 mm Hg
Question 7: According to Table 1 and Table 2, which species shows the greatest difference in average mercury concentration between cold and warm climates?
A. Crab B. Swordfish
C. Shark D. The greatest difference . cannot be determined from info . provided
B. Swordfish
Question 14: If the student had tested a fifth light bulb during Excercise 2 and measured the current passing through it to be 1.2 A, the Z associated w/ this bulb would have been:
F. 1 Ω
G. 10 Ω
H. 14.4 Ω
J. 100 Ω
G. 10 Ω
Question 34: According to the passage, molecules in conformation states with relatively low energy tend to:
F. convert to the totally eclipsed conformation
G. convert to the eclipsed conformation
H. maintain their shape
J. chemically react
H. maintain their shape
Question 2: According to Table 2. daily average air pressures were recorded to the nearest:
F. 0.01 mm Hg G. 0.1 mm Hg
H. 1 mm Hg J. 10 mm Hg
G. 0.1 mm Hg
Question 8: Given that shark and swordfish are both large predatory animals, and catfish and crab are smaller non-predatory animals, do the results of Experiment 2 support the hypothesis that the tissue of larger predatory fish exhibits higher levels of Hg than does the tissue of smaller species?
F. Yes; the lowest concentration of Hg was found in swordfish
G. Yes; both swordfish and shark had Hg concentrations that were higher than those found in either catfish or crab
H. No; the lowest concentration of Hg was in catfish.
J. No; both catfish and crab had concentrations of Hg that were higher than those found in either swordfish or shark.
G. Yes; both swordfish and shark had Hg concentrations that were higher than those found in either catfish or crab
Question 15: Based on the results of Exercise 2, a circuit including the combination of which of the following batteries and light bulbs would result in the highest current in the circuit? (Assume Z is constant)
A. A 10 V battery and Bulb 1
B. An 8 V battery and Bulb 2
C. A 6 V battery and Bulb 3
D. A 5 V battery and Bulb 4
D. A 5 V battery and Bulb 4
Question 35: The information in the passage indicates that when a compound changes from one straight-chain conformational isomer to another, it still retains its original:
A. energy state B. shape.
C. number of single carbon bonds. D. temperature
C. number of single carbon bonds.
Question 3: Which of the following graphs best represents a plot of the daily average air temperature versus the daily average air pressure for Room 4?
C.
Question 9: A researcher, when using the CVAFS, was concerned that lead (Pb) in the tissue samples might be interfering with the detection of Hg. Which of the following procedures would best help the researcher explore this trouble?
A. Flooding the sample with a large concentration of Pb before using the CVAFS
B. Using the CVAFS to examine a non-biological sample
C. Collecting tissue from additional species
D. Testing a sample w/ known concentrations of Hg and Pb
D. Testing a sample w/ known concentrations of Hg and Pb
Question 16: With bulb 3 in place in the circuit in Exercise 1, how many of the sensors were unable to detect any incident light?
F. 1
G. 2
H. 3
J. 4
F. 1
Question 36: Student 2's views differ from Student 1's views in that only Student 2 believes that a butane molecule's active shape is partially determined by its:
F. initial isomeric state. G. energy state
H. hydrogen binding angles. J. proximity of methyl . groups
F. initial isomeric state.
Question 4: Which of the following most accurately describes the changes in the daily average air pressure in Room 3 during days 1-5?
F. The daily average air pressure increased from days 1 to 4 and decreased from days 4 to 5
G. the daily average air pressure decreased fro, days 1 to 2, increased from days 2 to 4, and decreased again from
H. The daily average air pressure increased only
J. the daily average air pressure decreased only
J. the daily average air pressure decreased only
Question 11: Which of the following factors was intentionally varied in Experiment 2?
A. The volume of tissue tested
B. The method by which the marine organisms were caught
C. The species of marine organism tested
D. The method of sample analysis
C. The species of marine organism tested
Question 19: Exercise 1 and Exercise 2 differed in that in Exercise 1:
A. 4 light sensors were used
B. 4 different light bulbs were used.
C. the electromotive force of the battery was varied
D. the current was highest for Bulb 1
A. 4 light sensors were used
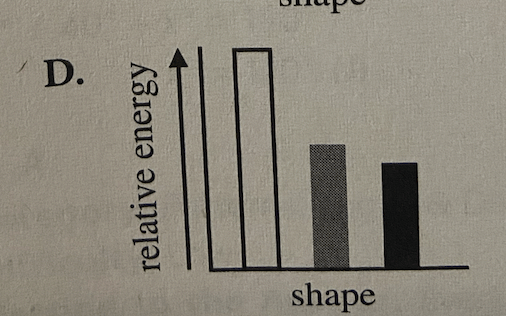
Question 39: Which of the following diagrams showing the relationship between a given butane molecule's shape and its relative energy is consistent with Student 2's assertions about the energy of butane molecules, but is NOT consistent with Student 1's assertions about the energy of butane molecules?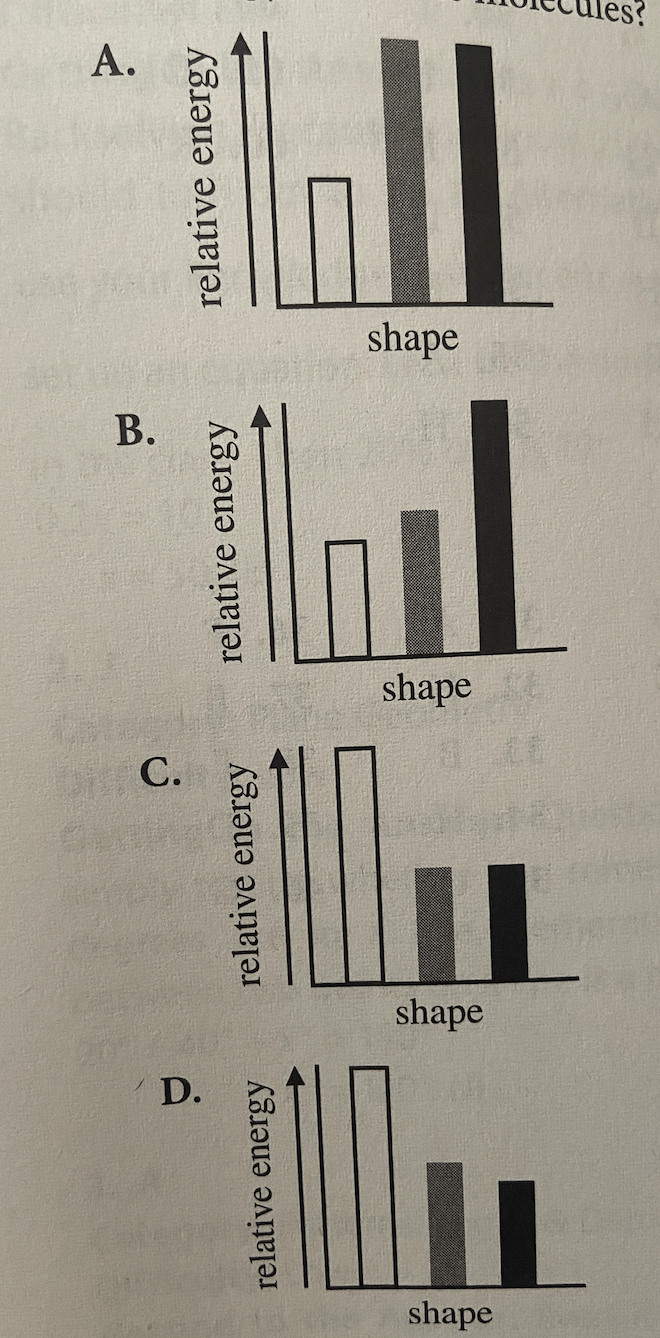
Question 6: If the geologists were to use equipment that malfunctions in warm environments, which room would be most likely to cause the equipment to malfunction?F. Room 1
G. Room 2
H. Room 3
J. Room 4
F. Room 1
Question 12: Which of the following specimens would most likely have the highest concentration of Hg?
F. A crab caught in cold water
G. A swordfish caught in cold water
H. A catfish caught in warm water
J. A swordfish caught in warm water
G. A swordfish caught in cold water
Question 20: According to Table 3, which light bulb with a brightness greater than 0.30 W/m^2 has the lowest power consumption?
F. Bulb 1
G. Bulb 2
H. Bulb 3
J. Bulb 4
H. Bulb 3
Question 40: Student 2 says that a butane molecule may settle into a moderately high-energy conformation. Which of the following findings, if true, could used to counter this argument?
F. Once a molecule has settled into a given conformation, all of its single carbon bonds are stable.
G. Enough energy is available in the environment to overcome local energy barriers, driving the molecule into its lowest-energy conformation
H. During molecule formation, the hydrogen bonds are formed before the carbon bonds
J. Molecules that change their isomeric conformation tend to lose their chemical functions
G. Enough energy is available in the environment to overcome local energy barriers, driving the molecule into its lowest-energy conformation