What are the four main biological macromolecules AND their monomers?
Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides
Lipids: Fatty Acids + (Glycerol sometimes)
Proteins: Amino Acids
Nucleic Acids: Nucleotide
300 POINTS
In 1855 Rudolf Virchow did what?
Contributed the final component of the cell theory: "All cells come from pre-existing cells."
(200 points)
What organelle is attached to the nucleus and what is its function?
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (makes and transports proteins)
(200 points)
What are the 4 reasons cells divide?
Growth, Repair, Replace, Regulate cells for efficiency
(200 points)
Draw a replicated chromosome and label it
Should have CENTROMERE and SISTER CHROMATIDS
(200 POINTS)
Describe a hypothetical meal for stomach contents that contained a POSITIVE test for Lugol's Iodine and a POSITIVE for Biuret Test.
Complex carbs: Pasta
Protein: Chicken
200 points
What are 3 functions of proteins?
BONUS: Double Points for EXAMPLES!
-Control rate of chemical reactions (Enzymes)
-Regulate cell processes (Hormones)
-Build & repair muscles (Collagen)
-Transport substances in/ out of cell (Hemoglobin--> oxygen)
-Help flight diseases (Antibodies)
-Energy storage as a LAST RESORT! (Ketones)
300 points!
Who was Anton Van Leeuwenhoke?
"Father of Microbiology" - improved the microscope and was first to observe bacteria and protozoa
400 points
Which organelle contains the centrioles?
Centrosome
(300 points)
What is the difference in CYTOKINESIS in plants and animal cells?
Animal: Cleavage furrow forms and cells pinch apart
Plants: Cell plate forms between the daughter cells
(300 points)
What is METASTISIS?
Spread of cancer cells
(100 points)
Describe the process for BREAKING a polymer
HYDRATION: ADD WATER
(200 POINTS)
What are the functions of Carbs and Lipids?
Carbs: short term energy storage and structural component in plant cell wall
Lipids: long term energy storage, insulation, absorption of vitamins, hormone signaling, waterproofing
100 points
What is the purpose of the nucleus?
Stores DNA
(100 points)
What is the function of a ribosome?
Make proteins
(100 points)
What are the 3 sub-phases of Interphase and what happens in each?
S-Synthesis: chromatin replicates
G2- growth
(100 points)
What do you call the DNA during INTERPHASE?
CHROMATIN
(100 POINTS)
Give an example of a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell.
Prokaryotic: bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotic: Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists
(200 points)
Which example goes with which macromolecule?
DNA - Enzymes - Triglycerides - Starch
DNA: Nucleic Acids
Enzymes: Proteins
Triglycerides: Lipids
Starch: Carbs
(200 points)
What are the 3 components of the Cell Theory?
All living things are made of one or more cells.
Cells are the basic unit of life.
All cells come from existing cells.
(600 points)
What is the function of the lysosome?
uses enzymes to digest bacteria, viruses, and old organelles
(200 points)
Draw and label ANAPHASE.
(300 points)
A cell has 42 chromosomes. It goes through the cell cycle and the daughter cells have 21 chromosomes. Is this cell DIPLOID or HAPLOID?
HAPLOID
(100 POINTS)
What is a MULTIPOTENT stem cell?
Stem cell that has a limited potency (limited potential)
(200 points)
What is the polymer of EACH macromolecule:
Carbs: Polysaccharides
Lipids: Phospholipids, Triglycerides, Steroid, Wax
Proteins: Polypeptide
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
(200 points)
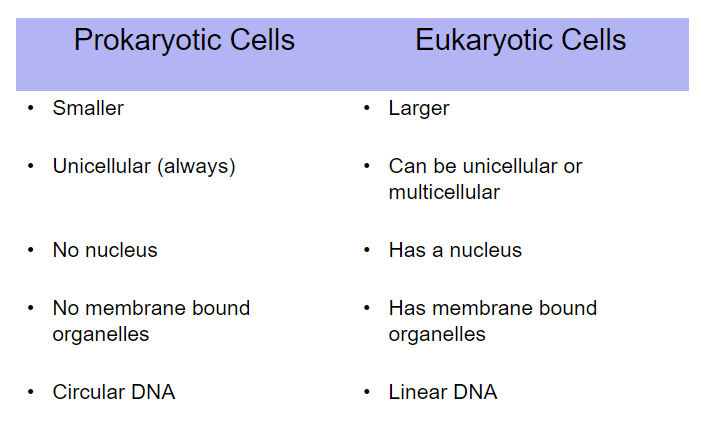
What are the differences between a Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell?
Each Difference 100 points.
Name the organelle that is analogous to a SOLAR POWER PLANT
Chloroplast
(100points)
METAPHASE
(100 POINTS)
Programmed cell death
(100 points)
(300 points)
Draw and correctly label a phospholipid
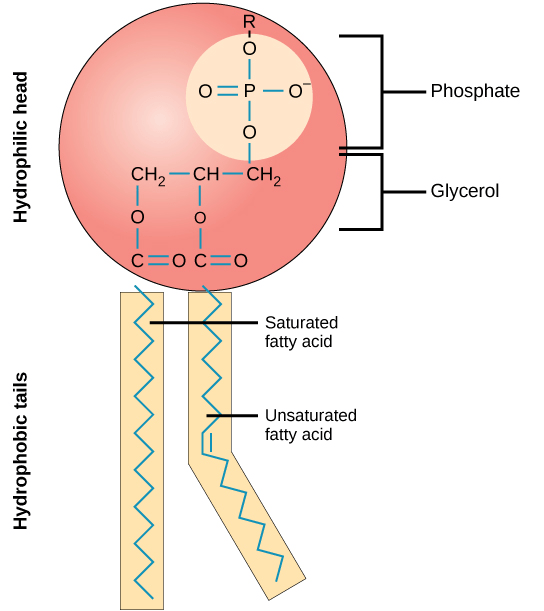
(200 POINTS)
Who was Robert Hooke?
First to describe cells of cork
200 points
What suspends the organelles and provides an environment for chemical reactions within the cell?
Cytoplasm
(200 points)
What is G0 and when does it occur?
The resting phase when the cell is not actively dividing. During Interphase- (before DNA replication)
(300 points)
Gametes
(100 points)
Draw an animal cell on the board. Must have 8 organelles.
(400 points)
Why is the shape of a protein important?
FORM DICTATES FUNCTION: proteins having specialized shapes allow for a better performance in completing a specific function
(300 POINTS)
What are the 3 organelles common to all cells?
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes
(300 points)
What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus?
Modify, sort and ship proteins
(300 points)
DNA sends a signal to rigger apoptosis. Is this an example of internal or external regulation?
INTERNAL
(100 POINTS)
What are INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS?
artificial stem cells that are reprogrammed from a patient's skin or blood cells to an embryonic-like state
(300 points)
Which phase comes before METAPHASE?
PROPHASE
(100 POINTS)
Pair the macromolecule with the test:
Lugol's Iodine
Sudan III Stain
Biuret Test
Benedict's Solution
Lugol's Iodine : Complex Carbs
Sudan III Stain : Lipids
Biuret Test: Proteins
Benedict's Solution: Simple Carbs
(200)
What polymer makes up the cell membrane?
Phospholipids
(100 points)
What is the organelle that is analogous to a water tower? Which cell is this found in?
Central Vacuole in a Plant Cell
(200 points)
Draw, label and describe what happens during PROPHASE.
(500 POINTS)
uncontrollable cell division
(200 points)
What are the ethical issues that arose from HeLa cells?
They were taken without her consent and then given to many scientists all over the world without the families knowledge. Researchers profited without the family benefiting.
(400 points)