Slowed heart rate, increased gastric secretions, bladder and bowel emptying, pupil constriction for improved near vision, and smooth bronchial muscle contraction are functions of what system?
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Medications that bind to a receptor and "activate" its behavior are known as?
Agonists
This is an "action" drug. Consider epinephrine, which stimulates the heart and blood pressure
The movement of a drug out of the body. It occurs mostly through kidneys. Other pathways are bile, saliva, sweat, and even breastmilk.
Elimination
A patient is given a medication that causes increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, bronchial dilation, relaxation of uterine smooth muscle, vasodilation, and an increase blood glucose levels, has received what type of medication?
Non-selective beta-agonist (examples are epinephrine and isoproterenol)
b1 receptors-heart and kidneys
b2 receptors- arterioles, heart, lungs, skeletal muscles, bronchi, uterus, liver,
When prescribing a 0.1% topical corticosteroids, what change can the NP make to reduce risk of systemic toxicity
Change the base of the cream to a lower base like a 2.5% hydrocortisone base
These medications are used to treat cardiac dysrhythmias, heart failure, hyperthyroidism, test anxiety, stage fright, and public speaking.
Beta-adrenergic antagonist
Regulation of the cardiovascular system and body temperature and implementing the acute stress response known as "fight or flight" are the functions of what system?
Sympathetic Nervous System
Medications that bind to receptors but do not activate. It works by either inhibiting the receptor's natural response or counteracts an agonist that may be present.
Antagonist
Think of this as an "anti" action drug. Naloxone is an antagonist that blocks the effects of morphine.
Phase of pharmokinetics that refers to the movement of a drug to various tissue sites
Distribution
This medication decreases intraocular pressure by activating the muscarinic receptors in the eye by 1)miosis (pupillary constriction) and 2) contraction of the ciliary muscles.
Pilocarpine
The ciliary muscle contraction facilitates the outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular meshwork, thereby reducing intraocular pressure.
What determines whether a drug can be administered orally for hepatic metabolism?
First pass elimination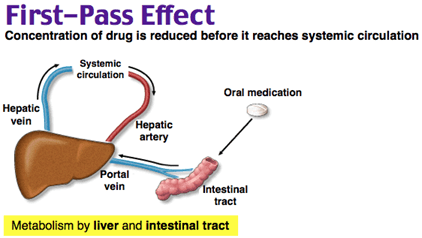
True or False
Alzeheimers medications help to reverse the underlying disease?
False
The important feedback loop that helps regulate blood pressure
Baroreceptor Reflex
These bind irreversibly with the receptor. The effects of the binding go away only after the cell breaks down old receptors and replaces it with new ones that the drug is not attached to. This can take a long time which is why these are rarely used therapeutically.
Non-competitive (insurmountable) antagonist
The required amount of time for a drug to be eliminated from the body by 50%
Drug half-life
A patient presents after being gon a cruise and wearing scopolamine patches. s/s hot, dry, red, confused, and blurred vision? 1. what is wrong with the patient? 2. what is the treatment?
1. muscarinic poisoning
2. physiostigmine
What drug characteristic is the most likely thing to impact bioavailability
Route of administration
What is the next step when a patient on a seizure medication is still having seizures?
Draw drug levels
What is the underlying principle behind why an infant may experience more sensitive responses to CNS drugs?
Blood-brain barrier
An agonist with moderate intrinsic activity produces a maximal effect that is lower than a full agonist.
Partial Agonist
A patient who has been on medication for 1 year reports the medication is not working as well as 6 months ago. What is this?
Drug tolerance
Which of these meds are used to treat spasticity?
baclofen, dantrolene, valium, Flexeril, tizanidine
baclofen, dantroline, valioum
Considering all the different drug routes: transdermal patch, oral, intravenous, sublingual, and extended release, which one would have the least amount of side effects?
transdermal patch
A patient on valproate for seizures is wanting to get pregnant. What should be done?
Change seizures medications to lamotrigine or levetiracetam
Phenytoin
A measure of drug safety is defined as the ratio of a drugs LD (average lethal dose) and ED (average effective dose)
Therapeutic Index
the activation of this receptor causes blood vessel constriction, which is great for a stuffy nose
Alpha-1 activation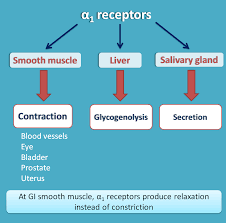
What is the treatment of an autoimmune disease that produces antibodies that attack the nicotinic receptors on skeletal muscles?
Cholinesterase inhibitors
Adaptation
When prescribing lamotrigine for seizures or bipolar etc, what can the prescriber do to lessen the risk of SJS?
start low and go slow when increasing the dose and educate the patient of the risk