What is autotroph? What is a heterotroph?
Autotroph- organisms that make their own food
Heterotroph- organisms that do NOT make their own food/consume autotrophs for food
What types of organisms are at the bottom of an energy pyramid?
Producers/plants/autotrophs
What is biodiversity?
The amount of different types of organisms in a given environment and/or the amount of different traits present in a species.
Carbs, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
What are the inputs/reactants of photosynthesis?
What are the outputs/products of photosynthesis?
Inputs- carbon dioxide, water (sunlight is needed for energy)
Outputs- glucose, oxygen
What's the original source of energy in a food web?
The sun
Which level of the energy pyramid can support the least amount of organisms?
The top.
Which ecosystem is more biodiverse?
Ecosystem A- grass, 3 types of trees, 2 types of bushes, flowers, 3 types of insects, robins, crows, sparrows, mice, rabbits, deer, coyotes, hawks, and eagles
Ecosystem B- grass, 1 type of tree, 1 type of bush, flowers, 1 type of insect, robins, and squirrels
Ecosystem A
What's another term for macromolecule?
organic molecule- all have carbon and hydrogen
What are the inputs of cellular respiration? What are the outputs of cellular respiration?
Inputs- glucose, oxygen
Outputs- carbon dioxide, water, energy (ATP)
What determines the direction of the arrows in a food web? What do the arrows point to?
The arrows point to the organism that is doing the consuming.
If there's 10,000 kcals at the bottom of this energy pyramid, how many will be available to the primary consumers?

1,000 kcals
Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiverse ecosystems are more stable and more resilient to changes.
What are the 2 categories of carbohydrates?
starches and sugars
What types of organisms complete photosynthesis?
What types of organisms complete cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis- only plants
Cellular respiration- plants and animals
What trophic level(s) does the owl belong to?
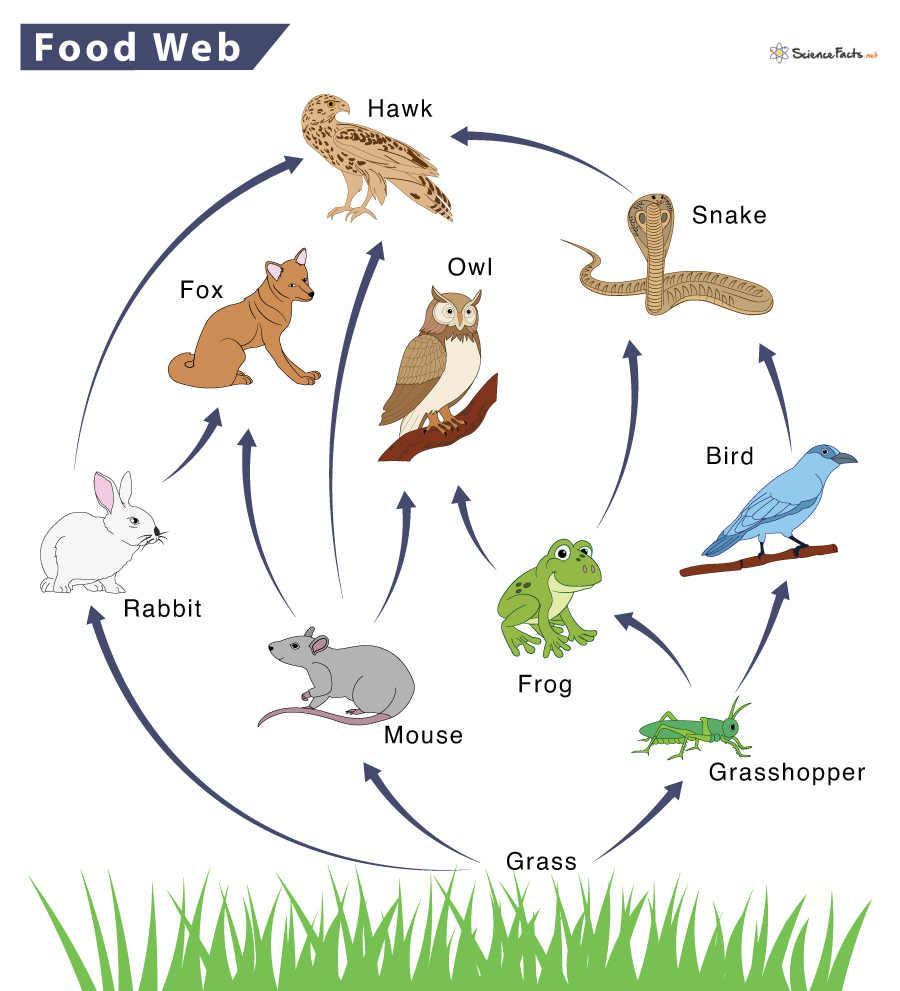
Secondary consumer, tertiary consumer
Why is so much energy lost as you move from one trophic level to the next?
Egested waste, heat loss, respiration, other bodily processes
What is natural selection?
Process by which organisms that are most suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully; also called survival of the fittest
What do all macromolecules contain?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What's the relationship between the formulas for photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
The reactants of one are the products of the other and vice versa.
A disease comes and wipes out all the grasshoppers in the food web. How would this affect the rest of the food web?

Acceptable answers
- populations of frogs and birds will decrease because they consume the grasshoppers
-population of grass will increase because the grasshoppers typically eat it
-the entire food web will be affected
Why are there so few organisms at the top of the energy pyramid and so many at the bottom?
Only 10% of an the energy available at one level of the energy pyramid is passed on to the next. Less energy is available as you move up the pyramid. The smallest amount of energy is available at the top so it can support the smallest number of organisms.
Give an example of natural selection taking place. Make sure to use the terms "survive" and "reproduce" in your answer.
Answers will vary- up to teacher discretion
Proteins. How do plants and animals obtain nitrogen?
Through the nitrogen cycle. Plants take up nitrates through their roots (after being "fixed" by bacteria). Animals eat the nitrogen rich plants.
How do heterotrophs benefit from photosynthesis?
The are able to get the oxygen they need to breathe and the glucose they need for energy.