Risk may have positive or negative outcomes. True or false?
What type of risk is easily mitigated by insurance?
hazard
What two decades did risk management begin in ag risk?
1970's and 1980's
What does ERM stand for?
Enterprise Risk Management
In general, organizations will tolerate a ________ level of hazard risk
minimal
impact
What are the three general time periods of risk impact?
short, medium, long term
One of the first tools of risk management in ag was called
risk financing
What makes ERM different that other types of risk management?
It is more integrated or holistic
opportunity risk
What are the three levels of risk if no control is in place?
Inherent, current or residual, and target
If an organization becomes too concerned with control management, it can suppress the _________________ __________
Entrepreneurial effort
During the 1990's, risk financing was paired with what to provide better risk management?
insurance with derivatives
Two types of risk assessment are
top-down and bottom-up
A new type of technology being used to speed up data analysis and provide a more dynamic approach to emerging trends in risk management is called
crowd sourcing
A type of risk that can only be negative is called
hazard risk
The risk of an organization not being in line with regulations in their industry is called
compliance risk
The ability of a company to make sure all employees are aligning with the goals and policies of the company is called ______________ _______________
corporate governance
What are the four areas of benefits of ERM?
Financial, infrastructure, reputational, marketplace
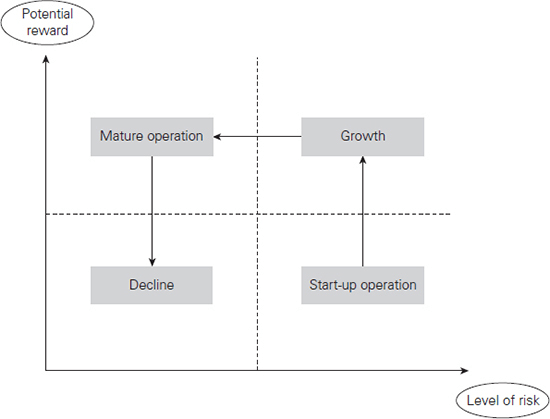
What is the four stages of a business related to level of risk and the potential reward?
What are the four types of risk?
compliance (or mandatory) risks;
hazard (or pure) risks;
control (or uncertainty) risks;
opportunity (or speculative) risks.
What is the type of risk that is derived from the deviation of the required or expected outcome such as a project for a company?
Uncertainty or control risks
Name 4 of the 6 specialist areas in risk management we discussed in class.
project risk management;
clinical/medical risk management;
energy risk management;
financial risk management;
IT risk management;
information security risk management.
What is the most common type of risk assessment technique?
Risk workshops
A bottom-up risk assessment exercise will tend to focus on risks identified as (4 of them) in that order.
compliance, hazard, control and opportunity