The nurse in a community-based setting is teaching clients strategies for preventing cardiovascular disease. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include? Select all that apply.
Encouraging regular physical exercise
Promoting a diet high in saturated fats
Advising smoking cessation
Recommend no more than 5 alcoholic drinks a day
Educating about the importance of regular blood pressure monitoring
Instructing on the importance of regular cholesterol screenings.
Encouraging regular physical exercise
Advising smoking cessation
Educating about the importance of regular blood pressure monitoring
Instructing on the importance of regular cholesterol screenings.
EXPLANATION
Choices A, C, E, and F are correct. Regular physical exercise is important for maintaining cardiovascular health. It helps to strengthen the heart, improve circulation, and control weight. Exercise can also help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. The nurse should educate clients about the harmful effects of smoking on the heart and blood vessels. Encouraging smoking cessation is crucial for reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Cholesterol screenings help identify individuals with high cholesterol levels, including elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly referred to as "bad" cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol are a significant risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Identifying high cholesterol levels early allows for early intervention and management.
Choice B is incorrect. A diet high in saturated fats can contribute to high cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. The nurse should promote a heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium while being rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Choice D is incorrect. Excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health. 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that adults of legal drinking age can choose not to drink, or to drink in moderation by limiting intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men or 1 drink or less in a day for women.
The nurse assessed a client's cardiac rhythm strip. The nurse should plan to document this rhythm as which of the following? See the image below.

A. Ventricular fibrillation
B. Complete (3rd degree) heart block
C. Sinus tachycardia
D. Sinus bradycardia
C. Sinus tachycardia
Choice C is correct. Based on the information provided, this rhythm is sinus tachycardia. The PR and QRS intervals, as well as the rhythm, are normal. The rate of 105 is high, suggesting tachycardia.
Choices A, B, and D are incorrect. Ventricular fibrillation is irregular and has no discernible P or QRS waves. The rate of ventricular fibrillation is also having a rate ranging anywhere from 150 – 500. A complete heart block has a variable PR interval because it is completely separate from the QRS. The rate of a complete heart block is typically less than 60. Sinus bradycardia has a normal rhythm and a normal PR and QRS interval, but the rate is less than 60.
The nurse has performed a cardiovascular assessment on a client, and while auscultating heart tones, the nurse auscultates a harsh blowing sound. The nurse should document this finding as a
A. pericardial friction rub.
B. heart murmur.
C. normal lub-dub sounds.
D. S3 heart sound.
B. heart murmur.
Choice B is correct. The whooshing or blowing sound sometimes heard upon cardiac auscultation is known as a heart murmur and may indicate valve incompetency. "Stenosis" refers to a narrowing of the heart valve, whereas regurgitation indicates a "leaky" valve. An aortic stenosis murmur is best heard at the second intercostal space in the right upper sternal border (aortic area). A mitral stenosis murmur is best heard at the apex (mitral area).
Choice A is incorrect. Pericardial friction rub originates from the pericardial sac and occurs with the movements of the heart during the cardiac cycle. Rubs are a sign of inflammation, infection, or infiltration.
Choice C is incorrect. Whooshing and blowing do not indicate normal lub-dub sounds. The lub-dub sounds are indicative of the S1 and S2 heart sounds.
Choice D is incorrect. S3 is a third heart sound, sometimes referred to as a gallop. This gallop is not the same thing as a murmur. An S3 heart sound may be physiological or pathological. It is physiological if the client is pregnant because of the increased blood volume. However, it can also be pathological when it presents as an early sign of systolic heart failure.
The nurse in the ER is caring for an Asian-American with an acute asthma attack. When assessing the client, the nurse understands that which of the following information holds the least priority?
A. History of present illness
B. Psychosocial assessment
C. Neurological status
D. Vital signs and oxygen saturation
B. Psychosocial assessment
EXPLANATION
Choice B is correct. In Asian American culture, asking personal questions during the initial meeting is uncomfortable and indiscreet. The nurse can put off this assessment until the patient is already relaxed and comfortable.
Choice A is incorrect. Assessing for the history of present illness is necessary, providing information that will help direct client care.
Choice C is incorrect. Following the hierarchy of needs, the physiological concerns of the patient should be prioritized over other aspects. Neurological status should be assessed as soon as possible.
Choice D is incorrect. Following the hierarchy of needs, the physiological concerns of the patient should be prioritized over other aspects. Oxygen saturation and vital signs should be assessed with a high priority.
The nurse is watching the monitor of a client wearing a continuous cardiac monitor when it begins to alarm and fails to display any QRS complexes. Which nursing intervention should the nurse do first?
A. Press record on the electrocardiogram
B. Check the client's lead placement
C. Call the code team
D. Contact the health care provider
B. Check the client's lead placement
Choice B is correct. Before calling a code or contacting the physician, the nurse should ensure that the leads are correctly placed on the client and have not been removed. Physically looking and assessing the client as well as the associated equipment should be the first action when an abnormal rhythm is noticed on the cardiac monitor.
Choice A is incorrect. The first action is to ensure proper lead placement.
Choice C is incorrect. Calling a code is not appropriate until the nurse has confirmed the client is experiencing asystole.
Choice D is incorrect. Contacting the care provider should not be completed until the nurse is sure that the client leads are working correctly.
A client has been placed on a sodium-restricted diet following a myocardial infarction. Which of the following would be the most appropriate meals to suggest?
A. Turkey, 1 fresh sweet potato, 1/2 cup fresh green beans, milk, and 1 orange.
B. Broiled fish, 1 baked potato, ½ cup canned beets, 1 orange, and milk.
C. Canned salmon, fresh broccoli, 1 biscuit, tea, and 1 apple.
D. A bologna sandwich, fresh eggplant, 2 oz fresh fruit, tea, and apple juice.
A. Turkey, 1 fresh sweet potato, 1/2 cup fresh green beans, milk, and 1 orange.
Choice A is correct. People with heart failure may improve their symptoms by reducing the amount of sodium in their diet. Sodium is a mineral found in many foods, especially salt. Overeating salt causes the body to keep or retain too much water, worsening the fluid buildup. Patients should be encouraged to follow a low-sodium diet to help manage symptoms of hypertension and to reduce edema. One of the most natural things a patient can do at home is to reduce the amount of sodium intake. They can also eat fresh vegetables rather than canned. If canned vegetables are the only option, the patient should rinse the plants with clean water and cook them with unsalted water.
Choice B is incorrect. Canned vegetables should be avoided.
Choices C and D are incorrect. Canned or processed meats are higher in sodium and should be avoided.
The nurse is caring for a client with the following tracing on the electrocardiogram (ECG). The nurse should anticipate a prescription for which medication? See the image below.
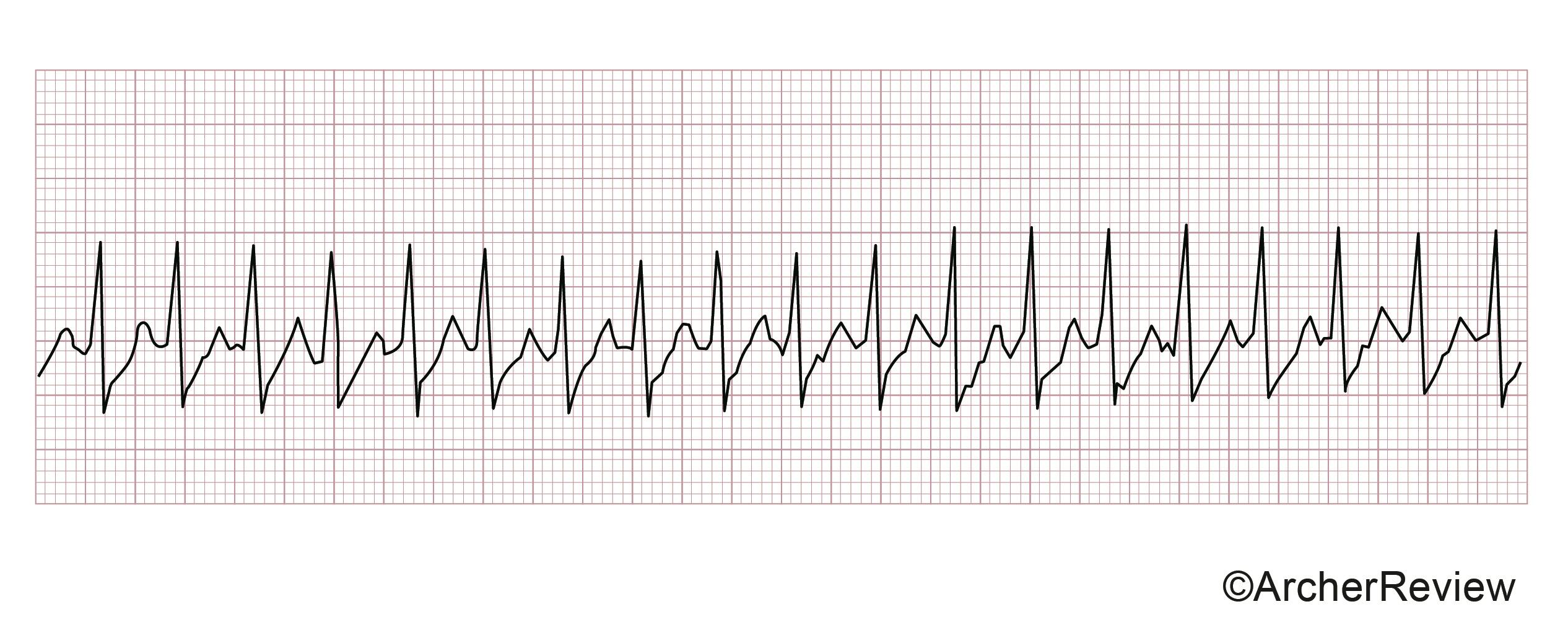
A. Adenosine
B. Atropine
C. Labetalol
D. Amiodarone
A. Adenosine
EXPLANATION
Choice A is correct. The tracing reflects supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). The preferred medication for individuals experiencing SVT includes the rapid administration of adenosine followed by a rapid flush of 0.9% saline. Adenosine slows the electrical conduction time through the AV node.
Choices B, C, and D are incorrect. Atropine is indicated for the treatment of symptomatic sinus bradycardia. Labetalol is indicated for a hypertensive emergency and sinus tachycardia. While labetalol lowers heart rate, it would not treat the underlying cause of SVT. Amiodarone may be utilized for refractory SVT, but this drug is not the initial drug of choice for SVT. Amiodarone is a preferred drug for AFIB and VTACH.
The nurse is caring for a client with congestive heart failure (CHF). The nurse should anticipate a prescription for which medication?
A. Enalapril
B. Verapamil
C. Lovastatin
D. Gemfibrozil
A. Enalapril
EXPLANATION
Choice A is correct. Enalapril is an ACE inhibitor and this drug class is indicated in the treatment of heart failure to prevent ventricular remodeling.
Choices B, C, and D are incorrect. Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker, which is contraindicated in the management of heart failure because of its adverse effects on cardiac output. Lovastatin and gemfibrozil are medications used to reduce cholesterol and are not directly used in the management of heart failure.
The nurse is assessing a client who has a pneumothorax. Which of the following assessment findings should the nurse expect?
A. Blood-tinged sputum
B. Increased anterior-posterior diameter
C. Reduced breath sounds on the affected side
D. Auscultation of a loud, rough, grating sound
C. Reduced breath sounds on the affected side
EXPLANATION
Choice C is correct. A pneumothorax has clinical features such as reduced breath sounds on the affected sides, tachypnea, dyspnea, and pleuritic chest pain. Some clients may be asymptomatic, depending on the size of the pneumothorax.
Choices A, B, and D are incorrect. A pneumothorax does not have features such as blood-tinged sputum, increased AP diameter (this is a feature in COPD), or auscultation of a loud, rough, grating sound.
The nurse is caring for a client with congestive heart failure experiencing an exacerbation. Which of the following of the client's vital signs would indicate that the client is experiencing a complication?
A. Decrease in blood pressure
B. Increase in temperature
C. Decrease in respiratory rate
D. Increase in blood pressure
A. Decrease in blood pressure
EXPLANATION
Choice A is correct. Congestive heart failure (CHF) is characterized by the heart's inability to pump sufficient blood to meet the body's demands. It can result in fluid overload and increased pressure in the blood vessels. A potential complication in a client with CHF is decreased cardiac output, which can lead to decreased blood pressure. Initially, the blood pressure may increase. However, a complication is decompensation which may cause the compensatory mechanisms to fail.
Choice B is incorrect. Fever can be a sign of an underlying infection, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infection, which can trigger or exacerbate CHF symptoms. This needs to be addressed. However, it is not the most immediate priority in the question provided.
Choice C is incorrect. Decreased respiratory rate is not directly related to heart failure. However, in severe cases of heart failure, fluid may accumulate in the lungs, causing shortness of breath and increased respiratory rate.
Choice D is incorrect. While hypertension can contribute to the development of heart failure, it is not a direct complication of heart failure itself. In heart failure, the primary concern is the heart's inability to pump blood effectively, leading to decreased cardiac output and fluid overload. This fluid overload can eventually result in increased pressure in the blood vessels, contributing to the development of hypertension. However, increased blood pressure alone would not indicate a potential complication of heart failure. In this scenario, it is important to focus on decreased blood pressure as the primary indicator of a possible complication.
A client is being discharged following the insertion of a permanent pacemaker. Which of the following should be included in the client’s discharge instructions?
A. Air travel will not be possible due to airport screening equipment.
B. You will need to discard any radios at home that have antennas.
C. Computed tomography (CT) scans are not permitted with this device.
D. You should use your cellular phone on the opposite side of the generator.
D. You should use your cellular phone on the opposite side of the generator.
EXPLANATION
Choice D is correct. For a client with a pacemaker, it is recommended that they talk on their cellular phone opposite of the pulse generator to prevent electromagnetic interference.
Choices A, B, and C are incorrect. Air travel is not prohibited for a client with a pacemaker. They should carry their medical alert card if they are stopped by airport security. Discarding radios and other home appliances is unnecessary as they do not cause any interference. CT scans are permitted for a client with a pacemaker. Diagnostics with an MRI are contraindicated.
The nurse cares for a client with suspected congestive heart failure (CHF). Which of the following laboratory tests would the nurse expect the primary health care provider (PHCP) to prescribe to confirm the diagnosis?
A. Basic metabolic panel (BMP)
B. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
C. Complete Metabolic Profile (CMP)
D. C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
B. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
EXPLANATION
Choice B is correct. Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) may be confirmed by an elevation of the B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). This peptide is elevated when it is cleaved from the ventricle wall because of increased ventricular filling pressures.
Choices A, C, and D are incorrect. CHF is a condition that may lead to consequential fluid retention and decreased cardiac output. BMP, CMP, and CRP are not tests indicated for CHF. C-Reactive Protein may be used to detect atherosclerosis but not utilized in diagnosing heart failure.
An emergency department (ED) nurse establishes continuous cardiac monitoring for a client. The following tracing is observed on the monitor. The nurse should take which initial action? See the image below.

A. Establish vascular access and request a prescription for atropine
B. Assess the client's blood pressure and level of consciousness
C. Obtain and review the client's current medications
D. Document the findings and reassess the client in one hour
B. Assess the client's blood pressure and level of consciousness
Choice B is correct. The nurse should prioritize assessing the client's vital signs and level of consciousness. This tracing reflects sinus bradycardia. While sinus bradycardia may be benign, if the client should experience unstable blood pressure or dizziness, the nurse will need to act by establishing vascular access and administering atropine. However, this is predicated on the client's overall stability, which can only be discerned by assessment.
Choices A, C, and D are incorrect. These actions are plausible but do not prioritize assessing the client and their overall condition. Reviewing the client's current medications may determine the origin of the bradycardia but will not yield clues as to the client's current level of stability. Documentation should only occur once the nurse has determined that the client is stable.
Following a persistent cough, chills, and fever, a client was admitted for a possible respiratory infection. The admission orders include a regular diet, vital signs every 4 hours, ampicillin 250 mg PO every 6 hours, and sputum culture. Before beginning antibiotic therapy, the nurse should perform which of the following?
A. Provide the client a full meal
B. Collect the sputum sample
C. Assess the client's vital signs
D. Assess the client's oxygen saturation
B. Collect the sputum sample
EXPLANATION
Choice B is correct. When caring for a client requiring a sputum culture, the sputum sample should be obtained before initiating antibiotic therapy. Obtaining the sputum sample prior to initiating antibiotic therapy allows for accurate detection of the organism(s) causing the infection through the sputum culture.
Choice A is incorrect. Ampicillin should be given on an empty stomach (at least 30 minutes before or two hours after a meal).
Choice C is incorrect. Overall, the assessment of a client's vital signs are an essential nursing action. Conversely, although obtaining new vital signs for any client prior to administering medication is always a sound practice, there is no specific indication or need to do so before administering oral ampicillin.
Choice D is incorrect. Overall, assessing a client's oxygen saturation is an essential nursing action. Conversely, although obtaining a new oxygen saturation for any client before administering medication is always a sound practice, there is no specific indication or need to do so before administering oral ampicillin.
The nurse cares for a client with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The nurse anticipates the physician will order an emergent
A. exercise electrocardiography.
B. computed tomography (CT) of the chest with contrast.
C. percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
D. echocardiogram
C. percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Choice C is correct. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is cardiac catheterization that involves the insertion of a large catheter into the femoral or radial artery to access the coronary arteries. A stent may be placed to keep the lumen of the artery open. This test can diagnose narrowing in the coronary arteries and intervene with angioplasty and stenting, if necessary. If this is not available, the physician may order an intravenous thrombolytic to bust the clot in the coronary artery.
Choice A is incorrect. Exercise electrocardiography is commonly known as a stress test. This is a planned procedure that examines exercise tolerance and its cardiovascular effects. The client is having an acute infarction, and this test would be inappropriate.
Choice B is incorrect. A chest CT may assist in diagnosing an occlusion in the coronary artery, but this test does not allow for intervention.
Choice D is incorrect. An echocardiogram is performed to examine the heart's structures and its output. This is not appropriate during an acute myocardial infarction.
The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client with a wet-suction chest tube prescribed wall suction. Which interventions would be appropriate to include?
Select all that apply.
Apply clamps to the tubing to secure it to the bed.
Strip the tubing at least once every eight hours.
Report any bubbling in the suction control chamber.
Ambulate the client with the device below the insertion site.
Palpate around the insertion site for any crackles or popping.
Ambulate the client with the device below the insertion site.
Palpate around the insertion site for any crackles or popping.
EXPLANATION
Choices D and E are correct. Ambulation with a chest tube is not contraindicated. If the nurse has an order from the primary healthcare provider (PHCP) and it is safe for the client to ambulate, the nurse should ambulate the client with the device distal to the insertion site. Palpating around the insertion site should be done and any crackles or popping should be reported to the PHCP because that indicates an air leak.
Choices A, B, and C are incorrect. The tubing should not be clamped to the bed as this would cause an obstruction. It would be appropriate to keep extra tubing loose on the bed. Stripping the tubing would be inappropriate because it would increase the intrathoracic pressure, counterproductive to chest tube therapy. Continuous bubbling in the suction control chamber is normal because wall suction is prescribed for this client.
The nurse assesses a client with acute left leg swelling and calf tenderness following a long car ride. The nurse anticipates that the primary healthcare provider (PHCP) will order which diagnostic test?
A. D-dimer test
B. Ankle-Brachial Index
C. Radiograph (X-Ray)
D. Venous Duplex Ultrasonography
D. Venous Duplex Ultrasonography
EXPLANATION
Choice D is correct. Based on the acute symptoms (unilateral leg swelling and tenderness) following a risk factor (a long car ride), the client has a high clinical probability of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The gold standard for diagnosing a DVT is venous duplex ultrasonography. This noninvasive test is an ultrasound that assesses the flow of blood through the veins of the arms and legs.
Choices A, B, and C are incorrect.
- A D-dimer is a protein fragment obtained after clot breakdown. D-dimer is elevated in deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, malignancy, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). However, false-negative and false-positive D-dimer tests are fairly common. Therefore, a D-dimer is useful in excluding a deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism when there is low clinical suspicion, not when the clinical suspicion is high (choice A). When there is high clinical suspicion, a venous duplex ultrasound should be ordered.
- The ankle-brachial index (ABI) can be used to assess the vascular status of the lower extremities and is primarily used to determine distal arterial blood flow (choice B).
- Radiography is not used because it does not provide the necessary view of the veins (choice C).
A nurse is caring for a client with heart failure. Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement to manage fluid volume overload? Select all that apply.
Administer diuretics as prescribed
Monitor daily weights
Restrict fluid intake to 500 mL per day
Assess lung sounds for crackles
Encourage high-sodium diet
Assess lung sounds for rhonchi
Administer diuretics as prescribed
Monitor daily weights
Assess lung sounds for crackles
EXPLANATION
Choices A, B, and D are correct. Several interventions may be necessary to manage fluid volume overload in a client with heart failure. Administering diuretics helps promote the excretion of excess fluid and decrease fluid volume. Monitoring daily weights is crucial to assess changes in fluid status. Assessing lung sounds for crackles is important to detect pulmonary congestion, a sign of fluid overload.
Choice C is incorrect. Restricting fluid intake to 500 mL per day is incorrect. Fluid restriction is typically not necessary unless the client's condition worsens. Typical fluid restrictions for clients range from 1500-2000 mL per day.
Choice E is incorrect. Sodium restriction is usually recommended for heart failure clients to prevent fluid retention and edema. This will generally be a recommendation of 2g or lower of sodium per day.
Choice F is incorrect. Rhonchi lung sounds are typically associated with conditions that cause airway obstruction or narrowing, such as bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or asthma.
The nurse is precepting a graduate nurse caring for a client with a chest tube. Which of the following statements made by the graduate nurse would indicate an expected finding? Select all that apply.
"The drainage system was below the insertion site."
"Vigorous bubbling was in the water-seal chamber."
"The client reported pain at the insertion site."
"An occlusive dressing was over the chest tube."
"The chest tube was clamped for ten minutes to determine if a leak was present."
"The drainage system was below the insertion site."
"The client reported pain at the insertion site."
"An occlusive dressing was over the chest tube."
EXPLANATION
Choices A, C, and D are correct. It is expected that the drainage system will be at a level below the client's chest. This is what allows gravity to help drain fluid from the pleural space. If the drainage system were above the client's chest, the chest tube would not work properly (Choice A). An occlusive dressing placed over the chest tube is appropriate. This is important to ensure that air does not enter the pleural space causing a pneumothorax. The nurse should check the dressing to ensure it is airtight (Choice D). The dressing is changed daily. Pain at the insertion site is expected and typically is aggravated when the client changes positions.
Choices B and E are incorrect. Gentle bubbling in the water chamber is an appropriate finding, but the bubbling should not be vigorous. Gentle bubbling indicates that air is draining from the client, but if vigorous or excessive bubbling is noted, there may be an air leak, which must be addressed quickly. It is not expected for the water in the tube of the water-seal chamber to be stable during inhalation and exhalation. The water in the tube of the water-seal chamber should fluctuate during inhalation and exhalation. If it does not, the chest tube could be occluded, the lung could have re-expanded, or air could leak into the pleural space. The nurse must notify the physician of this finding to investigate the cause and take appropriate action. A chest tube should never be clamped because this could cause tension pneumothorax. While a clamp should be readily available, chest tubes are not routinely clamped. They are clamped when changing the system to a new device or the system is to be discontinued.
The nurse in the intensive care unit (ICU) is caring for 58-year-old male client
Hx
- atrial fibrillation
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- hyperlipidemia
- chronic back pain
VS

Meds
- 0.9% saline via continuous infusion at 100 mL/hr
- diltiazem 5 mg/hr via continuous infusion at 5 mg/hr
The ICU nurse reviewed the client's medical record
Based on the 2000 vital signs, select two (2) immediate actions the nurse should take
stop the diltiazem infusion
apply supplemental oxygen via nonrebreather face mask
stop the 0.9% saline infusion
notify the primary healthcare provider
assess the client for back pain
request a prescription to change the intravenous fluids to hypertonic saline
stop the diltiazem infusion
notify the primary healthcare provider
EXPLANATION
- The client is receiving a continuous infusion of diltiazem, a standard treatment for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response.
- Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker that may adversely cause bradycardia and hypotension.
- The client's blood pressure has trended downward, with the lowest reading at 2000
- The nurse should immediately turn off the infusion and notify the PHCP because the condition change.
- The diltiazem infusion should be stopped because this medication is causing low blood pressure.
- If the nurse fails to act, the client may develop severe hypotension causing cardiac collapse.
- The PHCP should be notified of the condition change because an alternative medication may need to be prescribed.
- The 0.9% saline infusion should not be stopped. This infusion is beneficial because the saline will increase the blood volume and cause the blood pressure to reach a normal range.
- The client has a history of COPD, and the client's oxygen saturation is not of concern. The optimal oxygen saturation for a client with COPD is 88% or greater.
- Providing oxygen via a nonrebreather would be detrimental because it could contribute to respiratory acidosis (which is likely already experienced by the client with COPD).
- Assessing the client for pain is not an immediate action.
- The client's clinical concern is the low blood pressure caused directly by the diltiazem infusion, not their chronic back pain.
- Hypertonic saline would not increase circulatory volume. The client needs the diltiazem stopped and potentially an isotonic fluid bolus to increase cardiac output.
The nurse is caring for a client with the below tracing on the electrocardiogram (ECG). The nurse should anticipate which prescription from the primary healthcare provider (PHCP)? See the exhibit.

A. captopril
B. atropine
C. adenosine
D. diltiazem
D. diltiazem
Choice D is correct. The tracing in the exhibit shows irregularly irregular rhythm with no identifiable p-waves. This rhythm can be identified as "atrial fibrillation." Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker (CCB) that controls the atrial fibrillation rate. Atrial fibrillation leads to increased ventricular rate and reduced ventricular diastolic filling. If the ventricular rate is uncontrolled, cardiac output is reduced, resulting in hypotension and congestive heart failure. Initial treatment in atrial fibrillation is aimed at ventricular rate control with calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, verapamil), a beta-blocker (atenolol, metoprolol), or digoxin. If the atrial fibrillation remains persistent, cardioversion is considered.
Choices A, B, and C are incorrect.
- Captopril is an ACE inhibitor used to treat heart failure and hypertension.
- Atropine increases the heart rate and is efficacious for symptomatic sinus bradycardia, not atrial fibrillation.
- Adenosine is approved for supraventricular tachycardia when vagal maneuvers are not efficacious. Note that the term " supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)" refers to a wide variety of atrial arrhythmias (atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia) when the rhythm can not be clearly identified. During an SVT, the heart rate is very high at 150 to 220 beats per minute. The rate needs to be slowed to identify and treat the rhythm appropriately. Vagal maneuvers (carotid sinus massage, Valsalva maneuver) are applied first. IV adenosine is used to slow down or terminate if the SVT is refractory to vagal maneuvers. Adenosine's principal purpose in an SVT is to slow the rate to allow for appropriate rhythm identification. Because the rhythm strip in the exhibit can clearly be identified as atrial fibrillation, adenosine is unnecessary and must be treated with more specific rate-controlling medications (CCBs, beta-blockers).
The nurse is caring for a client brought to the emergency department reporting dyspnea
Item 1 of 1
- History And Physical
An 86-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by his wife. After sleeping for eight hours, the client woke up reporting chest heaviness, non-productive cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. The client took a dose of his prescribed albuterol inhaler and reported no efficacy. The client repeatedly stated that 'something does not feel right.’ The respiratory exam yielded that the client's lung sounds were clear, normal chest excursion, and a respiratory rate of 24 breaths per minute. Two days ago, returned from a sixteen-hour road trip to visit their son at college. The client has a medical history of asthma and diabetes mellitus.
Which orders does the nurse anticipate from the primary healthcare provider (PHCP)? Select all that apply
chest physiotherapy
pulmonary function tests
purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test
d-dimer level
albuterol via nebulizer
Chest computed tomography (CT) scan
d-dimer level
Chest computed tomography (CT) scan
- This client is strongly suspected of developing a pulmonary embolism (PE).
- The client's cough, shortness of breath, and chest heaviness are consistent findings of a PE. This is further supported by the client having tachypnea. The PE may have developed from the client's prolonged immobility during the recent road trip. The diagnostic testing supporting the potential diagnosis of a PE includes a D-Dimer and a CT scan.
- While the client has asthma, the assessment does not support an asthma exacerbation. Clients with an asthma exacerbation exhibit wheezes that are often time audible. This classic manifestation is absent. Thus, albuterol via nebulizer would not be helpful or anticipated by the PHCP. This further excludes pulmonary function tests, as this is used to determine a client's ventilation status.
- A PPD is unnecessary as this testing is required if the client has been exposed to pulmonary tuberculosis. The client has no fever or night sweats mentioned in the H&P.
- Chest physiotherapy is not indicated as this is helpful for conditions such as bronchitis as it assists with mobilizing respiratory secretions.
The nurse is caring for a client experiencing a myocardial infarction. The nurse should prepare to take which action? Select all that apply.
Start a peripheral vascular access device (VAD)
Obtain a prescription for albuterol via nebulizer
Obtain a prescription for chewable aspirin
Obtain a prescription for nitroglycerin
Obtain an order for a chest radiograph (x-ray)
Establish continuous cardiac monitoring
The nurse is caring for a client experiencing a myocardial infarction. The nurse should prepare to take which action? Select all that apply.
4/5
Your Score/Max
+/- Scoring Rule
Start a peripheral vascular access device (VAD)
Obtain a prescription for chewable aspirin
Obtain a prescription for nitroglycerin
Obtain an order for a chest radiograph (x-ray)
Establish continuous cardiac monitoring
Choices A, C, D, E, and F are correct. This client is experiencing a myocardial infarction (MI), a medical emergency. Starting a vascular access device and obtaining laboratory work such as troponin is especially crucial for the future administration of drugs and assessing the chemical damage done to the heart. The nurse should obtain prescriptions for chewable aspirin, sublingual nitroglycerin, and antiplatelet medications such as clopidogrel. Aspirin is used to exert its antiplatelet effects, and nitroglycerin promotes vasodilation of the coronary arteries. A client experiencing an MI would also get a chest radiograph (x-ray). This is useful in determining if the client is experiencing pulmonary edema due to the MI. Additionally, the radiograph will identify any other pathologies, such as cardiomegaly. Performing continuous cardiac monitoring is appropriate because the nurse needs to watch for the development of dysrhythmias closely.
Choice B is incorrect. Albuterol would be contraindicated during myocardial ischemia because it increases myocardial oxygen demand. Raising the oxygen demand will increase ischemia, which may cause dysrhythmias.
A client was admitted for an acute exacerbation of asthma. Auscultation findings reveal nearly absent breath sounds, and an albuterol nebulization treatment was promptly administered. Thirty minutes later, upon auscultation, the nurse hears diffuse inspiratory and expiratory wheezes throughout the lung fields. This finding means:
A. There is increased airflow
B. There is no improvement in the airflow
C. There is worsening of the condition
D. The airflow issue was not addressed
A. There is increased airflow
EXPLANATION
Choice A is correct. Changes in breath sounds indicate that the client has responded to the albuterol nebulizer. Upon the initial auscultation by the nurse, there were nearly absent breath sounds, indicating severe airflow obstruction was present. Thirty minutes after the medication administration, diffuse inspiratory and expiratory wheezes throughout the lung fields demonstrate that airflow has improved (even though the lung fields remain partially obstructed).
Choice B is incorrect. The initial auscultation of the client's lungs revealed nearly absent breath sounds. According to this finding, little to no air was moving within the client's lungs. Thirty minutes after the albuterol nebulizer, auscultation by the nurse reveals diffuse inspiratory and expiratory wheezes throughout the lung fields. Unlike the previous auscultation, lung sounds are now prominent within the lung fields, indicating improved airflow throughout the client's lungs.
Choice C is incorrect. The initial auscultation of the client's lungs revealed nearly absent breath sounds. According to this finding, little to no air was moving within the client's lungs. In order for a worsening of the condition to occur, auscultation by the nurse thirty minutes after the albuterol nebulizer would need to reveal a complete lack of all breath sounds throughout the client's lungs.
Choice D is incorrect. According to the question, "auscultation findings reveal nearly absent breath sounds, and an albuterol nebulization treatment was promptly administered." Albuterol sulfate is a beta2-adrenergic bronchodilator used to treat asthma, bronchospasm, and reversible obstructive airway disease. Therefore, the airflow issue was not only addressed, but addressed in a prompt, effective manner.
The nurse is caring for a client newly admitted with infective endocarditis (IE). The nurse should plan for which intervention in the client's care plan?
A. initiating contact and droplet precautions
B. obtain a prescription for intravenous antivirals
C. obtain a prescription for enoxaparin
D. monitor renal function
D. monitor renal function
Choice D is correct. An array of complications may occur from IE including stroke, heart failure, splenic infarction, pulmonary (septic) emboli, and renal infarction. Monitoring the client's renal function is key because an increase in creatinine, flank pain, and hematuria all suggest renal infarction. A renal infarction occurs when a piece of vegetation breaks off and lodges itself into the renal artery, subsequently disrupting perfusion.
✓ Infective endocarditis occurs primarily in clients with injection drug use (IDU) and those who have had valve replacements, have experienced systemic alterations in immunity, or have structural cardiac defects.
✓ This condition is caused by the invasion of bacteria that enter the client through contaminated needles, oral cavity following dental procedures, and/or skin abscesses.
✓ Classic manifestations of IE include
• Fever associated with chills, night sweats, malaise, and fatigue
• Anorexia and weight loss
• Cardiac murmur (newly developed or change in existing)
• Petechiae • Splinter hemorrhages
• Osler nodes (on palms of hands and soles of feet)
• Janeway lesions (flat, reddened maculae on hands and feet)
• Roth spots (hemorrhagic lesions that appear as round or oval spots on the retina)
• Positive blood cultures
✓ Treatment of IE is antibiotic therapy for several weeks.
✓ Complications include myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, renal infarction, stroke, and septic arthritis.