Which organelle manufactures ribosomes using rRNA and proteins
Nucleolus
Name three organelles all cells contain
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes
Name the covalent bond between carbohydrate monomers
Glycosidic bond
Name the covalent bond between the glycerol & fatty acids
Ester bond (linkage)
Name the covalent bond between protein monomers
Peptide bond
Which type of microscope produces extremely detailed, 3D images of the exterior of cells
Scanning electron microscope
What is the major difference in DNA between prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic DNA is circular, Eukaryotic DNA is linear
What is one of the major functions of carbohydrates?
Short term energy, structure, energy storage
What is one of the major functions of lipids?
Long-term energy storage, insulation, hormones
What is one of the major functions of proteins?
Enzymes, membrane passage, some hormones, antibodies, structure
This organelle is surrounded by a double membrane, contains its own circular DNA, and is the site of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells
Mitochondria
Which types of organelles do prokaryotic cells not have?
Plants store carbohydrates as this
Starch
This class of lipid is solid at room temperature, contains no double bonds between carbon atoms, and is typically found in animal fats
The specific three-dimensional shape of a protein is largely determined by interactions like hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bridges at this structural level
Tertiary structure
This organelle is composed of two subunits, lacks a membrane, and is responsible for synthesizing polypeptides by translating mRNA
Ribosomes
This organelle is used for locomotion in both prokaryotes and some eukaryotes, but it has a simpler structure in prokaryotes
Flagellum
The two types of polymers found in starch.
Amylose & amylopectin
This type of reaction joins three fatty acids to a glycerol molecule to form a triglyceride, producing water as a byproduct
Dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction)
What are the names of two of the types of folding in secondary structure of proteins?
α-helix & β-sheet
Which organelle is in the following micrograph

Golgi body (apparatus)
What is different about the cell walls of prokaryotes as opposed to eukaryotes?
Prokaryotic cell walls are made of peptidoglycan, eukaryotes are made of cellulose or chitin.
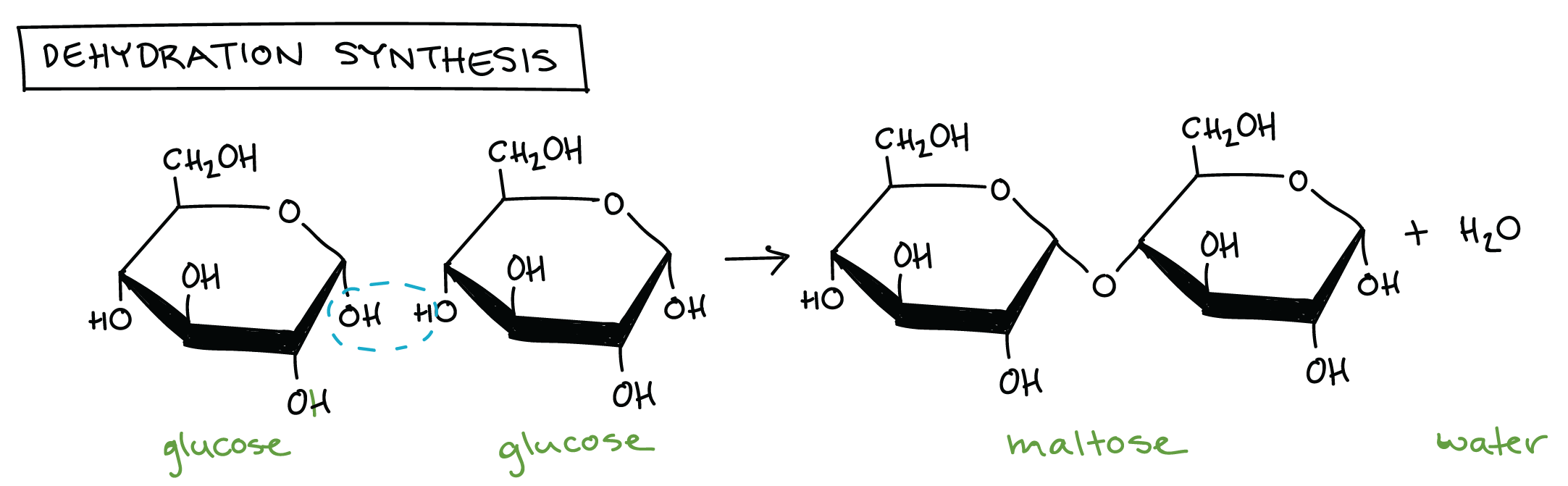
Draw the dehydration synthesis reaction between two glucose monomers.
What is the major difference between a triglyceride & a phospholipid
One fatty acid molecule in a triglyceride is replaced with a phosphate group
If there is a mutation in DNA that causes a change in amino acid sequence, which protein structure will be affected first?
Primary structure