The upper airway ends with what structure?
Larynx or Vocal Cords
Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Respiration
These stimulate the medulla to increase the respiratory rate based on the level of CO2 or hydrogen ions in the body.
Chemoreceptors
Your adult patient is breathing at 20bpm with a Cheyne-Stokes rhythm. Is this an adequate or inadequate example?
Inadequate
You are assessing your patient's airway and note snoring respirations. What do you do next?
Reposition airway - head tilt/chin life or jaw thrust
The two airway structures open to the exterior of the body are the what? Must get both for points.
Active part of breathing
Inhalation
Condition in which the carbon dioxide levels in the body increase
Hypercarbia
Irregular, ineffective respirations which may or may not have a recognizable pattern are called what?
Ataxic Respirations
You are called to a patient who fell off a ladder while cleaning gutters on their single-story residence. They are not breathing when you assess airway. What do you do first?
Jaw thrust
The gas exchange takes place in this location on the alveoli.
Pulmonary Capillary Beds
The portion of tidal volume that does not reach alveoli and does not participate in gas exchange
Dead Space
Binds to hemoglobin 250x more than oxygen, prohibiting delivery of oxygen to the cells
Carbon monoxide
The numeric ETCO2 reading
Capnometry
Give an example/name of a hard tip, or tonsil tip, suction catheter.
Yankauer or DuCanto
The space between the vocal cords; the narrowest portion of the adult airway
Glottis or glottic opening
The back-up breathing trigger or system
Hypoxic Drive
Drowning victims and patients with pulmonary edema have fluid in which specific structures?
Alveoli
Level of consciousness and what are considered excellent indicators or signs of adequate respiration?
Skin Condition
There are two airway adjuncts. You must give both to get the points.
OPA (oropharyngeal airway adjunct) and NPA (nasopharyngeal airway adjunct)
The nerves which stimulate the diaphragm to contract
Phrenic Nerves
The series of chemical processes during which cells create energy and expel waste
Metabolism
When this system becomes compromised, hypoperfusion occurs
Circulatory (page 431)
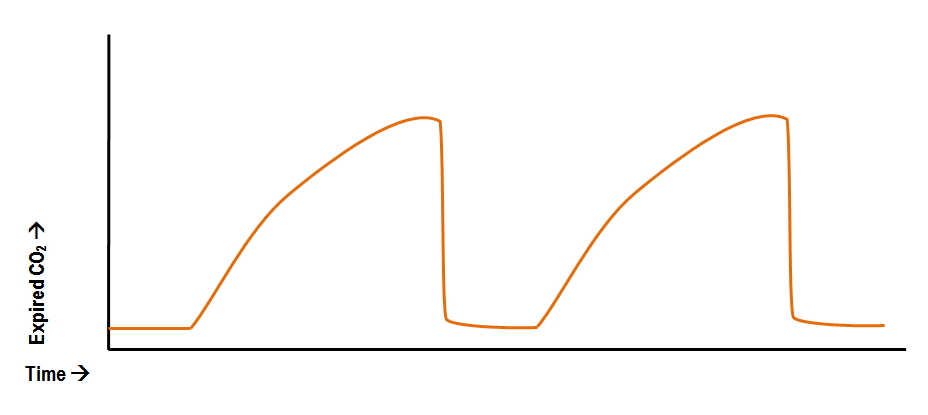 Is this a normal or abnormal ETCO2 waveform? Why? Must answer both for full points.
Is this a normal or abnormal ETCO2 waveform? Why? Must answer both for full points.
Abnormal
A protective, natural mechanism to keep food and other particles from entering the airway
Gag Reflex