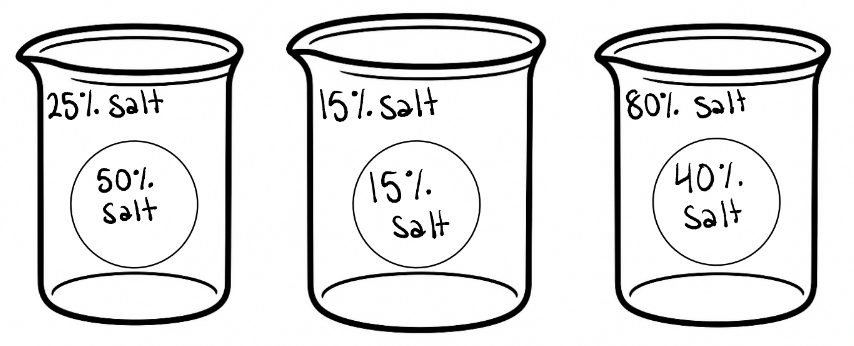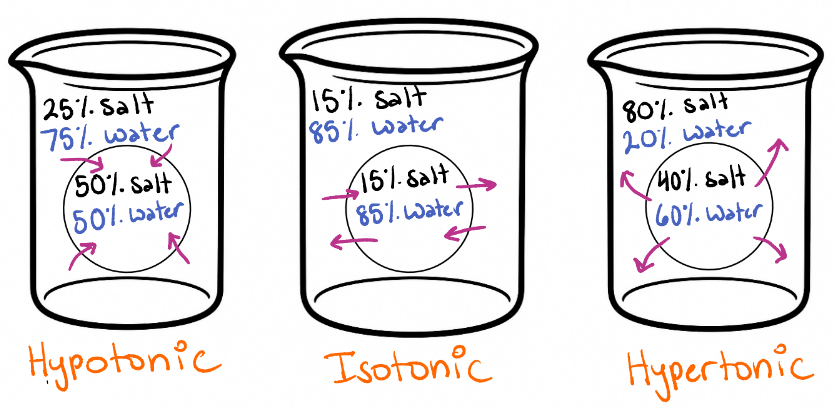This first theory states that all living things are composed of one or more of these.
What are cells?
The total area of all the outside surfaces of an object
Bacteria are a common example of this type of cell.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Specialized structures within the cell with unique functions
What are organelles?
The main structural component of the cell membrane, made of two layers.
What are phospholipids?
In the 1830s, this German scientist concluded that all plants are made of cells.
Who is Matthias Schleiden?
The amount of space in an object
What is volume?
This type of cell is generally much larger and more complex.
What is a eukaryotic cell?
The organelle that is responsible for making proteins
What are Ribosomes?
Difference between endocytosis and exocytosis.
What is...
Endocytosis: taking in larger molecules by engulfing them in the membrane
Exocytosis: removing large particles from the cell
The cell theory was only complete after this physician stated in 1855 that new cells are produced from existing cells.
Who is Rudolf Virchow?
A cube-shaped cell has sides that are 3.75cm long. Calculate the surface area
What is 84.375?
List the four common organelles that are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What are the Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, DNA, and Ribosomes?
This organelle contains enzymes to break down waste products within the cell
What are lysosomes?
Determine the term for the diffusion of water molecules across a membrane and whether it is active or passive transport.
What is osmosis & passive transport?
The development of this tool was essential for the formulation and acceptance of the entire cell theory.
What is the microscope?
A cube-shaped cell has sides that are 4 cm long. Calculate the surface area/volume ratio?
What is 1.5:1?
Between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, this one is more complex.
What are eukaryotic cells?
Structures that are found only in plant cells and not in animal cells.
What are the cell wall, chloroplast, and large vacuole?
Determine the concentration gradient and whether it requires energy for active and passive transport.
Passive Transport: doesn't require energy, high to low concentration gradient
Active Transport: requires energy, low to high concentration gradient
Name the three parts of the cell theory.
What are all living things are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all new cells arise from pre-existing cells?
The type of surface area/volume ratio (large or small) that is the most efficient for cells in terms of transporting materials.
What is a large surface area/volume ratio?
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of where they store their DNA.
What is... prokaryotic cells store in the cytoplasm, and eukaryotic cells store in the nucleus?
This is the collective term for the specialized internal structures, such as the mitochondria, chloroplasts, and the nucleus, that carry out specific functions within a eukaryotic cell.
What are membrane-bound organelles?
Draw each beaker, fill in water concentrations, draw arrows to show how water is moving, and determine if it is a hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic solution.