This subatomic particle has a positive charge...
PROTON
The memory trick “MAN” was used in class. What does each letter stand for in MAN?
M =
A =
N =
How do these values compare for “MAN”?
M =Mass number
A = Atomic number
N = neutrons
How do these values compare for “MAN”?
Mass number - Atomic number = # neutrons
Element: Nitrogen
_____ total electrons
Shell 1: _________
Shell 2: _________
Shell 3: _________
Element: Nitrogen
7 total electrons
Shell 1: ____2_____
Shell 2: ___5______
Shell 3: ____0____
Are they ions? isotopes? different elements
Element A has 6 protons and 7 neutrons
Element B has 7 protons and 7 neutrons
different elements
Atoms that spontaneously emit radiation through nuclear decay are called
Radioactive
This subatomic particle has a neutral charge and is a component of the nucleus
NEUTRON
If I need the neutron number and I have the mass number, I need to look at the number of....
protons
 What kind of model is this?
What kind of model is this?
Bohr Model
What happens to the electrons of a neutral sodium atom (Na) when it is changed into a sodium ion (Na 1+)?
1 electron is lost
How can you tell if an atom is radioactive or not? (What influences this?)
The larger the nucleus the more unstable the atom; therefore it is more radioactive.
The ______________________ is always equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons.
ATOMIC MASS
Determine the following for : Chlorine atom
Atomic number:
Mass number:
Proton:
Neutron:
Electron:
Atomic number: 17
Mass number: 35
Proton: 17
Neutron: 18
Electron: 17
The rule for filling the electron shells is:
___ electrons can fit in the first shell and _____ electrons can fit in the 2nd and 3rd shell.
2 and 8
How do they relate:
-Different elements?
-Isotopes of the same element?
-Ions of the same element?
_______________________________________
-J has 27 protons, 27 electrons, and 32 neutrons
-L has 27 protons, 25 electrons, and 32 neutrons
Ions of the same element
Which of the following isotopes would be most likely to be radioactive?
Carbon-12 or Thorium-232
Explain why.
Thorium-232
Elements with high atomic numbers, like uranium and thorium, are more likely to have unstable isotopes due to the large number of protons in their nucleus
1. In an atom, electrons are found ....
2. What is the charge of an electron?
1. outside the nucleus in orbits/ shells
2. negative
A =
P =
E =
How do these values compare for “APE” IF the atom is neutral?
Atomic Mass equals the number of protons and electrons
*** this only applies to a neutral atom!
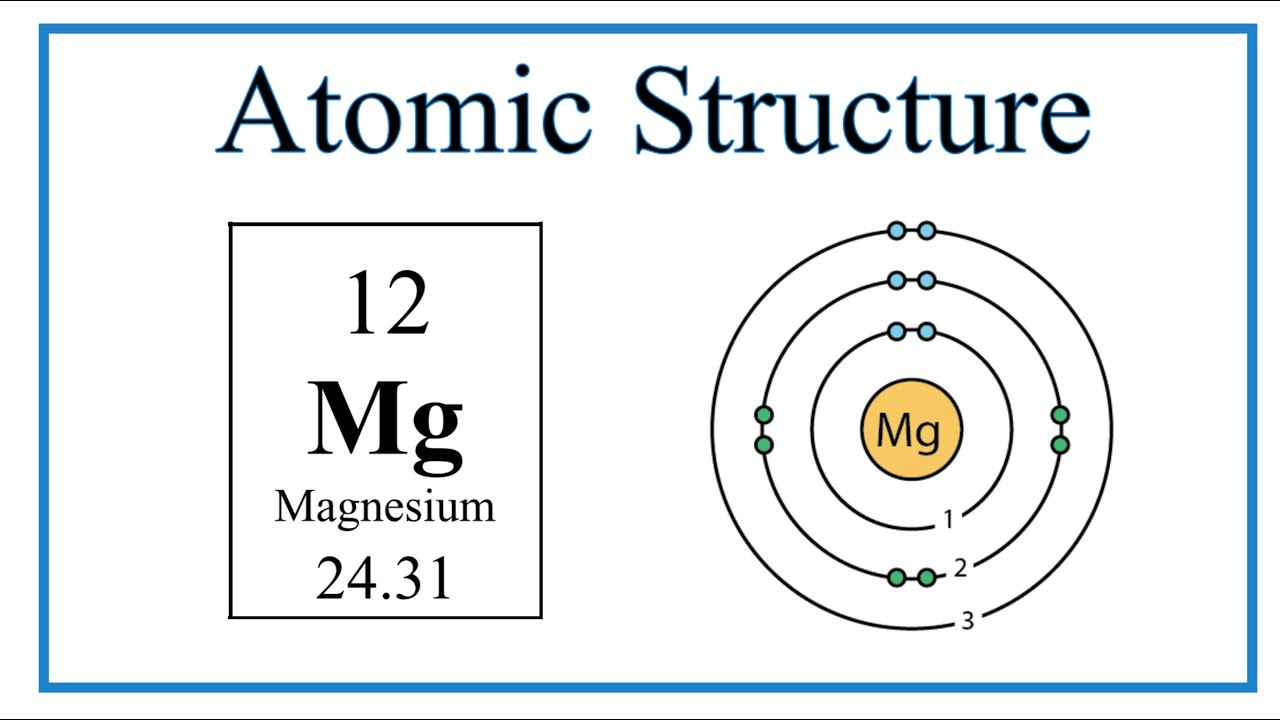
Provide the Following Info :
Magnesium Atom:
Atomic number
Mass number
Proton
Neutron
Electron
Drawing:
Magnesium Atom:
Atomic number 12
Mass number 24
Proton- 12
Neutron- 12
Electron- 12
How do they relate?
Different elements
Isotopes of the same element
Ions of the same element
X has has an atomic number of 92 and an atomic mass of 238
Y has has 92 protons and 143 neutrons
Isotopes of the same element
The most dangerous type of radioactivity is…
Explain why.
Gamma
gamma radiation because of its high penetrating power, allowing it to travel through most materials and damage tissue deep within the body
1. The atomic number is always equal to..
2. Explain why it's not always equal to the number of electrons!
1. The number of protons
2.The atomic # is only equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom. When electrons are lost or gained - it becomes an ion.
Look at the periodic table entry for Phosphorus above. How many neutrons does this atom have?
How did you determine this?
16
Mass number- atomic number = # neutrons
Draw a Bohr model of neutral atom: Carbon- 6.

Explain the difference between an isotope, an ion and a new element in terms of different numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Ion- Atoms of the same element who's electrons are different.
Different Element- # of protons are different
Isotope- atoms of the same element that have the same # of protons BUT different #of neutrons.
Describe how radioactive atoms return to a stable state.
Explain why!
Radioactive atoms return to a stable state through a process called radioactive decay, in which the nucleus of the atom loses energy by emitting radiation.
This process occurs because the nucleus is unstable due to an imbalance of protons and neutrons. The atom "decays" in an attempt to achieve a more stable configuration.