Where can speed brakes be mounted on an aircraft?
Top/bottom of the wings and top/bottom of the fuselage
What secondary flight control wont be visible when approaching the aircraft and why?
Balance panel, it is located inside the airfoil. Differential pressure builds up on one side of the panel and assists the flight control with movement
When compared to main rotor blade rotation in what direction is torque?
Torque acts in the opposite direction as main rotor rotation
Where is the throttle control normally located in a helicopter?
It is incorporated on the collective pitch control
What auxiliary flight control can self-deploy automatically from air pressures at high AOA?
Slats
What is a “Balance Surface”?
Portion of the surface extending out ahead of its hinge line, assists pilot in deflecting the control surface and to hold in deflected position.
What is the importance of a tail rotor?
To maintain directional control of the helicopter when in hover, compensates for torque produced by the main rotor.
Cyclic pitch controls a helicopter on what axes?
Changes direction of flight, movement along the longitudinal and lateral axis
What is the purpose of a leading edge slat?
When retracted forms LE; When extended creates a duct that forces high-energy air across the top surface of the wing to delay airflow separation reducing stall speeds.
What tab only aides in moving the control surface at high speeds?
Spring Tab. When aerodynamic loads are too high.
What type of rotor uses a feathering axis for blade pitch, an individual flapping hinge for each blade and a lead-lag hinge for each blade?
Fully Articulated Rotor
Explain the function of the collective pitch
Changes the pitch angle of all rotor blades collectively (vertical movement)
Explain how spoilers can be used as speed brakes and as air spoilers?
Spoilers deployed upward simultaneously on both wings act as speed brakes; as air spoilers when acting independently to assist ailerons in roll control.
What tab can operate the primary flight control, not just reduce the force required to operate it?
Servo Tab. Moves in the opposite direction, producing an aerodynamic force that moves the PFC surface
Define Gyroscopic Precession.
An action occurs 90 degrees in the same direction of rotation from where the force is applied
What does a free-wheeling unit in a helicopter do?
Disengages main rotor system when engine is INOP to allow autorotation, main rotor to rotate “freely” and allow a safer landing
Name the 2 types of leading edge flaps?
Kruger Flap and Droop Flap
Which flight control tab moves in the same direction of the primary control surface and why?
Anti-servo (anti-balance) tab; to increase the force needed by pilot to change flight control position.
Why does the Coriolis Effect, effect flapping hinge systems more than see saw systems?
The flapping motion of the blades cause change in blade velocity, accelerating and decelerating the blade.
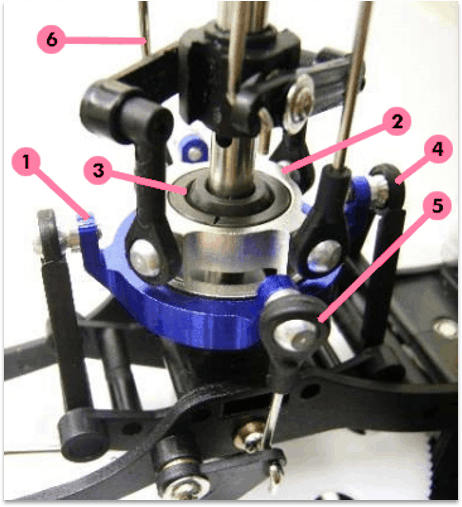
Explain the function and components of a swashplate.
Transfers the movement of cyclic and collective from stationary push-pull to rotating push-pull movements that are transferred to the rotor system. Components: (1) Non-rotating outer ring (2) turning inner ring (3) ball joint (4&5) roll & pitch control (6) links to rotor blades.