Explain a rate gyro (used in a Turn and Bank Indicator)
- Only free on 1 axis (plus spin); uses precession to give flight data, measuring rate of turn of A/C.
When are pressure pumps required over vacuum pumps?
At higher altitudes where there is not enough air pressure to provide a good vacuum.
How does an AMT correct deviation error?
By swinging the compass and adjusting compensating magnets.
Why are shock mounts used with instruments?
To absorb low-frequency, high- amplitude shocks, protecting the instruments.
What is the differences between a “turn and bank indicator” and a “turn coordinator”?
Turn coordinator has a “canted gyro” (gyro at upward angle) and will indicate rate of roll as well of as rate of turn
Explain how air pumps can be lubricated?
- Wet pumps are lubricated with engine oil
- Dry pumps are self-lubricated with internal carbon vanes
Briefly explain the procedure of “swinging” a compass and where this procedure takes place.
Performed at an airports “compass rose”.
With all electronics on and engines running, adjust aircraft on “compass rose” markings while adjusting compensating screws.
Explain the proper tooling and procedure used to remove/install cannon plugs?
Proper wrenches (electrical connection pliers/cannon plug pliers). Align the CORRECT cannon plugs properly; do not over tighten.
Explain the two properties of a spinning gyro.
- Rigidity in space: a spinning gyro maintains the same position even if its base is moved or twisted. (Attitude Indicator/Heading Indicator).
- Precession: an outside force will cause the gyro to tilt as if the force was applied 90 degree ahead in the direction of rotation. (Turn and back indicator and turn coordinator).
Explain the components of a gyro instrument air system?
Air pump, pressure regulator, air filter(s), vacuum/pressure gage, associated plumbing, oil separator (for wet pumps)
Explain the three compass errors and which one concerns AMTs the most.
Variation error: Magnetic NP is not true NP
Deviation error: magnetic influences with an aircraft (AMT Concern)
Dip errors: Acceleration errors, northerly turning error, oscillation (pilot concern)
Where can you find operating limits for instrument range markings? Who is responsible to ensure these markings are correct?
TCDS, POH, AMM. A&P mechanic’s responsibility
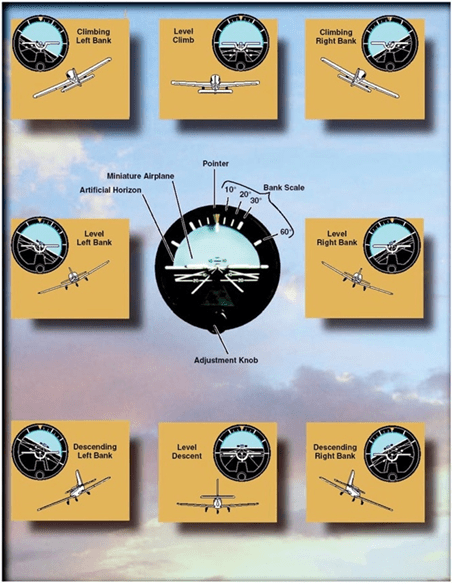
Explain what the Artificial Horizon instrument does and how you read it?
Gives pilot accurate reference to the aircrafts attitude for level flight and maneuvers.
Explain how a ring laser gyro works.
Instead of a spinning gyro wheel it uses laser beams and mirrors, two different laser beams are routed to a sensor, if the received pattern changes there was movement about the axis.
Name the components of a (Wet) magnetic compass and explain how it works?
Rotating magnet, compass card, oil, jewel post and pivot, compensating magnets, expansion diaphragm, lamp, lubber line.
Rotating magnet interacts with earths magnetic field to give directional reference.
How are instruments mounted/secured? How are computers mounted in electronic bays?
Bolted and clamped in place either front, rear, or clamp mounted. Usually slid onto a rack and have a holding/locking mechanism (do not over tighten)
What is an inclinometer and how does it work?
A ball inside a tube that is filled with kerosene. Apart of a Turn and Bank indicator and Turn Coordinator. Shows if a turn is coordinated. With centrifugal force and horizontal lift acting on the ball, if one is higher than the other the aircraft will skid or slip deflecting the ball. CF exceeds HL = Skid; HL exceeds CF = Slip
What creates power to spin a gyro?
- Vacuum (suction)=Venturi or air pumps
- Pressure=air pumps (pressure required up altitudes) electric motor driven
Explain how a Flux Gate compass works?
A remote mounted auxiliary compass. Alternates between 400 Hz and the earths lines of flux. Iron core with 3 pick up coil winding 120 degrees apart sensing the earths flux lines. Each heading will produce a different strength signal from each of the 3 coils.
Name 5 things that you must check before installing an instrument?
P/N, S/N, Parts tag/info, remove protective caps, inspect for defects/damage