Requirements for Life
This body system focuses on treating illnesses of the gastrointestinal region.
The breakdown of nutrients into into useable forms at the cellular level is done by this process
What is catabolism?
A tattoo artist's canvas
Integumentary
The physiological value around which a normal range fluctuates
What is set point?
Cells are the smallest, independently living organism on earth but is made up of even smaller particles
What are atoms (or organelles)
The smallest independently functioning biological unit of an organism
What is a cell?
The function of both breaking down and building up sources of energy from food makes up this biological function
What is metabolism?
This body system is generally active before an exam
What is nervous system?
The set point for the temperature of the human body
What is 98.6?
The human body can be organized or broken down into this number of systems
11
What is an organ?
A key component of the chemical reactions that keep the body alive. Without it survival is generally less than 10 minutes
What is oxygen?
Includes the pituitary gland and its 8 hormones
endocrine system
Control centers in the brain and other parts of the body monitor and react to deviations from homeostasis using this
negative feedback
almost all functions of human physiology are performed in cells or are initiated by this structure
Cells
The sum of all catabolic and anabolic activities in the body are part of this process
What is metabolism?
Unspecialized cells become specialized in structure and function to perform certain tasks in the body.
What is differentiation?
Body system includes the heart and blood vessels
cardiovascular system
One of the three components of the negative feedback loop, also referred to as a receptor.
anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types.
organ
The increase of sweat gland output is a result of stimulating this area to cool the body
What is the heat-loss center?
Carbohydrates, fats and proteins are broken down into substances that are used in metabolic process and converted to this substance
What is ATP?
It's the frame of the body, but you also might see one on Halloween
Skeletal system
 This part returns the chemical/hormone value to the normal range
This part returns the chemical/hormone value to the normal range
What is effector?
a group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body.
organ system
This type of feedback controls biological processes to prevent accumulation of hormones in the body
What is negative feedback loop?
Six categories of nutrients include vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, proteins and this substance
What is water?
This system might just make an appearance at a gun show
Muscular system
Blood vessels in the skin begin do this to allowing more blood from the body core to flow to the surface of the skin allowing the heat to radiate into the environment.
What is dilate?
The highest system of living organisms within a specific region on the earth
Ecosystem
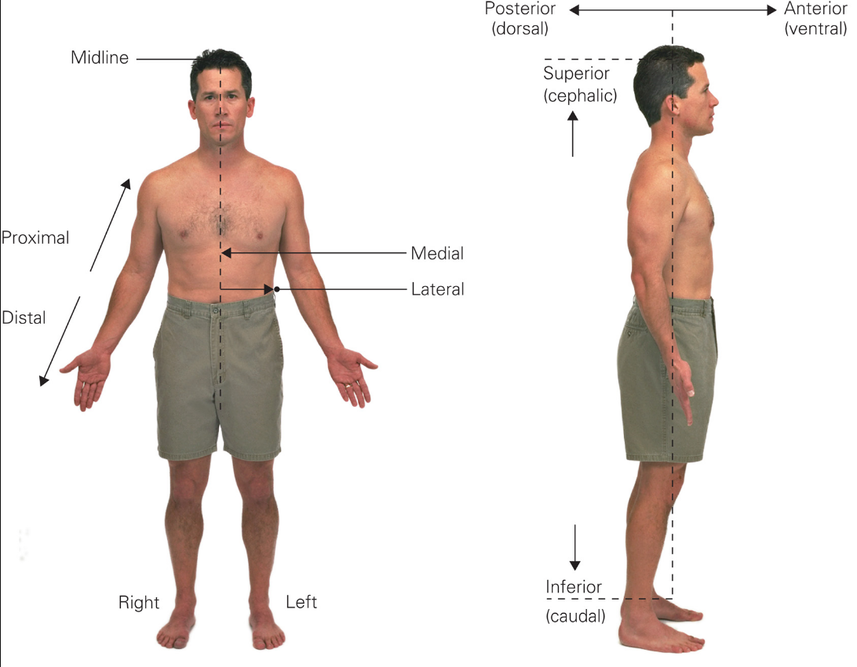
What is anatomical position?
The ability of an organism to adjust to changes in the internal and external environment make this a critical function of human life
What is responsiveness?
This system removes carbon dioxide from the body
Respiratory system
The muscle contractions in response to cold do this
What is shivering?
similar cells (though sometimes composed of a few related types) that work together to perform a specific function.
Tissue
The glucose/glucagon feedback loops begins with this stimulus
What is food? (Or increase in blood glucose)
Water is the largest component of cells, blood, and the fluid between cells, and makes up about this amount of an adult’s body mass.
what is 70%?
Eat something toxic and this system will keep you in the bathroom all night
Digestive system
This function results in a change in the body’s status, rather than a return to homeostasis.
What is positive feedback loop?
In multicellular organisms, including humans, all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems of the body work together to maintain these two things of the organism.
Life and health
The pleural serous membrane surrounds this vital organ in the thoracic cavity
What are the lungs?
This function of the cardiovascular system requires blood flow to be great enough to enable blood to reach all body tissues, and yet low enough to ensure that the delicate blood vessels can withstand the friction and force of the pulsating flow of pressurized blood.
What is blood pressure?
Not only does this system produce gametes, it's also a song from the Grease 2 soundtrack
Reproduction system
The stimulus resulting from eating a large meal
increased blood glucose
The smallest parts of an atom
protons, neutrons and electrons
What is sustaining human life?
Your ability to breathe, that is- take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide is dependent on this requirement
What is atmospheric pressure?
Controls water balance by eliminating waste from the body in a sterile form you can drink
This positive feedback loop results in this 
stop hemorrhaging
The highest system of living organisms
biosphere