Name two divisions of the nervous system and their components.
Central Nervous System (brain + spinal cord)
Peripheral Nervous System (everywhere else)
Gray matter vs white matter
gray =cell bodies
white = myelinated axons composed of mostly lipids
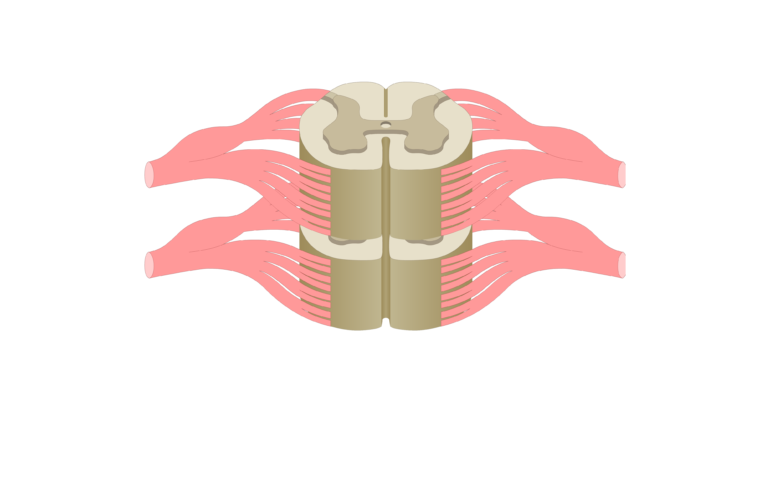
Posterior horn is associated with _____. Anterior horn is associated with _____.
sensory, motor
 What is between the tympanic membrane and oval window?
What is between the tympanic membrane and oval window?
ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
purple (name + functions)
pectoralis major: flexes, adducts, medially rotates arm
Contrast parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems.
Parasympathetic = rest & digest
Sympathetic = fight or flight
Take me, layer by layer, from the skin to the brain organ.
Skin -> bone -> dura mater -> arachnoid layer -> pia mater -> brain
 name for divot in the front, back, hole in the middle, & center space where crossing of nerves happens.
name for divot in the front, back, hole in the middle, & center space where crossing of nerves happens.
anterior median fissure, posterior median sulcus, central canal, gray commissure

semicircular canals + cochlea
Green
trapezius: extends the neck
Name the neuroglia cells of the nervous system & give their functions.
Schwann cells (PNS) - insulate
Satellite cells (PNS) - filter what go in and out of neurons to the interstitial fluid
Astrocytes (CNS) - maintain blood-brain barrier
Microglia (CNS) - phagocytic functions
Oligodendrocytes (CNS) - insulate
Ependymal Cells (CNS) - secrete CSF
red
thalamus: relays sensory information to the appropriate processing centers
# of pairs of spinal nerves: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
8, 12, 5, 5, 1

A, B & C
lens, sclera, optic nerve
Pink + yellow
Pink: sternocleidomastoid (rotates the head, flexes the neck)
Yellow: trapezius (extends the neck)
Where is Na concentration greater? K concentration greater?
Na greater outside. K greater inside. (salty banana)

green
corpus callosum: connects left/right hemispheres
Name the 4 nerve plexuses & give an example of each.
cervical: phrenic
brachial: ulnar
lumbar: femoral
sacral: sciatic

I, J, K
aqueous humor, cornea, pupil
purple
latissimus dorsi: extends, adducts, medially rotates the arm
Describe each step in an action potential.
depolarization (Na channels open, Na ions flow in)
repolarization (Na channels close, K channels open, K ions flow out)
hyperpolarization/refractory period (all channels close, Na/K pump uses energy to send 3 Na out, 2 K in)
Olfactory bulb, optic nerve, oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, trigeminal nerve, abducens nerve, facial nerve, vestibulocochlear nerve, glossophyrangeal nerve, vagus nerve, accessory nerve, hypoglossal nerve
Explain the reflex arc. Why is it essential for signals to go to your brain as well?
hand touches something hot -> sensory information travels through afferent nerves to the spinal cord + brain -> signals through efferent nerves to contract muscles -> hand removed from hot item -> brain processes that this thing is hot, lesson learned!
What are the 3 tunics of the eye & their components?
Fibrous: sclera + cornea
Vascular: Iris, ciliary body, choroid
Neural: retina (rods + cones)
name abdominal muscles superficial to deep + functions
external oblique: flexes + rotates vertebral column
internal oblique: rotates vertebral column
transversus abdominis: compresses the abdomen
rectus abdominis: flexes vertebral column