You start shivering when you go outside in the wintertime. What is the key function of the body that allows for this to happen?
Responsiveness/thermoregulation
Where is your humerus?
upper arm bone
What muscle is responsible for turning your head?
Sternocleidomastoid
This tissue is the outermost layer of the skin. What is this called and what kind of cells make up this tissue?
Epidermis, stratified squamous epithelium
upright, feet shoulder-width apart, palms facing forward
Daily Double: when looking at the patient, which side is right and which side is left?
What is the purpose of cell division?
growth, repair, reproduction
Identify the type of break is present in this xray
closed transverse
Activate your deltoid and describe its function
Arm circles
shoulder muscle for arm abduction
Identify the muscle type
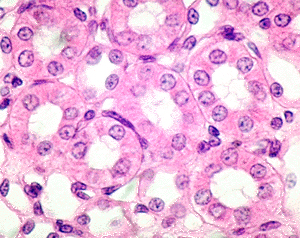
simple cuboidal epithelium
anatomically how do we communicate above, below, front, and back?
above = superior
below = inferior
front = anterior
back = posterior
How do tumors develop?
Mutations in tumor suppressor genes and the genes that regulate the speed of division
Describe the process of bone repair after an injury
Hematoma formation --> callus formation --> bone production --> remodeling
 Identify what type of tissue present above
Identify what type of tissue present above
smooth muscle, single nucleus, spindle shaped
responsible for involuntary contraction to pump blood, nutrients, waster, etc
Describe cardiac muscle (histology and function)
Hist: branched, multi-nucleated, cylindrical but not parallel
Func: constant involuntary contraction to pump blood, oxygen, nutrients, and waste from the body
The sagittal body divides the body in what way?
Separates left and right sides of the body
Daily double: what is it called when the plane is not down the body's midline? (skewed)
What happens when the body goes into oxygen debt?
heavy breathing, anaerobic respiration, lactic acid production from converting pyruvate into ATP
Name the bones that form the cranial cavity
frontal, temporal (2), parietal (2), occipital, sphenoid bone, and ethmoid bone
 Name 2, 3, 10, and 12
Name 2, 3, 10, and 12
2. Trapezius
3. Deltiod
10. Abdominal external oblique
12. Rectus femoris
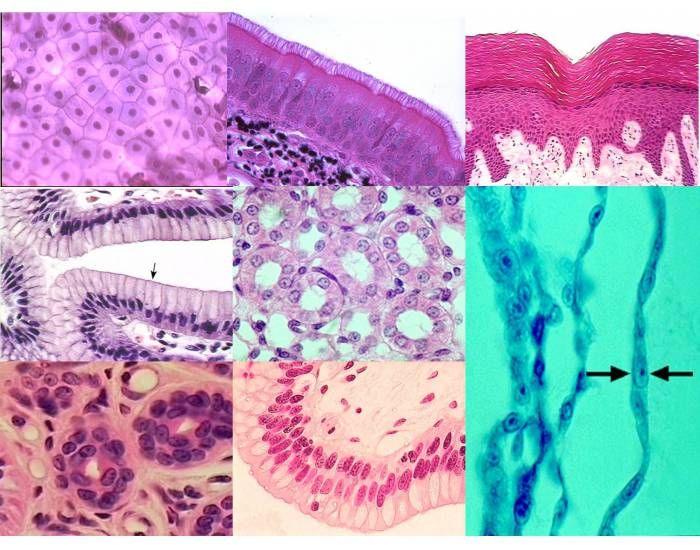 ID at least 3 tissue types (L-->R 1-->8)
ID at least 3 tissue types (L-->R 1-->8)
INCLUDE layering pattern and cell shape
1. stratified squamous epithelium
2. Psuedostratified columnar epithelium
3. Transitional epithelium
4. Simple columnar epithelium
5. Simple cuboidal epithelium
6. (big) Simple squamous epithelium
7. Stratified cuboidal epithelium
8. Stratified columnar epithelium
What body cavity houses the cranial and spinal cavity?
Dorsal cavity, cranial and spinal cavities
Herndon burns their hand on the stove. Heck! Why did that hurt so much?
The layers of the skin were damaged. Epidermis (protective layer), dermis (nerves and blood vessels) and potentially so severe that the hypodermis (connective tissue)
This bone has a characteristic butterfly shape and makes up the skull floor. Who is this bone?
Sphenoid bone
Rotate your foot the ankle (ankle circles). What major muscles are involved in this movement?
tibialis anterior, soleus and gastrocnemius
Describe the three types of connective tissues found in the body and their functions.
Connective tissue proper: loose and dense CT, supports and protects the body.
Supportive CT: bone and cartilage for structure and support
Fluid CT: blood and lymph, tranports oxygen, nutrients, and waste
Identify the following tissue and describe its function

adipose tissue (look for large empty spaces)
Long term energy storage (fat)