Name the classifications of joints
Synarthrosis, Ampiarthrosis, Diarthrosis
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, Synovial
The two major cells of the epidermis
Keratinocytes and Melanocytes
#11
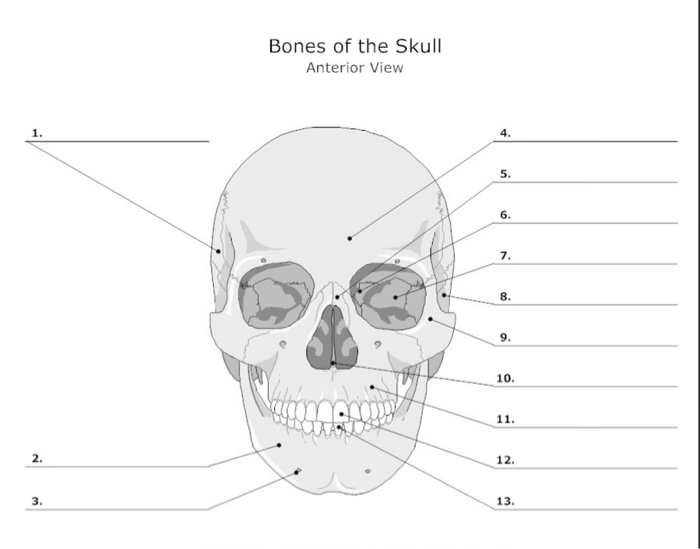
Maxilla
What are the 3 main types of muscles
Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth
Central Nervous System and the Peripheral Nervous System
The structure that secretes synovial fluid
Synovial Membrane
Highly vascularized connective tissue that allows nutrients to diffuse
Dermis
#3

Tibia
How do muscles create movement?
Muscles must cross at least one joint to create movement
The function of the central nervous system
Receives info from the outside world from the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system processes it
The first sternocostal joint is an example of what classification of joint?
FIbrous Joint
Name the hair follicle location
Located in the dermis and surrounding the hair root, is formed from epidermal layers that project into the dermis
#4

Fibula
An origin that stays still and insertion that moves
The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls muscle movement and relays information from ears, eyes, and skin to the central nervous system
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Name the 7 common features of synovial joints
Synovial Cavity, Articular Cavity, Articular Capsule, Fibrous Capsule, Synovial Membrane, Synovial Fluid
The layer of the epidermis that contains melanocytes and starts to form keratinocytes
Stratum Basale
Red part

Cerebellum
The ability to recoil when stretch force is removed and muscle returns to its resting length
Elasticity
The function of GABA
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid that functions as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter for the central nervous system (CNS). It functions to reduce neuronal excitability by inhibiting nerve transmission.
A fibrous joint between two flat bones of the skull
Suture
Explain the process of Keratinization
As new keratinocytes are formed, they push the older cells toward the surface and undergo keratinization which produces tough, water-repellant cells in the superficial layer.
#4

Thoracic Cavity
As a muscle pulls on a bone, the bone matter is laid down at the stress point and the shape of the bone changes.
Your bones will adapt based on the stress or demands placed on them. When you work your muscles, they put stress on your bones. In response, your bone tissue remodels and becomes stronger
Similar to amphetamines and cocaine, bath salts are stimulants, meaning that they improve mood and energy levels and make users feel more alert by increasing levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain. This increase in dopamine also means that bath salts can be addictive