Which ventricle is larger?
Bonus: Why is it largerLeft side is larger because it pumps blood to the whole body
What is the purpose of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the oxygen and carbon dioxide carrying protein in red blood cells
Which plane is it being cut through?
Coronal
What is the primary muscle responsible for inspiration
The diaphragm
What role does surfactant play in the lungs
Bonus: What is something else it helps with in the body (related to another system perhaps)
It reduces surface tension in the alveoli, this prevents them from collapsing through exhalation
It also helps fight off pathogens!
In the following image, identify the left and right lung and what separates the lobes (Provide at least one of the 2 correct answers)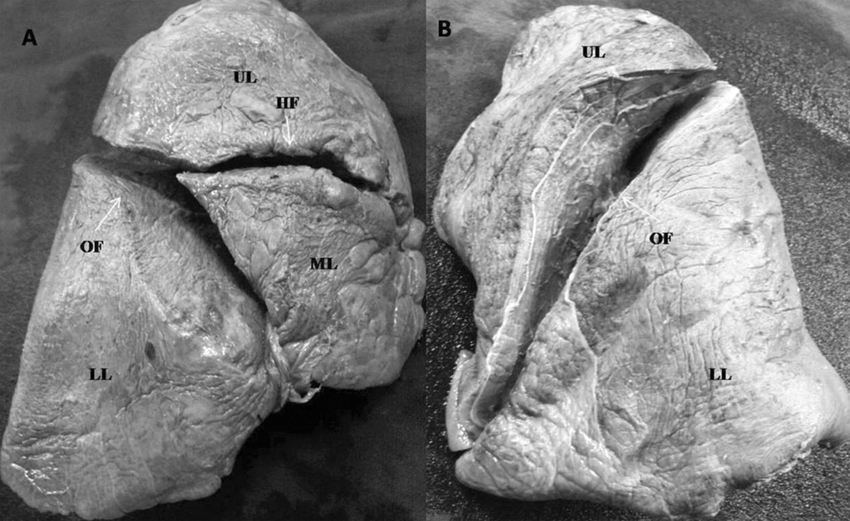
The lung on the left is the RIGHT LUNG (3 lobes)
The lung on the right is the LEFT LUNG (2 lobes)
Lobes are separated by horizontal and oblique fissures.
Name the two valves in the heart
Bonus: What are their functions
Atrioventricular and Semilunar valves
Function: Prevent blood from flowing back into the atria and from flowing back into the ventricles, respectively
Why would an athlete have a lower resting heart rate
Athletes develop a stronger myocardium, especially the left ventricle. Since the heart is stronger it can pump more blood with each beat. This leads to a lower heart rate since it doesn't need to pump as often to get the blood out
What are the parts of an ECG wave, and what does it represent?
P-wave = Atrial depolarization
QRS Complex = Ventricular depolarization
T-wave = Ventricular repolarization
When you take a breath, what is the order of the structures that the air passes through?
Oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and the alveoli
Explain the steps of inspiration
The diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract. This expands the chest cavity and thoracic cavity volume, which also results in the lungs expanding. As the volume within the lungs increase, the pressure falls below atmospheric pressure. Air moves from high to low pressure and it flows down this gradient.
Explain: A shift to the right on this curve reflects decreased oxygen affinity to hemoglobin
This is the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
List the order in which blood exits and enters the heart through blood vessels
Body → vena cavae → RA → tricuspid → RV → pulmonary valve → pulmonary artery → Lungs → pulmonary veins → LA → mitral → LV → aortic valve → Aorta → Body
What causes the 'lub dub' sound (Provide the specific name for full points)
It comes from the closure of the atrioventricular valve, specifically the tricuspid and mitral valves. The dub is the closure of the aortic valve and the pulmonary valves, which are the semilunar valves.
Which hormone increases blood pressure and what is the mechanism?
The hormone is aldosterone and the mechanism is that it acts on the distal tubules and collecting ducts which cause an increase in sodium reabsorption and water retention, and therefore potassium excretion. This results in an increase in blood volume which increases blood pressure.
What structure holds the lungs in place?
Hint: Prevents them from collapsing
Visceral and Parietal pleura
What term refers to the volume of air within the lungs after maximal inspiration
Total Lung Capacity
How is cardiac output (CO) affected by a patient with asthma?
Hint: Patients with this condition have narrowed bronchi/bronchioles AND reduced venous return
We can assume that there is reduced airflow when inhaling and exhaling. This means less air reaches the alveoli, which leads to impaired gas exchange. O2 levels drop and CO2 levels rise. The heart will try to compensate for this by increasing heart rate (not significant). The reduced venous return means stroke volume decreases severely. Therefore, CO drops.
What are the top 3 muscles/tissues found within the arteries
Elastic tissue, smooth muscle, and fibrous tissue
What determines whether fluid moves into or out of a capillary bed
Starling forces. It all depends on the net pressure and is the difference between hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure. If the number is > 0, there is net filtration which the movement of fluid out of the capillary. If it is < 0 there is net absorption, which is movement into the capillary.
Where is the prosthetic located?
Hint: Think about the most common surgical replacements that occur within the heart
Mitral valve
What type of epithelial tissue lines the trachea?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells
Explain how gas exchange occurs at the alveoli, what happens to oxygen and carbon dioxide?
Gas exchange at the alveoli occurs by simple diffusion. The air in the alveoli has a higher partial pressure of oxygen, so oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood. The deoxygenated blood that is returning from the body to the lungs is rich in carbon dioxide so it diffuses from the blood into the alveoli
How does anemia affect both the cardiovascular and respiratory function?
Hint: Anemia is a condition where a patient has less red blood cells (RBC) or less hemoglobin than baseline levels.
Their tissues will receive less oxygen and the respiratory system will respond by increasing rate of breathing while the cardiovascular system will compensate by increasing cardiac output to deliver more blood to tissues.
What are myocardial cells separated by and what two components make them up
They are separated by intercalated discs. These are made up of desmosomes and gap junctions
Why is the refractory period in the cardiac muscle longer than in skeletal muscle
The refractory period in cardiac muscle is longer than in skeletal muscle to prevent sustained contractions. This ensures the heart has enough time to fill with blood between beats.
Why does left-sided heart failure cause pulmonary edema?
Hint: Think about where the blood will go and what the build up in pressure might result in
The left ventricle is responsible for pumping blood into the aorta, while the right side pumps blood into the lungs. When the left ventricle stops working normally, it does not pump enough blood into the aorta which causes a backup into the left atrium. The back up of blood causes a rise in hydrostatic pressure, which results in fluid buildup. This leads to a pulmonary edema.
What are the two types of alveolar cells, and which one is the most prevalent in the body?
Type I and Type II Alveolar cells
Type I are the most prevalent (make up 95%)
How does our body maintain normal arterial pH during exercise despite an increase in lactic acid?
During exercise, lactic acid is produce when oxygen deliver can't keep up with demand (anaerobic respiration). Our respiratory system responds by increasing our breathing rate. When the chemoreceptors in our body sense H+ ions the bicarbonate buffer system shifts to the left and carbon dioxide is exhaled. Additionally, cardiac output is increased to deliver oxygen which helps clear the ions faster
Identify the condition in the following x-ray
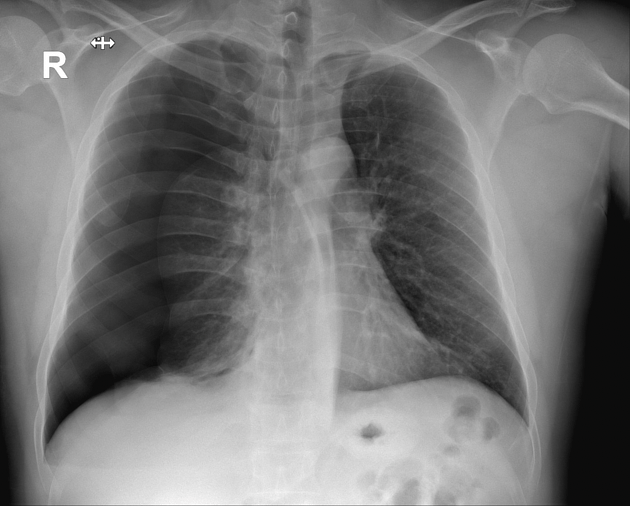
Hint: To identify this condition, physicians will look for a shape cured white line as well as tissue that is pulled towards the center
Pneumothorax