this kind of macromolecule stores energy for later
what are lipids
this kind of plane divides the body into left and right halves
what is sagittal/midsagittal
these are the 5 senses
what are sight, smell, hearing, taste, and touch
a single layered epithelial cell
what is simple
true or false; connective tissue is the most abundant kind of tissue in your body
True
this kind of macromolecule holds and processes your DNA
what are nucleic acids
this is the opposite of deep
what is superficial
true or false; humans SHOULD have 206 bones in the body
this kind of epithelial cell is stretchy
this kind of cartilage is smooth like glass at the end of the joints
what is hyaline cartilage
this macromolecule burns energy fast
what are carbohydrates

wut dis
what is the anatomical position
true or false, there are more stars in the sky then nerves in our body
wut dis

what is stratified squamous
this produces fibers
what is fibroblasts
this macromolecule shares the same name as a food group
what are proteins
this anatomical position is related to a dolphins top fin
what is dorsal
bones provide this
what is structure
wut dis
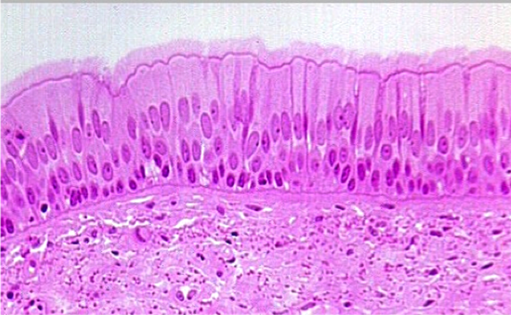
What is Cilia
The two main types of fibers are this
what is elastic and collagenous
these are the 4 types of macromolecules
what are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
the ear is this to the nose
what is posterior and or lateral
this kind of major organ system is home to the largest organ in the body
what is the integumentary system
this kind of epithelial cell helps diffusion and filtration and is found in the lungs
what is simple squamous
this kind of tissue provides protection, insulation, and stores energy
what is Adipose tissue