These are the attachments and actions of the subclavius (answer in 2 parts
What are the 1st rib and its costal cartilage, inferior surface of the clavicle?
What are depress the clavicle and protecting neurovascular structures?
The ______ is the only scapular protractor
What is the Serratus anterior?
The _______ _______ runs inferiorly along the surface of the anterior scalene muscle?
What is the phrenic nerve
There are 4 supraclavicular peripheral branches from the brachial plexus. The two from the roots are the _______ and the __________ (and spinal levels)
What are the dorsal scapular nerve (C5), and the long thoracic nerve (C5,6,7)?
A midshaft humeral fracture might damage this nerve
What is the radial nerve?
At 7 weeks, the upper limb buds have a 90 degree _______ rotation
What is external
These are the contents of the cubital fossa from medial to lateral
What are the median nerve, the brachial artery, biceps tendon?
This is the ________ muscle, it is innervated by the _____
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13041/Supinator_muscle.png)
What is the Supinator, PIN
The highlighted muscle is the ________, it is innervated by the _____________ branch of the median nerve and it attaches proximally at the _______, _________, and __________

what is the abductor pollicis brevis, recurrent branch of the median nerve, transverse carpal ligament, trapezium, scaphoid
The structure highlight in green is the ______ portion of the __________ ligament
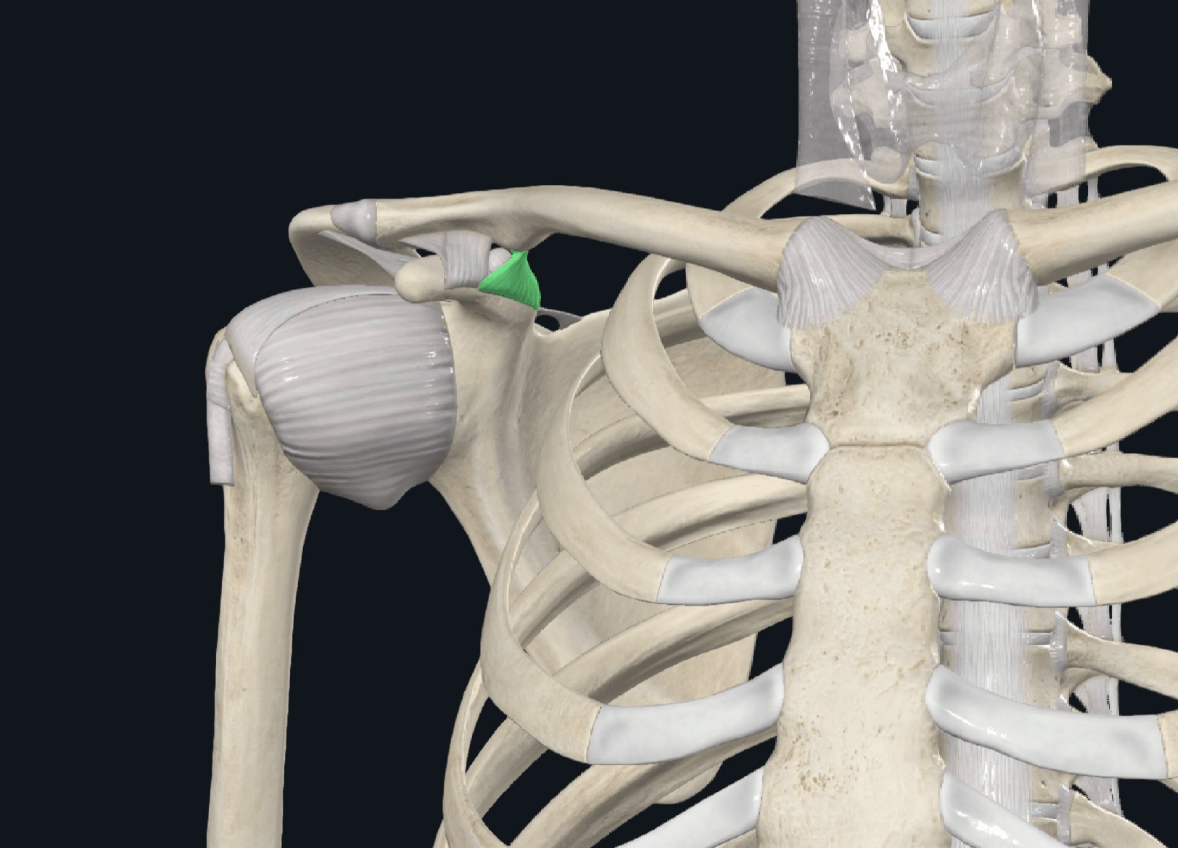
What is the conoid portion of the coracoclavicular ligament
These muscles are the glenohumeral internal rotators
What are the subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres major, pectoralis major, anterior deltoid?
Triceps brachii is innervated by the ________ nerve, and is supplied by _____, ______, and _____
This structure drains the lateral aspect of the arm, forearm, and hand; it runs in the deltopectoral groove
What is the cephalic vein
These are the primary actions and innervation of the subscapularis
What are GH internal rotation, GH adduction
What are the upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5,C6)?
These muscles make up the floor of the posterior triangle (from posterior to anterior)
What are: the splenius capitis, levator scapulae, posterior scalene, middle scalene, anterior scalene?
This is the anatomical structure where you will find the roots of the brachial plexus
What is the scalene triangle
The image in green is ____________. The _________ runs below it, while the ___________ runs above it.

What is the superior transverse ligament, what is the suprascapular nerve, what is the suprascapular artery?
the ______ (muscle in green below) has a proxmial attachment of _________ and a distal attachment of ___________

what is the coracobrachialis, apex of the corocoid process, midshaft of humerus on the medial side
The deep layer of anterior compartment of the forearm consists of these muscles
What are the flexor digitorum profundus, flexor policis longus, and pronator quadratus
The 2nd extensor compartment of the wrist contains the _______ and the _______, while the 4th contains the _________ and the __________
What are the extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis?
What are the extensor digitorum and extensor indicis?
These are the contents of the carpal tunnel
What are the median nerve, flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus, and 2 synovial sheaths
The middle glenohumeral ligament limits __________ translation of the humeral head
What is anterior translation?
This is a _____ hand, Letter F is referring to the ________

What is Right, what is the pisiform
The pec minor is innervated by the __________, and these spinal roots
The structure in green is the ________, it is pierced by the _______, __________, and ______________
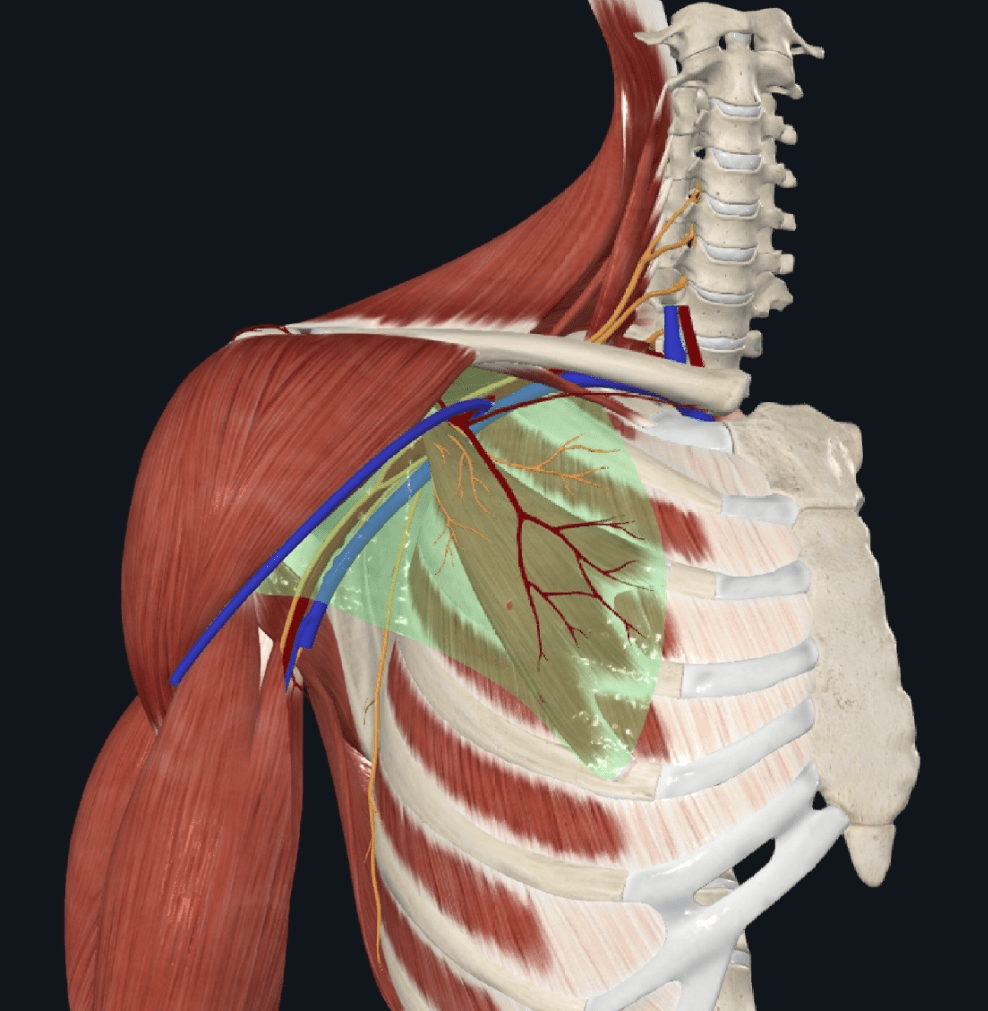
What are the clavipectoral fascia, the cephalic vein, lateral pectoral nerve, and thoracoacromial vessels
These are the contents of the axillary sheath
What are the lateral cord, medial cord, posterior cord of the brachial plexus, axillary vein, and axillary artery?
This muscle attaches to the transverse processes of C2-7 and the 1st rib
What is the middle scalenes
This nerve provides sensory innervation to the dorsal lateral aspect of the hand
What is the radial nerve?
These are the proximal and distal attachments for the infraspinatus (be specific)
What is the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus
The _______ and __________ nerves pass through the brachium, but do not innervate anything there
what are the median and ulnar nerves
This structure is the ____________, you would expect to find the ________ artery and the __________ nerve
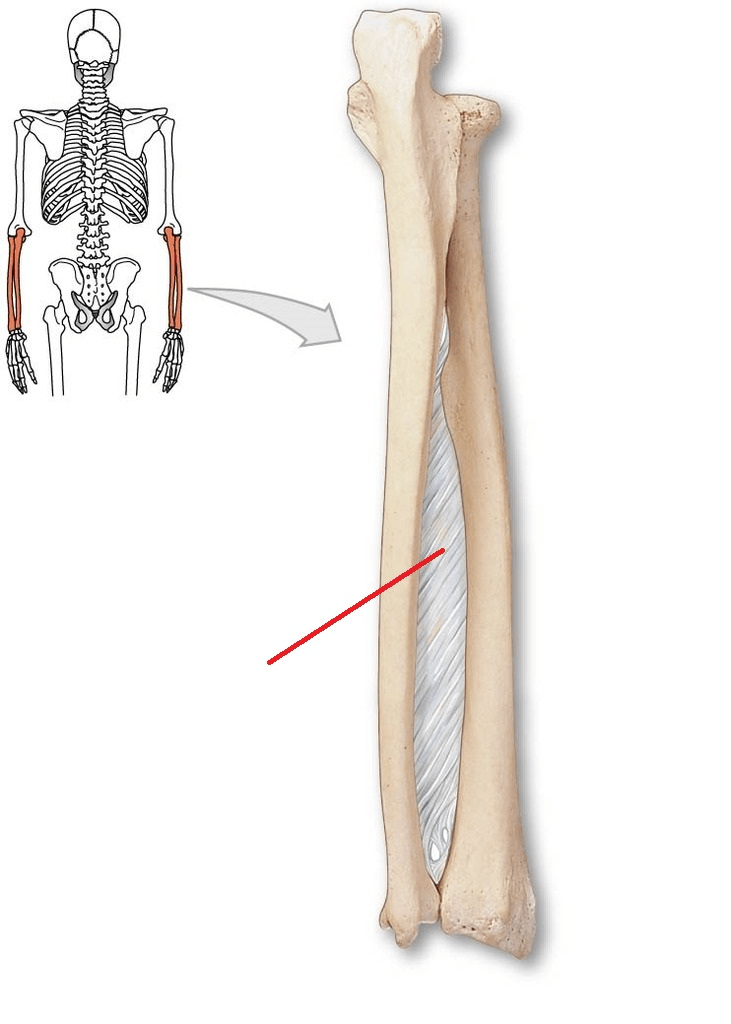
What is the (posterior) interosseous membrane, posterior interosseous artery, posterior interosseous nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) will pierce the _______, and run next to this artery
What is the supinator, what is the posterior interosseous artery
these are the components of the fiborous digital sheaths (3)
What are annular ligaments, cruciate ligaments, and volar plates?
The anterior fibers of the medial collateral ligament of the elbow limit ______ and _________ of the elbow.
What is valgus and extension?
You find Noah unconscious on the ground with a bruise on his elbow. He likely just hit this nerve
What is the ulnar nerve
The serratus anterior is innervated by the ________ nerve, which emerges from the ________ of spinal nerve ____, _____, and _________
what is the Long thoracic nerve, roots, C5, C6, C7
these are the landmarks that differentiate the subclavian, axillary (landmark that helps define its 3 parts), and brachial arteries (in order)
What are the 1st rib, pec minor, and teres major?
These are the attachments of the latissimis dorsi
What are the spinous processes of the inferior 6 thoracic vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia, most inferior 3-4 ribs, iliac crest, and bicepital groove (or floor of the intertubercular groove)?
These are the boundaries of the posterior triangle from: anterior, posterior, Base, Apex
What are the SCM, Upper traps, Mid 1/3 of the clavicle, and mastoid process?
A person with weakness of the deltoid and teres minor might have a lesion in this nerve
What is the axillary nerve?
These are the proximal attachment and innervation for the long head of the triceps
What are the infraglenoid tubercle and the radial nerve
This is a _________ humerus. The area shaded in pink is the _______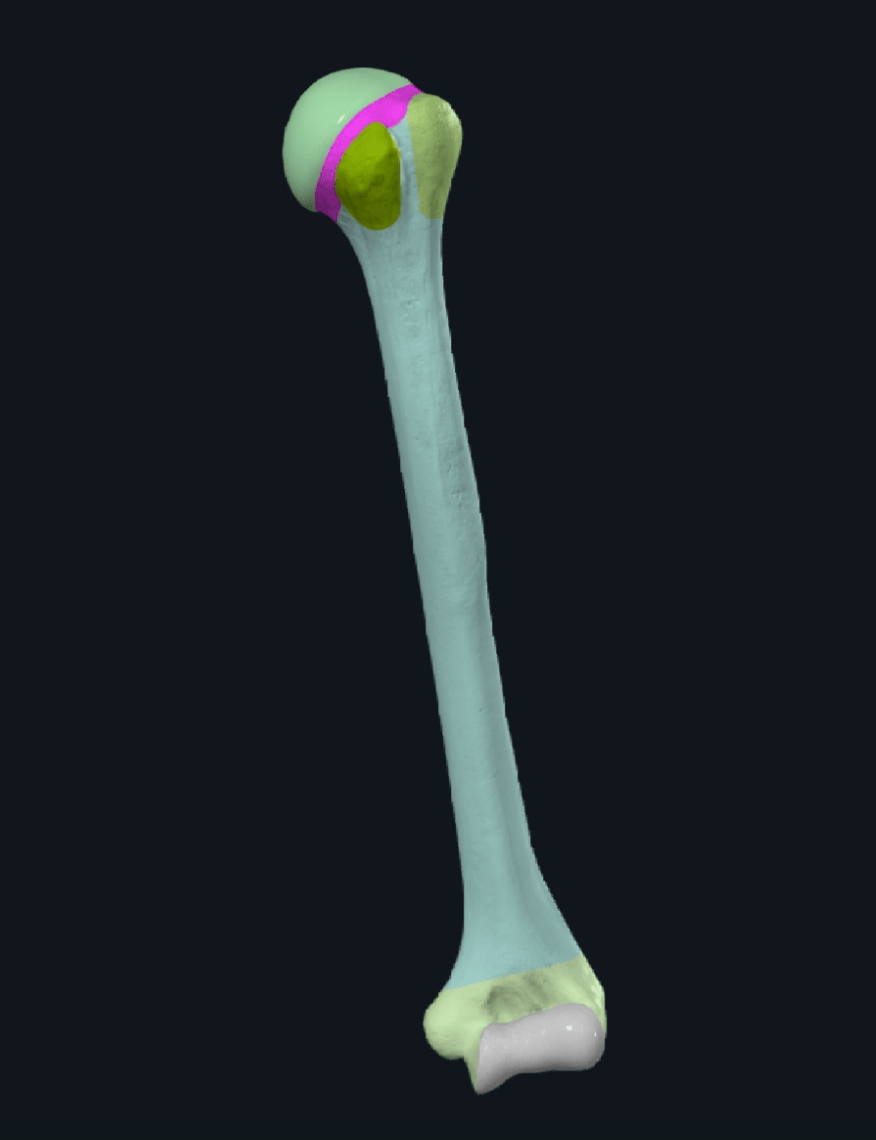 _ ________
_ ________
What is Left humerus, anatomical neck
the Flexor Pollicis longus, Lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus, and Pronator quadratus are all innervated by the _______ which is a branch off of the ________
This muscle is the _________, it's innervated by the ________
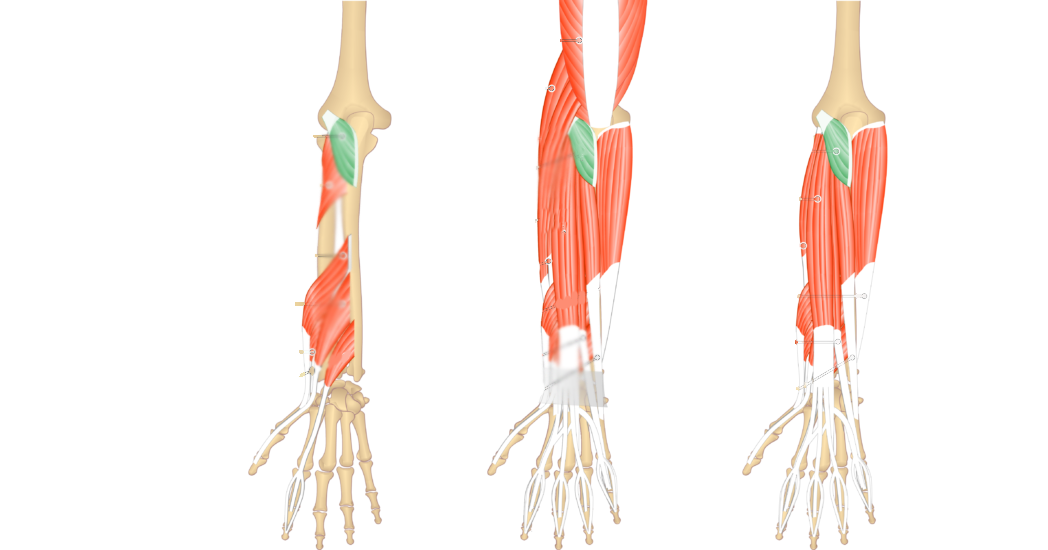
What is the anconeus, radial nerve
These make up the "central column" of the hand
What are the 3rd metacarpal, capitate, lunate, and radius
At the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, the radial collateral ligament limits all movements to varying degrees, except for _______ and _________
what is extension and radial abuduction
A patient presents to treatment with reduced pectoralis major and minor strength, reduced sensation in arm and forearm. This cord is the most affected
what is the medial cord
The medial two lumbricals are innervated by the ______ ________ ________, which stems from spinal segments ____, ______
Deep branch of the ulnar nerve, C8,T1
These are the attachments of the pectoralis major and its innervation (answer in 2 parts)
what are the anterior surface of the clavicle, anterior surface of the sternum, first 6 costal cartilages, aponeurosis of the external oblique, and crest of the greater tubercle?
What are the medial and lateral pectoral nerves
These are the boundaries of the axilla (anterior wall, posterior wall, medial wall, lateral wall)
What are:
(anterior) pectoralis major, minor, subclavius
(posterior) teres major, latissimus dorsi, subscapularis/anterior surface of the scapula
(medial) serratus anterior, intercostal muscles, thoracic wall
(lateral) intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
The structure highlighted in pink is the _________ ________ ________, it lies on top of the _________ _________

These nerves might be impacted in someone with a complete T1 spinal cord injury
what are the ulnar nerve, median nerve, radial nerve, medial pectoral nerve, medial brachial cutaneous nerve and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
These structures make up the boundaries of the rotator cuff interval (superior, floor, inferior, medial, lateral)
what is (superior)supraspinatus, (floor) capsule + long head biceps, (inferior) subscapularis m, (Medial) coracoid process, and (lateral) long head biceps
The long head of the biceps brachii attaches proximally to the ______ _______, and its actions are to _______, ________, and __________
what are the supraglenoid tubercle, flex the elbow, flex the GH joint, and supinate the forearm
This nerve gives sensory from the area in green, and innervates these muscles proximally

What are the musculocutaneous nerve, brachialis, coracobrachialis, and biceps brachii
These are the borders and contents of the anatomic snuff box (Medial -> lateral -> floor -> contents)
What are the extensor pollicis longus tendon,
abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons
scaphoid bone and extensor carpi radialis longus tendon
radial artery and branch of the superficial branch of the radial nerve
The deep palmar arch is supplied by the ______ artery and has a branch going to the thumb called the ______ ________ artery
What are the radial artery and princeps pollicis artery?
The anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament is taut at 90 degrees of __________, full ________, and ____________ translation of the humeral head
what is 90 degrees of abduction, full external rotation, anterior translation of the humeral head
A lesion to the suprascapular nerve would cause these impairments
what is weakness in the supraspinatus and infraspinatus, scaption and external rotation
There are 3 branches off of the posterior cord. The middle of these is named the _____________ nerve and is innervated by these spinal levels
What is the thoracodorsal nerve, 6,7,8