This bone is inferior to your maxilla.
What is the mandible?
It's how you would describe the location of a body part that is above another, or it's a high level in hierarchy.
What is superior?
The 4 main types of tissue in the body are epithelial, connective, nervous, and this burly tissue.
What is muscle?
The cells that make up this luscious part of your body are dead and contain a protein called keratin.
What is hair?
What is sarcoma?
These bones are distal to the carpals or tarsals, but it's the same answer for both.
What are phalanges?
It can mean before (in time), or the front part of your body.
What is anterior?
Even though this circulatory body fluid is, well, a fluid, it's actually a type of tissue!
What is blood?
This layer of skin is sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous layers.
What is the dermis?
This is the cytoplasm of muscle cells where calcium can be stored.
What is sarcoplasm?
This bone is proximal to the arm (Hint: it's the one attached to the thumb).
What is the radius?
If you were to describe the lungs, or a treaty between two parties, it would be this.
What is bilateral?
Part of the name of this type of epithelial tissue has the Greek root for 'false', which makes sense as the nuclei trick us into thinking this tissue has layers.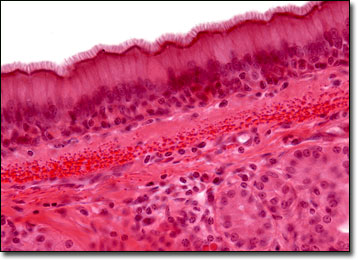
What is pseudostratified (ciliated) columnar epithelium?
This muscle in the epidermis will contract and, quite literally, give you the goosebumps.
What is the arrector pili?
We don't want to give away the answer, but it is the endoplasmic reticulum of the muscle cell that can control when the muscle contracts.
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
It is dorsal to the ilium and just inferior of the sacrum.
What is the coccyx?
If your understanding of the term is this, you wouldn't know that it's also a word for being close to the surface of your skin.
What is superficial?
This type of tissue is made of all 3 types of connective tissue fiber and can be found around our blood vessels.
What is areolar tissue (the 3 types of connective tissue fiber are collagenous, reticular, and elastic fiber)?
Pee-yew! Would you tell these sweat glands to stop releasing fat and protein when you perspire? It stinks!
What are the apocrine sweat glands?
The cell membrane of the muscle cell.
What is the sarcolemma?
This cervical vertebrae is deeper than the very head it carries, which gives it its name after the Greek God that carries the world on his shoulders.
What is the atlas?
It's one of the sutures of your skull, and it's the division of your body into right/left sides.
What is sagittal?
Connective tissue has fibroblasts to make fiber, macrophages for phagocytosis, and these cells that release heparin to prevent blood clots.
What are mast cells?
This may sound a little corny, but this layer of your epidermis is the closest to the surface of your body.
What is the stratum corneum?
The thick and thin filaments of the muscle cell make up this basic unit of contraction.
What is the sarcomere?