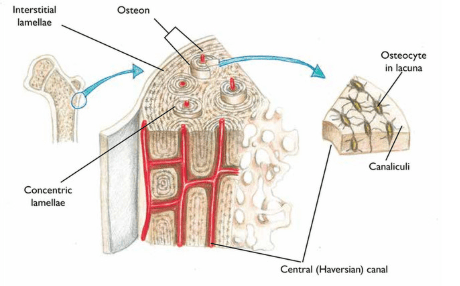
What are channels in bone through which osteocytes can communicate with each other?
Canaliculi
What is a mass of blood that is confined to a limited space?
Hematoma
What is a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid which extends well beyond a joint?
What is the motion to decrease the angle between the bones in a joint?
Flexion
What is the ionic compound that gives bone its compressive strength?
Hydroxyapatite
What is the bone that forms from the latticework of cancellous bone?
Trabeculae
What is the term for when a bone grows in diameter?
Appositional bone growth
What is a slightly moveable fibrous joint of bones that are relatively far apart (like the ulna and radius)?
Syndesmosis
The fibula is _______________ to the pelvis.
Distal
Which joints have the widest range of motion?
Ball and socket
What does NOT grow when a bone grows?
Epiphysial plate
Between the internal and external callus, which takes longer to form than the bone itself?
External calllus
Everything except rotation
What occurs when you have too much Growth Hormone? too little?
Too much GH: Gigantism
Too little GH: Dwarfism
The sacrum is ________ to the vertebral column.
Inferior
What is the difference between osteoblasts and oxteoclasts?
Osteoblasts build up bone
Osteoclasts break down bone
Where is calcitonin secreted from? PTH?
Which one is essential for life?
Calcitonin is released from the thyroid glands and is not essential for life (since you can just make less PTH).
PTH (parathyroid hormone) is released from the parathyroid glands and is essential for life.
What is the different between a synchondrosis and a symphysis?
Synchondrosis - joints made by hyaline cartilage (ex. epiphyseal plates)
Symphysis - joints made of fibrocartilage (ex. intervertebral disks)
What is the difference between inferior and superior?
Inferior means below
Superior means above
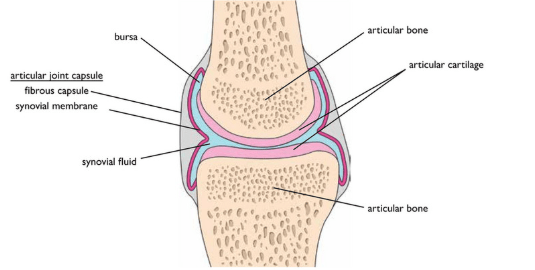
What are three characteristics of synovial fluid?
Very slippery
Lubricates the joint
Supplies chondrocytes with oxygen and nutrients
Label the following parts of a bone: osteon, osteocyte, concentric lamellae, interstitial lamellae, and canaliculi
How does your body respond to low blood calcium?
Parathyroid glands detect a decrease in blood calcium
Parathyroid gland release PTH
PTH stimulates more activity by osteoclasts
Osteoclasts break down more bone, releasing calcium into the bloodstream
Label the synovial fluid, bursa, articular cartilage, articular capsule, fibrous capsule, and synovial membrane of a joint.
What is the difference between pronation and supination?
Supination - rotating the forearm so the palm faces anteriorly
Explain the four steps of bone remodelling.
A hematoma forms. This will form a clot, which will eventually die off.
A callus, which is a bunch of connective tissue) forms around the ends of the broken bone
The callus ossifies. This includes blood vessels growing into the callus and fibroblasts producing collagen
The cancellous bone is remodeled into compact bone.