Which neuroglia cells engage in phagocytosis to fight infections?
Microglia
What type of neural circuit has several presynaptic neuron and one postsynaptic neuron?
Converging circuit
What is term for when no additional action can occur within an axon?
Absolute refractory period
What type of neuron has a lot of dendrites but only one axon?
Multipolar neuron
What system transmit action potentials from the CNS to smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands?
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
What is a neural circuit that would extend a neural response?
Oscillating circuit
Before an action potential is sent through an axon, what are the charges inside and outside the axon?
The outside is positive and the inside is negative
What is the ability of a single axon to carry several action potentials in a small amount of time?
Temporal summation
What are nerves?
Why can CNS nerves not regenerate?
They do not have Schwann cells
How do myelin sheaths affect the speed of action potentials?
Speed 'em up
What is the difference between spinal and cranial nerves?
Spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord.
Cranial nerves originate from the brain.
What is the difference between afferent and efferent neurons?
Afferent neurons - neurons that transmit action potentials from the sensory organs to the CNS
Efferent neurons - neurons that transmit action potentials from CNS to the effector organs
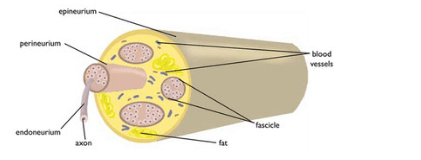
In a nerve, label: epineurium, perineurium, axon, endoneurium, fat, fascicle, and blood vessel.
What is the difference between excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials?
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials - the presynaptic neurons brings the postsynaptic neuron closer to undergoing an action potential
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials - decreases the chance of an action potential
Why are astrocytes important?
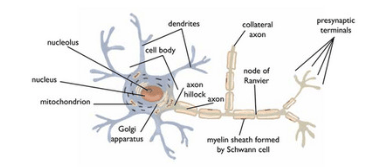
On a PNS neuron, label: dendrites, axon, collateral axon, node of Ranvier, presynaptic terminals, and myelin sheath.
Explain, in copious amounts of detail, how a stimulus can allow an action potential to move down an axon.
It starts with depolarization. After the stimulus, the potential difference changes (the inside goes from negative to positive). This is because channel proteins will allow Na+ to get into the cell to allow it to become more positive.
Next, the Na+ channel proteins close and K+ channels open. This allows K+ to rush into the cell, and therefore the inside of the cell is less positive. This is repolarization.
Then, the sodium-potassium pumps work again to help restore the Na+ and K+ balance.
The frequency of action potentials tells the CNS the strength of the stimulus.
Explain why myelination is important for muscle control, and explain how myelination develops in infants.
Myelination is important because it allows for more advanced and controlled movements, since the signal can happen quickly.
In infants, myelination works from the center of the body towards the edges. It goes brain, eyes, mouth, neck, forearms, fingers, legs, and then bladder.