What is cultural diffusion?
¿Qué es la difusión cultural?
the exchange of ideas, customs, goods and technologies among cultures
el intercambio de ideas, costumbres, bienes y tecnologías entre culturas
Two religions/belief systems that began in India
Dos religiones/sistemas de creencias que comenzaron en la India
Hinduism and Buddhism
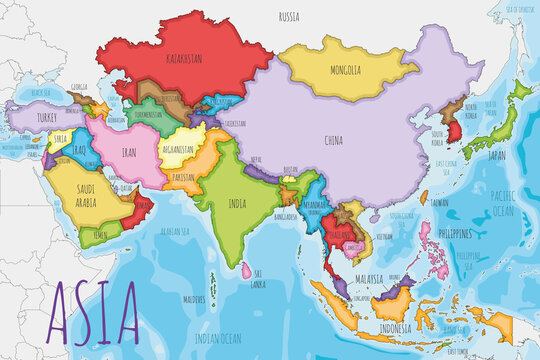
On which continent is India located?
Asia (India is in South Asia)
This symbol of Daoism shows a balance between two opposites.
Este símbolo del taoísmo muestra un equilibrio entre dos opuestos.
yin and yang

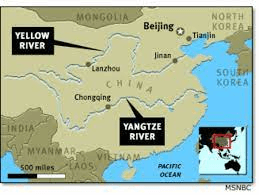
China's two largest rivers are ____.
Los dos ríos más grandes de China son ____.
The Yellow River and the Yangtze River
What is monotheism?
¿Qué es el monoteísmo?
The belief in one god.

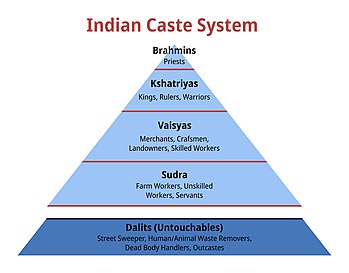
A rigid social hierarchy that still exists in rural areas of India today.
Una jerarquía social rígida que todavía existe en las zonas rurales de la India en la actualidad.
Caste system
What kind of landform is India?
¿Qué tipo de relieve es la India?
a peninsula
This is what kings believed gave them the divine right to rule over their subjects (people).
Esto es lo que creían los reyes que les daba el derecho divino de gobernar a sus súbditos (pueblo).
Mandate of Heaven

What is the name of the book that contains the teachings of Confucius?
¿Cómo se llama el libro que contiene las enseñanzas de Confucio?
The Annalects

What is polytheism?
¿Qué es el politeísmo?
The belief in more than one god.

Which dynasty came BEFORE the Gupta Empire in India?
¿Qué dinastía fue ANTES del Imperio Gupta en la India?
The Mauryan Empire

What are the two rivers that make up the Indus River civilization?
¿Cuáles son los dos ríos que componen la civilización del río Indo?
Indus and Ganges

Under this belief system, there are five key relationships built around respect and knowing your place in society.
Según este sistema de creencias, existen cinco relaciones clave construidas en torno al respeto y el conocimiento de su lugar en la sociedad.
Confucianism

Why was the Yellow River also referred to as the "River of Sorrow"?
¿Por qué al río Amarillo también se le conocía como el "Río del Dolor"?
The floods would destroy crops, villages and kill people.
What is a dynasty?
a ruling family
The Gupta Empire is often called the ________ _____ because there was peace and prosperity and many achievements.
Al Imperio Gupta a menudo se le llama ________ _____ porque hubo paz, prosperidad y muchos logros.
the Golden Age

This dynasty began building the Great Wall of China.
Esta dinastía comenzó a construir la Gran Muralla China.
The Qin Dynasty

Why did nomads settle near the Huang-He River?
¿Por qué se asentaron los nómadas cerca del río Huang-He?
Nomads were no longer nomadic. They were able to grow crops due to the fertile soil that was present due to the Yellow (Huang-He)river.
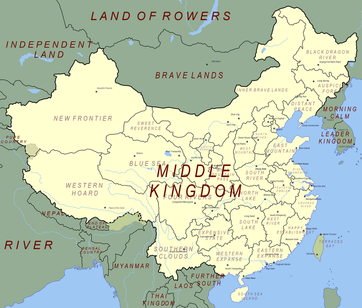
What is the Middle Kingdom?
¿Qué es el Reino Medio?
What the people of China called their country.
Name one similarity between Hinduism and Buddhism
Nombra una similitud entre el hinduismo y el budismo.
Both believe in reincarnation

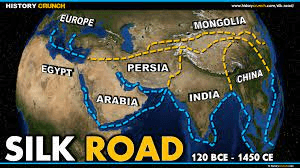
Indian merchants traded ivory, cashmere, spices, and cotton for Chinese silk and Roman ceramics along this which reached from Asia to Africa.
Los comerciantes indios intercambiaban marfil, cachemira, especias y algodón por seda china y cerámica romana a lo largo de esta ruta que se extendía desde Asia hasta África.
The Silk Road
This Chinese philosophy believes in harmony with nature.
Esta filosofía china cree en la armonía con la naturaleza.
Daoism
Name three geographic features that helped protect China from invasions but also kept them isolated.
Mountains- protection from invasion but isolation Deserts- protection from invasion but isolation
Rivers- FOOD! Fertile Soil but Floods!