This drug is white in color and commonly used to induce anesthesia. It can only be given IV.
What is PROPOFOL
This part of the anesthesia machine helps remove carbon dioxide from the patient. 
What is the CO2 absorber canister
This is the name of the tool used for intubation.
What is laryngoscope
Name one of the reflexes that help determine anesthetic depth.
Palpebral response
Jaw tone
Eye position
When providing breaths to most anesthetized patient, care must be taken to keep the pressure below this value to avoid damaging the lungs.
What is 20mmHg
This sedative drug commonly causes bradycardia and hypertension initially after administration.
What is dexmedetomidine
The ET tube should not be advanced past this anatomical landmark.
What is the thoracic inlet
This is an example of a _____________ circuit. 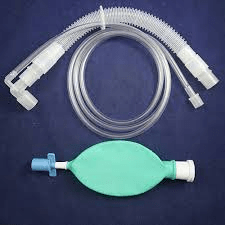
What is non-rebreather
This is the normal ETCO2 range for healthy patients under anesthesia.
What is 35-45mmHg
Your patient has experienced moderate blood loss under anesthesia and is now slightly tachycardic and hypotensive. This is the treatment for the condition.
What is a fluid bolus
This drug is commonly used in local blocks and can be given IV for analgesia and to treat arrhythmias.
What is lidocaine.
The Doppler gives you this blood pressure value on both cats and dogs.

What is systolic blood pressure
This is the proper limb to attach the black ECG lead to.
What is the left front limb
We should strive to keep our MAP (mean arterial pressure) above _________ to protect blood flow to the kidneys.
What is 65mmHg
Cat are typically considered bradycardic with a heart rate below _________.
What is 100 bpm
Morphine, hydromorphone, buprenorphine and methadone are all part of this drug class.
What are opioids
The CO2 absorber should be changed after ____________.
What is 8 hours of use or every 14 days (whichever comes first)
Nonrebreathing anesthesia circuits require higher oxygen flow rates for this purpose.
What is to remove CO2 from the patient since this circuit bypasses the CO2 absorber.
Large patients placed in lateral recumbency are at risk of this anesthetic complication.
What is atelectasis and/or hypoventilation
Our patient is both bradycardic and hypotensive and is NOT too deeply anesthetized. This is the medication to administer to treat the problem.
What is atropine
This drug blocks the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) and is commonly given to treat bradycardia.
What is atropine (or glycopyrrolate)
Confirming ET tube placement can be done multiple ways. Name one way.
What is:
Visualizing the tube pass into the trachea using the laryngoscope
Palpating the ET tube within the trachea
Observing the reservoir bag moving with each breath and obtaining an ETCO2 reading and capnograph waveform
Asculting the chest while giving a breath and hearing breath sounds
Leak testing the anesthesia machine should be completed before the first procedure of the day and when?
What is anytime anything is changed on the machine (refill inhalant, change of breathing circuit, changing CO2 absorber, change of reservoir bag)
The pictured capnograph waveform may indicate this problem.
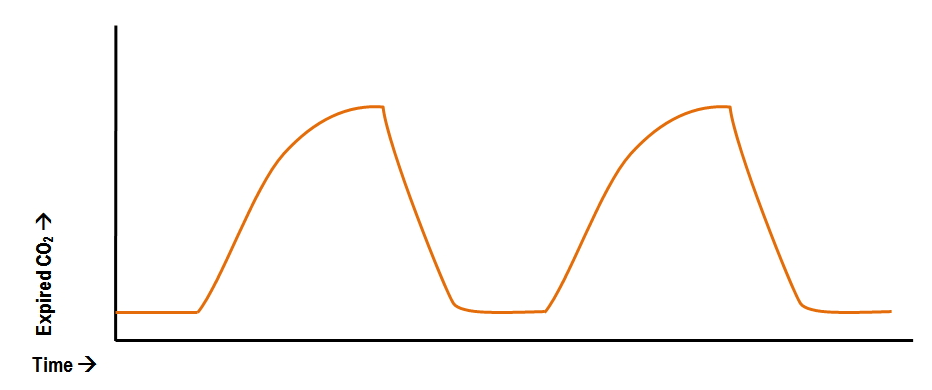
What is an obstructed ET tube or airway
Name the arrhythmia seen here.
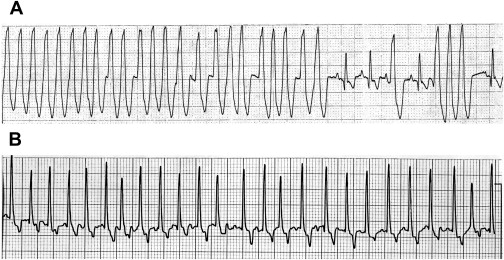
What is ventricular techycardia