What is the difference between delirium and dementia?
Give some investigations we do in dementia
Blood tests- FBC, ESR, vit.B12, U&E, glucose, calcium etc.
Imaging- CT or MRI
Neuropsychometric assessment
Other- CSF, genetic studies, brain biopsy, EEG
What 3 things need to happen for consent to be valid?
Voluntary
Informed
Capacity
What 3 sub-groups can anaesthesia be categorised into (location)
Local
Regional
General
What are the 4 main subtypes of dementia?
Alzheimer's
Vascular
Lewy Body
Frontotemporal
What is the management of vascular dementia?
Care plans- help with finances and ADL's
Lifestyle changes to address cause- lose weight, eat healthy, stop smoking
Medication to treat cause- high BP, cholesterol, diabetes
What are the 4 main aspects of capacity?
Understand information
Retain that information
Weigh up the information to make a decision
Communicate that decision
Give some advantages of spinal anaesthesia
Fixed anaesthetic time
Better pain transition
What type of dementia is being presented?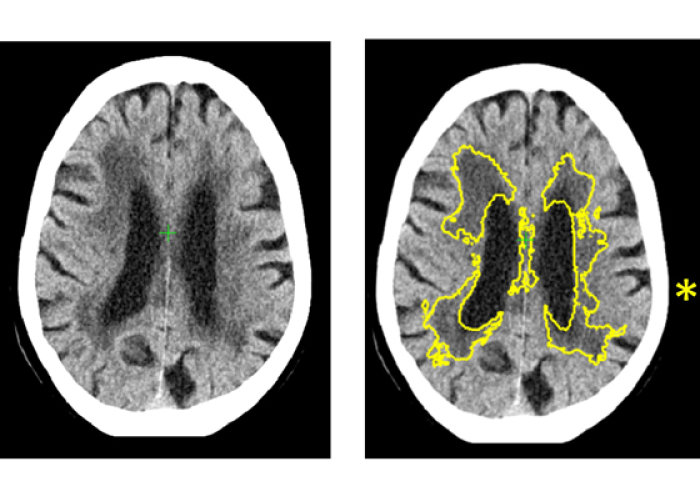
Vascular dementia
Give the mechanism of action and indication of donepezil
Donepezil selectively and reversibly inhibits the acetylcholinesterase enzyme. This enhances cholinergic transmission, which relieves the symptoms of Alzheimer's dementia.
It can also be effective in DLB and Parkinson's
What is a Lasting Power of Attorney?
A lasting power of attorney (LPA) is a legal document that lets you (the ‘donor’) appoint one or more people (known as ‘attorneys’) to help you make decisions or to make decisions on your behalf.
This gives you more control over what happens to you if you have an accident or an illness and cannot make your own decisions (you ‘lack mental capacity’).
Why must patients fast before having general anaesthesia?
To avoid vomiting and pulmonary aspiration
What abnormal protein is present in Lewy Body dementia?
α-synuclein
What are the limitations of the mini-mental state exam?
Insensitive to milder cognitive impairment
Insensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction
What are the 2 most common forms of advance directives?
Living will
Durable power of attorney
What is the mechanism of action of suxamethonium?
It is a depolarising neuromuscular blocker.
It binds to the post-synaptic cholinergic receptors found on motor endplates, thereby inducing first transient fasciculations followed by skeletal muscle paralysis
What gene confers an increased risk of AD?
The E4 allele of apolipoprotein E gene confers a 2-3 times increased risk.
If two copies of this allele are inherited, it confers a 6-8 times increased risk.
What tool has been developed to address the deficiencies of the MMSE (mini-mental state exam)?
Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination (ACE)
What are the limitations of an advance directive?
It cannot be used to:
Ask for specific medical treatment.
Request something that is illegal (eg assisted suicide).
Choose someone to make decisions for you, unless that person is given ‘lasting power of attorney’.
Refuse treatment for a mental health condition (doctors are empowered to treat such conditions under Part 4 of the Mental Health Act).
What is the mechanism of action of fentanyl?
Fentanyl binds to opioid receptors (mu)
Activation of opioid receptors causes GTP to be exchanged for GDP on the G-proteins which in turn down regulates adenylate cyclase, reducing concentrations of cAMP
Reduced cAMP decreases cAMP dependent influx of calcium ions into the cell
The exchange of GTP for GDP results in hyperpolarization of the cell and inhibition of nerve activity