What are the five dimensions of health and wellbeing?
Physical, social, mental, emotional, and spiritual health.
True or False: The five dimensions of health and wellbeing are interrelated.
True
What does "life expectancy" measure?
The average number of years a person is expected to live if the current death rates stay the same
Name five prerequisites for health, according to the WHO.
Peace, shelter, education, food, income, stable ecosystem, sustainable resources, social justice, and equity.
What are all five Sociocultural factors of health?
Family, Peer group, Education, Health literacy and Income
What is the definition of health and wellbeing?
The state of a person’s physical, mental, social, emotional and spiritual existence and is characterised by an equilibrium in which the individual feels happy, healthy, capable and engaged.
This dimension relates to managing emotions and resilience.
Emotional health.
If someone is physically injured and unable to socialize, what two dimensions are affected?
Physical and social health.
Name two indicators used to measure health status in a population
Morbidity, mortality, life expectancy, DALY, burden of disease
Why is education considered a prerequisite for health?
It improves health literacy, employment opportunities, and access to healthcare.
How can a higher income improve an individual’s health status
A higher income provides access to better healthcare, nutritious food, and safer living conditions, increasing life expectancy and reducing the burden of disease.
What health status indicator is being shown on this graph?
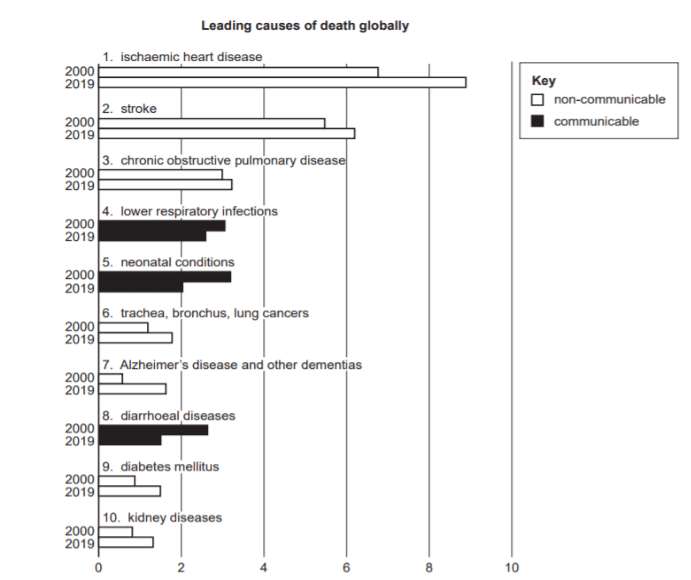
Mortality
Having a supportive network of friends and family is an example of which health
Social health.
A person experiencing discrimination may have lower self-esteem. Which two dimensions are primarily affected?
Mental and emotional health.
Define morbidity and mortality.
- Morbidity: Illness/disease levels in a population.
- Mortality: The number of deaths in a population
How does stable income contribute to better health outcomes? (Link to health status measure)
A stable income allows access to nutritious food, healthcare, and secure housing, reducing morbidity and mortality rates and increasing life expectancy.
How can peer groups influence adolescent health behaviors, and what impact does this have on health status?
Positive peer influences can encourage healthy eating, physical activity, and reduced risk-taking behaviors, leading to lower incidence of obesity, injury rates, and substance abuse (morbidity measure).
Explain the terms dynamic and subjective in relation to health and wellbeing.
- Dynamic: Health is constantly changing due to factors like illness, injury, or lifestyle choices.
- Subjective: Health is viewed differently by individuals based on personal experiences, age, or cultural background.
Define spiritual health and provide an example.
Relates to ideas, beliefs, values and ethics that arise in the mind and conscious of human beings. includes the concept of hope, peace and guiding a sense of meaning or value and reflection of a person's place in the world.
Example: Sense of belonging or peace
How can high stress (mental health) affect physical health?
High stress can lead to increased heart rate, high blood pressure, weakened immune system, and other physical health problems like headaches or digestive issues. This can lead to poor function of body systems such as heart or digestive system.
What is the difference between incidence and prevalence of a disease?
- Incidence: The number of new cases in a specific period.
- Prevalence: The total number of cases at a given time.
Explain how sustainable resources impact global health. (Link to a health characteristic)
Access to clean water, food, and healthcare materials supports efficient body functioning (physical health) and prevents diseases, reducing the burden of disease (DALY and YLL rates).
How can low health literacy contribute to higher prevalence and incidence rates of diseases in a population?
- Low health literacy can lead to poor understanding of disease prevention and management, increasing the incidence (new cases) of preventable diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- People with low health literacy may also struggle to follow medical advice or seek early treatment, leading to longer-lasting conditions and higher prevalence (total cases) of chronic diseases in the population.
What is the difference between illness and disease?
- Illness relates to a person’s experience with disease (or injury) and can be influenced by a
range of factors.
Disease is a physical or mental disturbance involving symptoms, dysfunction or tissue
damage.
Explain how mental health differs from emotional health.
Mental health is about cognitive function (e.g., stress management, self-esteem), while emotional health is about recognizing and expressing emotions effectively.
Explain how at least 3 dimensions could be impacted if a person loses their job.
Physical Health & Wellbeing – Energy levels
- Job loss can lead to stress and financial strain, which may cause poor nutrition, lack of exercise, and disrupted sleep, leading to low energy levels.
Mental Health & Wellbeing – Levels of stress and anxiety
- Losing a job can cause high stress and anxiety due to uncertainty about the future, impacting concentration, decision-making, and self-confidence.
Emotional Health & Wellbeing – Ability to express emotions
- The individual may feel frustrated, overwhelmed, or even embarrassed about losing their job, affecting their ability to cope with emotions in a healthy way.
Social Health & Wellbeing – Supportive network of friends and family
- They might withdraw from friends and family due to financial difficulties or embarrassment, leading to a weaker social support system.
Spiritual Health & Wellbeing – Sense of purpose in life
- Work often provides a sense of purpose and achievement, so job loss may lead to feelings of loss, meaninglessness, or detachment from personal values and goals.
Explain how DALY (Disability-Adjusted Life Years) is calculated.
DALY = Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature death + Years Lived with Disability (YLD).
Describe how peace can positively influence multiple dimensions of health and wellbeing. (Link to a health characteristic)
Peace promotes safety and security, reducing stress and anxiety (mental health), preventing injuries and violence-related mortality (physical health), and allowing social and economic stability, which supports a sense of belonging and purpose (spiritual health).
How does family support contribute to mental and emotional health in young people?
A supportive family provides emotional stability, security, and encouragement, which improves resilience, self-esteem, and the ability to cope with stress (mental/emotional health characteristics).
What Logo is this?

World health organization