List the chambers of the heart in proper order.
Right Atrium, Right Ventricle, Left Atrium, Left Ventricle
As the number of erythrocytes in circulation increases, the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood (increase or decrease)?
increases
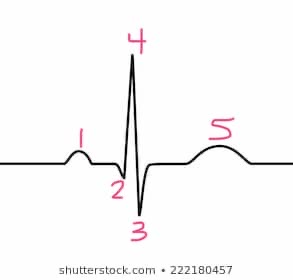
Label these parts.
1. P Wave
2. Q
3. S
4. R
5. T Wave
Which type of blood is the universal donor? Recipient?
Donor: O-
Receipient: AB+
What are some factors that determine blood pressure?
Water volume, blood volume, heart rate, vessel radius, SV, peripheral resistance, etc.
Why is it important that a vessel be able to stretch?
Accommodating blood flow and blood pressure.
Describe Sickle Cell Anemia. Is it an erythrocyte or leukocyte disorder?
An erythrocyte disorder that causes one globin chain
to become rigid. Deforms the shape and function of cells.
Which component of an EKG indicates the repolarization of the ventricles? What about atrial depolarization?
Ventricular repolarization: T Wave
Atrial depolarization: P Wave
What feedback mechanism is blood clotting regulated by? Why?
Positive feedback because the body needs to quickly stop bleeding and will do whatever it takes to stop it.
What is cardiac output?
Amount of blood that pumps through the circulatory system in 1 minute.
Cardiac myocytes are connected to one another by...
Intercalated discs
What happens to erythrocytes after 120 days of circulation?
Breakup/get recycled in the liver and spleen.
What portion of the conduction system is known as the "pacemaker"?
SA Node
What is secreted in response to lowered O2 carrying capacity in the blood? What is the target tissue of this?
Erythropoietin. The target tissue is the bone marrow for RBC production.
You are caring for a patient with a heart rate of 61 beats/min and a stroke volume of 125 mL/beat, what is your patient's cardiac output?
7625 mL/min or 7.6 L/min
Why is the wall of the artery thick?
To withstand high blood pressure from the heart
What are the 5 types of Leukocytes?
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils
Why is A. Fib not life-threatening?
Because blood is still flowing and being pumped, it is just happening rapidly and irregularly.
What would happen if a person with Rh- blood got a blood transfusion from Rh+ blood?
They are guaranteed to have an immediate immune reaction to the Rh-positive blood.
If a patient's heart rate is 120 bpm and they have a CO of 2.52 L/m, what is their stroke volume?
21 mL/beat or 0.021 L/beat
Blood returning from the lungs enters the heart in the _______________, passes through the ______________ valve, and then enters the
________________.
Left atrium, bicuspid valve, and left ventricle.
How is RBC production regulated?
A negative feedback mechanism that is regulated by erythropoietin and oxygen levels. Production takes place in the bone marrow.
What are the 5 steps in the cardiac conduction pathway?
1. SA Node
2. AV Node
3. Bundle of His
4. Bundle Branches
5. Purkinje Fibers
What is hemostasis? Can you explain the process?
Hemostasis is the body's response to stop bleeding after vessel injury. The body will reduce blood flow to the affected area (constriction of blood vessels). The body then forms a platelet plug at the affected area. Lastly, coagulation occurs.
Sarah is a 30-year-old woman who is at rest. Her stroke volume is measured at 70 mL. Her cardiac output is 5.6 liters. What is her heart rate?
80bpm