The loss of a predator population from a community can lead to an explosion of prey populations, allowing for intense competition between these species for resources. The result will be a drastic change in community structure. What name is given to a species that plays such a key role in maintaining community structure?
Keystone
The area species lives in and its use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment is called what?
ecological niche
Biodiversity is directly correlated to this in an ecosystem.
Stability
a locomotor response toward or away from an external stimulus by a motile (and usually simple) organism
Taxis
What term is defined as where plants and animals invade where soil has not yet formed?
Primary Succession
Salt water is an abundant resource but unusable for irrigation and drinking. As demands on freshwater sources increase, the use of desalination processes to remove salt from ocean water is increasing. A concern of desalinating water is the large amounts of recovered salts that are returned to the ocean. Which of the following describes the most likely impact of desalination on the surrounding ocean environment?
A Methane gas would pollute the ocean environment as shoreline organisms begin to die and decay
B Nonrenewable resources in the ocean environment would become depleted and upset the ecosystem's balance
C Alteration in ocean salt levels would cause loss of species and unbalanced populations in marine food webs.
D Increased levels of salts and minerals in the ocean would result in an overpopulation of marine bivalves due to strengthened shells.
C Alteration in ocean salt levels would cause loss of species and unbalanced populations in marine food webs.
Warmer climates, adequate rainfall and the older age of tropical communities has resulted in:
Less predation in tropical communities
Greater richness and evenness in tropical communities than in polar or temperate
Greater poaching in tropical communities
Less mutations
Greater richness and evenness in tropical communities than in polar or temperate
learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning).
Classical
Associative
Trial and Error
Spatial
Associative
Bright coloration of animals with effective physical/chemical defence as a warning;
A Batesian
B Aposematic
C Cryptic
D Mullerian
B Aposematic
What biome is characterized by the presence of permafrost, very cold temperatures, high winds, and little rainfall?
Tundra
What are the three major threats to biodiversity?
Habitat loss, habitat fragmentations, introduced species/diseases, over-harvesting, and global climate change, etc
Prairie dogs give an alarm call when a suspected predator is nearby. When prairie dog habitats are located near trails used by humans or located in a zoo, they do not give alarm calls each time human approaches.
Imprinting
Spatial Learning
Associative Learning
Habituation (Habit Forming)
Habituation
Competition for resources, territoriality, disease, and predation are examples of what kind of factors that reduce birth rates or increases death rates.
density-dependent factors
Differences in variation between populations living in separate locations is referred to as:
Geographic isolation
Geographic variation
Genetic Drift
The Founder Effect
Geographic variation
A study conducted on bumblebees in Colorado showed how different species of Bombus compete for nectar. Different species appeared to have adaptations that allowed them to exploit different species of plants based on the corolla length of the plant’s flowers. Different bumblebee species preferred different corollas in accordance with the length of their proboscis. In other words, bee species with a long proboscis preferred flowers with a long corolla, and bee species with a short proboscis preferred flowers with a short corolla.
Resource Partitioning
Competitive Exclusion
Character displacement
Relative abundance
Resource partitioning
If a mother graylag goose’s egg rolls out of its nest, the goose will instinctively roll it back with its beak. Interestingly, if the egg is removed from the goose while it is rolling it back to the nest, the goose will continue the behavior as if moving an imaginary egg. In addition, the goose will also try to retrieve other objects that are shaped like an egg, such as a golf ball, and return them to the next.
Kinesis
Taxis
Fixed Action Pattern
Habituation
Fixed Action Pattern
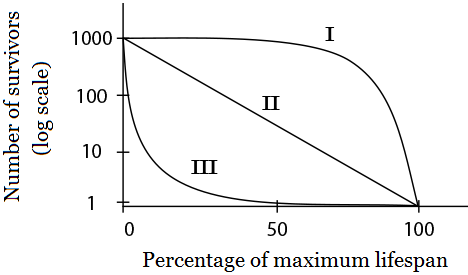
A sea turtle lays approximately 100 eggs at a time, yet on average only one of the eggs will survive to adulthood. Which type of survivorship curve represents a sea turtle population?
Type III
What states that when two species are vying for a resource in short supply, eventually the one with the slight reproductive advantage will eliminate the other?
competitive exclusion principle
What are the three main levels of biodiversity?
genetic diversity, species diversity, ecosystem diversity